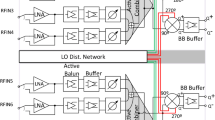
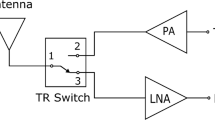
Abstract
This paper presents a four channel phased array transmitter at 15 GHz aimed for the upcoming 5G wireless systems. The circuit is designed and fabricated using 45 nm CMOS silicon on insulator technology. The design is programmable with exhaustive digital controls available for parameters such as bias voltage, resonance frequency, and gain. The phase shift required for the phased array is provided at RF using an IQ vector modulator (IQVM) topology, which provides both amplitude and phase control. Based on the measurement results, the IQVM provides 360° of phase shift and 15 dB of gain variation. Both phase and amplitude information are encoded in a 10 bit control word. The mean angular separation provided by the IQVM is 3° at optimum amplitude levels. Active area occupied is 2.88 square millimeter. Total DC power consumed by one transmit channel from 1 and 2.6 V supply is 268 mW. The maximum RF output power from one transmit channel is 1dBm. Measured EVM for a 256 QAM modulated signal is as low as 2.0%. All results include the impact of printed circuit board traces and pad parasitics. Based on the achieved results, the proposed architecture is well suited for the next generation of the wireless systems.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, J. G., Buzzi, S., Choi, W., Hanly, S. V., Lozano, A., Soong, A. C., et al. (2014). What will 5G be? IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 32(6), 1065–1082.
Bleicher, A. (2013). The 5G phone future [news]. IEEE Spectrum, 50(7), 15–16.
Aziz, D., Kusume, K., Queseth, O., Tullberg, H., Fallgren, M., Schellmann, M., Uusitalo, M., & Maternia, M. (2015). Metis final project report. Technical Report [Online]. https://www.metis2020.com/wp-content/uploads/deliverables/METIS_D8.4_v1.pdf. Accessed 9 Oct 2017.
Doan, C. H., Emami, S., Sobel, D. A., Niknejad, A. M., & Brodersen, R. W. (2004). Design considerations for 60 GHz CMOS radios. IEEE Communications Magazine, 42(12), 132–140.
Vieira, J., Malkowsky, S., Nieman, K., Miers, Z., Kundargi, N., Liu, L., et al. (2014). A flexible 100-antenna testbed for massive mimo. Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), 2014, 287–293.
Rebeiz, G.M., Kim, S.-Y., Inac, O., Shin, W., Gurbuz, O., Ou, Y.-C., Golcuk, F., Kanar, T., & Ku, B.-H. (2015). Millimeter-wave large-scale phased-arrays for 5G systems. In IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium (IMS) (pp. 30 – 60).
Zihir, S., Gurbuz, O. D., Karroy, A., Raman, S., & Rebeiz, G. M. (2015). A 60 GHZ single-chip 256-element wafer-scale phased array with eirp of 45 dbm using sub-reticle stitching. IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), 23, 2015.
Vook, F., Ghosh, A., & Thomas, T. (June 2014). MIMO and beamforming solutions for 5G technology. In IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), 2014 (pp. 1–4).
Parker, D., & Zimmermann, D. C. (2002). Phased arrays—Part 1: Theory and architectures. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 50(3), 678–687.
Parker, D., & Zimmermann, D. C. (2002). Phased arrays-part II: Implementations, applications, and future trends. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 50(3), 688–698.
Sethi, A., Aikio, J.P., Shaheen, R.A., Akbar, R., Rahkonen, T., & Pärssinen, A. (2017). A 10-bit active RF phase shifter for 5G wireless systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nordic circuits and systems conference (NORCAS): NORCHIP and international symposium of system-on-chip (SoC) (pp. 1–4).
Hashemi, H., Guan, X., & Hajimiri, A. (2004). A fully integrated 24 GHz 8-path phased-array receiver in silicon. In IEEE International solid-state circuits conference. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
Gingell, M.J. (1971). Polyphase symmetrical network. US Patent US3 559 042 A.
Pepe, D., & Zito, D. (2017). Two mm-wave vector modulator active phase shifters with novel IQ generator in 28 nm FDSOI CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 52(2), 344–356.
Aikio, J.P., Sethi, A., Shaheen, R.A., Akbar, R., Rahkonen, T., & Pärssinen, A. (2017). A fully integrated 13 GHz CMOS SOI stacked power amplifier for 5G wireless systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nordic circuits and systems conference (NORCAS): NORCHIP and international symposium of system-on-chip (SoC) (pp. 1–4).
Kaukovuori, J., Stadius, K., Ryynanen, J., & Halonen, K. A. I. (2008). Analysis and design of passive polyphase filters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 55(10), 3023–3037.
Zhang, T., Subramanian, V., Ali, M., & Boeck, G. (2011). Integrated k-band CMOS passive mixers utilizing balun and polyphase filters. In 2011 IEEE international symposium on radio-frequency integration technology (RFIT) (pp. 89–92).
Shahramian, S., Holyoak, M. J., & Baeyens, Y. (2015). A 16-element W-band phased array transceiver chipset with flip-chip PCB integrated antennas for multi-gigabit data links. In IEEE radio frequency integrated circuits symposium (RFIC) (Vol. 27).
Boers, M., Afshar, B., Vassiliou, I., Sarkar, S., Nicolson, S. T., Adabi, E., et al. (2014). A 16tx/16rx 60 GHz 802.11ad chipset with single coaxial interface and polarization diversity. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 49(12), 3031–3045.
Golcuk, F., Kanar, T., & Rebeiz, G. M. (2013). A 90–100 GHz \(4\times 4\) SiGe BiCMOS polarimetric transmit/receive phased array with simultaneous receive-beams capabilities. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 61(8), 3099–3114.
Acknowledgements
This research has been financially supported by Nokia Corporation Ltd. and Academy of Finland 6Genesis Flagship (Grant 318927). The authors would also like to acknowledge Global Foundries for the silicon processing and technical support. Support provided by Ganesh Venkatraman, Risto Vuohtoniemi, Nuutti Tervo and Saila Tammelin is highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sethi, A., Aikio, J.P., Shaheen, R.A. et al. A four channel phased array transmitter using an active RF phase shifter for 5G wireless systems. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 98, 419–428 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1244-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1244-z