Abstract
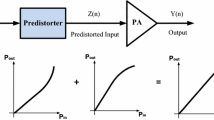
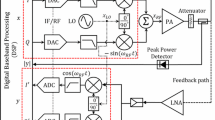
In this paper, a novel digital predistorter design based on the Hammerstein structure is proposed in order to linearize radio frequency power amplifiers. A genetic algorithm optimization method has been proposed to accurately identify the coefficients of a Wiener model for the power amplifier. Digital predistorter design based on the proposed Hammerstein model has been carried out according to the accurate Wiener model. The validation of the suggested model is carried out using the simulation of the power amplifier and the digital predistortion excited by 64QAM signals in the advanced design system software. According to the simulation results, the criterion of an adjacent channel power ratio decreased by about 16 dB. The simulation results show the adjacent channel power ratio of almost − 46 dBc. In order to assess the feasibility of the proposed predistorter, it is completely implemented in the Kintex FPGA using Vivado HLS. This proposed model enables a more accurate modeling of nonlinear distortion and memory effects compared to the previous linearization methods. This paper presents the new linearization method using the genetic algorithm based Hammerstein structure.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan, M. A., Aref, A. F., Tarar, M. M., & Negra, R. (2016). Analysis and design of class-O RF power amplifiers for wireless communication systems. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 89(2), 317–325.
Razavi, B. (2011). RF microelectronics (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Belabad, A. R., Masoumi, N., & Ashtiani, S. J. (2013). A fully integrated 2.4 GHz CMOS high power amplifier using parallel class A&B power amplifier and power-combining transformer for WiMAX application. AEU: International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 67(12), 1030–1037.
Belabad, A. R., Masoumi, N., & Ashtiani, S. J. (2012). A 33.2 dBm CMOS RF power amplifier using a novel on-chip transformer power combiner for 4G WiMAX applications. In Sixth international symposium on telecommunications (IST), Tehran, Iran (pp. 343–347).
Degani, O., Cossoy, F., Shahaf, S., Cohen, E., Kravtsov, V., Sendik, O., et al. (2010). A 90-nm CMOS power amplifier for 802.16e (WiMAX) applications. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 58(5), 1431–1437.
Qian, H., Huang, H., & Yao, S. (2013). A general adaptive digital predistortion architecture for stand-alone RF power amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 59(3), 528–538.
Hamm, O., Kwan, A., & Ghannouchi, F. M. (2013). Bandwidth and power scalable digital predistorter for compensating dynamic distortions in RF power amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 59(3), 520–527.
Zhu, A., Draxler, P. J., Yan, J. J., Brazil, T. J., Kimball, D. F., & Asbeck, P. M. (2008). Open-loop digital predistorter for RF power amplifiers using dynamic deviation reduction-based Volterra series. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 56(7), 1524–1534.
Marsalek, R. (2003). Contributions to the power amplifier linearization using digital baseband adaptive predistortion. Ph.D. dissertation, Universite de Marne La Vallee.
Jung, S., Park, H., Kim, M., Ahn, G., Van, J., Hwangbo, H., et al. (2007). A new envelope predistorter with envelope delay taps for memory effect compensation. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 55(1), 52–59.
Cha, J., Yi, J., Kim, J., & Kim, B. (2004). Optimum design of a predistortion RF power amplifier for multicarrier WCDMA applications. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 52(2), 655–663.
Ren, Z.-X., Zhang, K.-F., Liu, L.-Q., Chen, X.-Q., Liu, D.-S., Liu, Z.-L., et al. (2015). A 2.45-GHz W-level output power CMOS power amplifier with adaptive bias and integrated diode linearizer. Microelectronics Journal, 46(5), 327–332.
Lim, K., Ahn, G., Jung, S., Park, H., Kim, M., Van, J., et al. (2009). A 60 watt multi-carrier WCDMA power amplifier using an RF predistorter. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 59(4), 265–269.
Yi, J., Yang, Y., Park, M. G., Kang, W. W., & Kim, B. (2000). Analog predistortion linearizer for high-power RF amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 48(12), 2709–2713.
Nojima, T., & Konno, T. (1985). Cuber predistortion linearizer for relay equipment in 800 MHz band land mobile telephone system. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 34(4), 169–177.
Younes, M., & Ghannouchi, F. M. (2012). An accurate predistorter based on a feedforward Hammerstein structure. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 58(3), 454–461.
Karimi, G., & Lotfi, A. (2013). An analog/digital pre-distorter using particle swarm optimization for RF power amplifiers. AEU: International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 67, 723–728.
Belabad, A. R., Motamedi, S. A., & Sharifian, S. (2017). An adaptive digital predistortion for compensating nonlinear distortions in RF power amplifier with memory effects. INTEGRATION, the VLSI Journal, 57, 8.
Cho, Y., Lee, J., Jin, S., Park, B., Moon, J., Kim, J. S., et al. (2014). Fully integrated CMOS saturated power amplifier with simple digital predistortion. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 24(8), 533–535.
Muhonen, K. J., Kavehrad, M., & Krishnamoorthy, R. (2000). Look-up table techniques for adaptive digital predistortion: A development and comparison. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 49(9), 1995–2002.
Kenney, J. S., Woo, W., Ding, L., Raich, R., Ku, H., & Zhou, G. T. (2001) The impact of memory effects on predistortion linearization of RF power amplifiers. In Proceedings of the 8th international symposium on Microwave and Optical Technology (pp. 189–193).
Schetzen, M. (1989). The Volterra and Wiener theories of nonlinear systems. New York: Wiley.
Guan, L., & Zhu, A. (2010). Low-cost FPGA implementation of Volterra series-based digital predistorter for RF power amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 58(4), 866–872.
Liu, T., Boumaiza, S., & Ghannouchi, F. M. (2005). Deembedding static nonlinearities and accurately identifying and modeling memory effects in wide-band RF transmitters. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 53(11), 3578–3587.
Liu, T., Boumaiza, S., & Ghannouchi, F. M. (2006). Augmented Hammerstein predistorter for linearization of broad-band wireless transmitters. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 54(4), 1340–1349.
Ding, L., Zhou, G. T., Morgan, D. R., Ma, Z., Kenney, J. S., Kim, J., et al. (2004). A robust digital baseband predistorter constructed using memory polynomials. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 52(1), 159–165.
Moon, J., & Kim, B. (2011). Enhanced Hammerstein behavioral model for broadband wireless transmitters. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 59(4), 924–933.
Wu, Y., & Liu, W. (2013). Routing protocol based on genetic algorithm for energy harvesting-wireless sensor networks. IET Wireless Sensor Systems, 3, 112–118.
Patra, S. S. M., Roy, K., Banerjee, S., & Vidyarthi, D. P. (2006). Improved genetic algorithm for channel allocation with channel borrowing in mobile computing. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 5, 884–892.
Sperlich, R., Sills, J. A., & Kenney, J. S. (2005). Closed-loop pigtail predistortion with memory effects using digital predistortion and genetic algorithms. In IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium digest (pp. 1557–1560).
Wang, Y., Xie, L., Wang, Z., Chen, H., & Wang, K. (2010). An efficient algebraic predistorter for compensating the nonlinearity of memory amplifiers. In International conference on communications, circuits and systems.
Saleh, A. A. M. (1981). Frequency-independent and frequency-dependent nonlinear models of TWT amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 29(11), 1715–1720.
Teikari, I. (2008). Digital predistortion linearization methods for RF power amplifiers. Ph.D. thesis, Helsinki University of Technology.
Falconor, D., Kolze, T., Leiba, Y., & Leibetreu, J. (2000). IEEE 802.16. Proposed system impairment models, slide supplement. IEEE technical report.
Hagenblad, A., Ljung, L., & Wills, A. (2008). Maximum likelihood identification of Wiener models. Automatic, 44(11), 2697–2705.
Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on neural networks (pp. 1942–1944).
Ho, S. L., Yang, S., Ni, G., Lo, E. W. C., & Wong, H. C. (2005). A particle swarm optimization-based method for multiobjective design optimizations. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 41(5), 1756–1759.
Whitley, D. (1994). A genetic algorithm tutorial. Statistics and Computing, 4, 65–85.
Belabad, A. R., Iranpour, E., & Sharifian, S. (2015). FPGA implementation of a Hammerstein based digital predistorter for linearizing RF power amplifiers with memory effects. Amirkabir International Journal of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, 49(2), 9–17.
Jose, S. (2015). Vivado design suite user guide: High-level synthesis. California: Xilinx.
Yen, C.-C., & Chuang, H.-R. (2003). A 0.25-μm 20-dBm 2.4-GHz CMOS power amplifier with an integrated diode linearizer. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 13(2), 45–47.
Seo, M., Kim, K., Kim, M., Kim, H., Jeon, J., Park, M.-K., et al. (2011). Ultrabroadband linear power amplifier using a frequency-selective analog predistorter. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 58(5), 264–268.
Garcia-Hernandez, M., Prieto-Guerrero, A., Laguna-Sanchez, G., Mendoza-Valencia, P. J., & Sanchez-Garcia, J. (2012). Digital predistorter based on Volterra series for nonlinear power amplifier applied to OFDM systems using adaptive algorithms. International Meeting of Electrical Engineering Research, 35, 118–125.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahati Belabad, A., Sharifian, S. & Motamedi, S.A. An accurate digital baseband predistorter design for linearization of RF power amplifiers by a genetic algorithm based Hammerstein structure. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 95, 231–247 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1173-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1173-x