Abstract
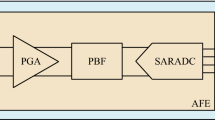
This paper proposes a configurable analog front-end (AFE) chain architecture used in the EEG detection system. The proposed chain consists of three stages: the first and the third stages are instrumentation amplifier and programmable gain amplifier, respectively, and the second stage is notch filter with low pass feature. The proposed architecture relaxes the design of the notch filter and the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) used in building the EEG detection system. A basic building block is the digitally programmable balanced output operational transconductance amplifier (DPOTA), which is proposed to realize the AFE blocks. A successive-approximation ADC (SA-ADC) architecture is mostly designed on digital circuits in order to lower the power dissipation. Based on this, PSpice post layout simulation results for the overall EEG detection system using 0.25-µm CMOS technology are also given. The overall configurable gain/filtering chain architecture has a total gain ranging from 61 to 84 dB, a total power dissipation of 32 µW and input referred noise spectral density of 4 µV/ \(\sqrt {\text{Hz}}\).
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Northrop, R. B. (2003). Analysis and application of analog electronic circuits to biomedical instrumentation (1st ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC.
Wu, R., Huijsing, J. H., & Makinwa, K. A. A. (2013). Precision instrumentation amplifiers and read-out integrated circuits, analog circuits and signal processing. New York: Springer.
Mahmoud, S. A. & Alhammadi, A. A. (2015). A CMOS digitally programmable OTA based instrumentation amplifier for EEG detection system. In IEEE international conference electronics, circuits, and systems (pp. 543–546). Egypt.
Mahmoud, S. A., Hashiesh, M. A., & Soliman, A. M. (2005). Low-voltage digitally controlled fully differential current conveyor. 0, 52(10), 2055–2064.
Alhammadi A. A., & Mahmoud S. A. “Fully differential fifth-order dual-notch powerline interference filter oriented to EEG detection system with low pass feature.” Microelectron Journal. unpublished.
Shaker, M. O., Mahmoud, S. A., & Soliman, A. M. (2006). New CMOS fully-differential transconductor and application to fully-differential Gm-C filters. ETRI Journal, 28(2), 175–181.
Lewinski, A. J., & Silva-Martinez, J. (2007). “A 30-MHz fifth-order elliptic low-pass CMOS filter with 65-dB spurious-free dynamic range”. IEEE Transactions Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 54(3), 469–480.
Mahmoud, S. A., & Soliman, E. A. (2013). Multi-standard receiver baseband chain using digitally programmable OTA based on CCII and current division networks. Journal of Circuits, Systems, and Computers, 22(4), 1350019.
Bult, K., & Geelen, G. J. M. (1992). An inherently linear and compact MOST-only current division technique. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 27, 1730–1735.
Hashiesh M. A., Mahmoud S. A., & Soliman A.M. (2004). Digitally controlled CMOS balanced output transconductor based on novel current-division network and its application. In The 47th IEEE international midwest symposium circuits system, Hiroshima (pp. 323–326).
Mahmoud, S. A., Elwan, H. O., & Soliman, A. M. (2000). Low voltage rail to rail CMOS current feedback operational amplifier and its applications for analog VLSI. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 25, 47–57.
Yazicioglu, R. F., Hoof, C. V., & Puers, R. (2009). Biopotential readout circuits for portable acquisition systems. New York: Springer.
Li J. T., Pun S. H., Vai M. I, Mak P. U., Mak P. I., & Wan F. (2009). Design of current mode instrumentation amplifier for portable biosignal acquisition system. In 2009 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference, BioCAS, pp. 9–12. IEEE, 2009.
Kwon, K., & Lee, K. (2011). A 23.4 mW 68 dB dynamic range low band CMOS hybrid tracking filter for ATSC digital TV tuner adopting RC and Gm-C topology. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 58(10), 2346–2354.
Kuo, K., & Leuciuc, A. (2001). A linear MOS transconductor using source degeneration and adaptive biasing. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 48(10), 937–943.
Mobarak, M., Onabajo, M., Silva-Martinez, J., & Sanchez-Sinencio, E. (2010). Attenuation–predistortion linearization of CMOS OTAs with digital correction of process variations in OTA-C filter applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 45(2), 351–367.
Mahmoud, S. A., Bamakhramah, A., & Al-Tunaiji, S. A. (2014). Six order cascaded power line notch filter for ECG detection systems with noise shaping. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing. doi:10.1007/s00034-014-9761-1.
Mahmoud S. A., Abdallah A., & Khalid S. (2013). A 5.2nV/√Hz noise density third-order FDNR filter for DVB-H mobile-TV receiver In The 20th IEEE International Conference on electronics, circuits and systems ICECS, 2013 (pp 739–742). Abu Dhabi: UAE.
Mahmoud S. A., Salem H. A., & Albalooshi H. M. (2015). An 8-bit, 10KS/s, 1.87 μW successive approximation analog to digital converter in 0.25 μm CMOS technology for ECG detection systems. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing 34(2).
Johns, D., & Martin, K. (2008). Analog integrated circuit design (2nd ed.). Hoboken: Wiley.
Schinkel D., Mensink E., Klumperink E., Tuijl E., & Nauta B. (2007). A double-tail latch-type voltage sense amplifier with 18 ps setup + hold time In IEEE International solid-state circuits conference (pp. 314–315). IEEE.
Shaker, M. O., & Bayoumi, M. A. (2013). A clock gated successive approximation register for A/D converters. Journal of Circuits, Systems, and Computers, 23(2), 1–11.
S. A. Mahmoud and T. B. Nazzal. (2015). Sample and hold circuits for analog-to-digital converters,” In UAE graduate students research conference (UGSR 2015) (pp. 223–224).
Mahmoud, S. A., Bamakhramah, A., & Al-Tunaiji, S. A. (2013). Low noise low pass filter for ECG portable detection systems with digitally programmable range. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 32(5), 2029–2045.
Soares, C., De Moraes, G., & Petraglia, A. (2014). A low-transconductance OTA with improved linearity suitable for low-frequency Gm-C filters. Microelectronics Journal, 45(11), 1499–1507.
Paraskevopoulou S. E., Eftekhar A., Kulasekeram N., & Toumazou C. (2015). A low-noise instrumentation amplifier with DC suppression for recording ENG signals. In 37th annual. international conference (pp. 2693–2696). IEEE EMBC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alhammadi, A.A., Nazzal, T.B. & Mahmoud, S.A. A CMOS EEG detection system with a configurable analog front-end architecture. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 89, 151–176 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0826-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0826-x