Abstract
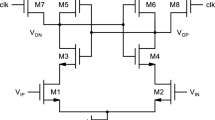
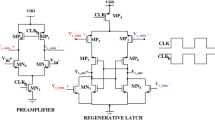
This paper presents a high speed CMOS hybrid comparator with reduced delay time and improved energy efficiency. The proposed hybrid comparator includes two stages with three stacked transistors which are suitable for low-voltage operation. The first dynamic amplifying stage uses PMOS input to reduce the common-mode voltage, while enhancing the positive feedback to reduce the discharging time in a low-power manner. The second quasi-dynamic latching stage uses NMOS input to gain the transconductance, thus reducing the latching time with negligible static power, while needing no additional clock signal. Therefore, the delay time and energy per conversion are both significantly reduced in the proposed hybrid comparator. Measurement results in 40-nm CMOS process show that the proposed hybrid comparator operates up to 6 GHz with 61.08-ps delay time. The power consumption is 345.9 \(\upmu \)W at 1.1-V supply, while the occupied die area is 64.5 \(\upmu \)m\(^2\) (7.5 \(\upmu \)m \(\times \) 8.6 \(\upmu \)m).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ragab, K., Chen, L., Sanyal, A., & Sun, N. (2015). Digital background calibration for pipelined ADCs based on comparator decision time quantization. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 62(5), 456–460.
Yamamoto, K., & Carusone, A. C. (2012). A 1-1-1-1 MASH delta-sigma modulator with dynamic comparator-based OTAs. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 47(8), 1866–1883.
Yang, B.-D. (2014). 250-mV supply subthreshold CMOS voltage reference using a low-voltage comparator and a charge-pump circuit. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 61(11), 850–854.
Kao, C.-K., Fu, K.-L., & Liu, S.-I. (2014). A 2 \(\times \) 25 Gb/s clock and data recovery with background amplitude-locked loop. In IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), pp. 281–284.
Wicht, B., Nirschl, T., & Schmitt-Landsiedel, D. (2004). Yield and speed optimization of a latch-type voltage sense amplifier. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 39(7), 1148–1158.
Okaniwa, Y., Tamura, H., Kibune, M., Yamazaki, D., Cheung, T.-S., Ogawa, J., et al. (2005). A 40-Gb/s CMOS clocked comparator with bandwidth modulation technique. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40(8), 1680–1687.
Schinkel, D., Mensink, E., Klumperink, E., van Tuijl, E., & Nauta, B. (2007). A double-tail latch-type voltage sense amplifier with 18ps setup+hold time. In IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) Digest Technical Papers, pp. 314–605.
Goll, B., & Zimmermann, H. (2009). A comparator with reduced delay time in 65-nm CMOS for supply voltages down to 0.65 V. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 56(11), 810–814.
Goll, B., & Zimmermann, H. (2009). A 65nm CMOS comparator with modified latch to achieve 7GHz/1.3 mW at 1.2 V and 700MHz/47 \({\mu }\)W at 0.6 V. In IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) Digest Technical Papers, pp. 328–329.
Abbas, M., Furukawa, Y., Komatsu, S., Takahiro, J., & Asada, K. (2010). Clocked comparator for high-speed applications in 65nm technology. In IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), pp. 1–4.
Ebata, T., Omae, U., Machida, K., Hoshi, K., & Waho, T. (2010). Enhancement of comparator operation speed by using negative-differential-resistance devices. In Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 3020–3023.
Chan, C.-H., Zhu, Y., Chio, U., Sin, S.-W., Seng-Pan, U., & Martins, R. (2011). A reconfigurable low-noise dynamic comparator with offset calibration in 90nm CMOS. In IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), pp. 233–236.
Gao, J., Li, G., & Li, Q. (2015). High-speed low-power common-mode insensitive dynamic comparator. Electronics Letters, 51(2), 134–136.
Xu, D., Xu, S., & Chen, G. (2015). High-speed low-power and low-power supply voltage dynamic comparator. Electronics Letters, 51(23), 1914–1916.
Baradaranrezaeii, A., Shino, O., Hadidi, K., & Khoei, A. (2015). An ultra high-speed high-resolution low-offset low-power voltage comparator with a reliable offset cancellation method for high-performance applications in 0.18 \({\upmu }\rm {m}\) CMOS technology. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 85(1), 181–192.
Chin, S.-M., Hsieh, C.-C., Chiu, C.-F., & Tsai, H.-H. (2010). A new rail-to-rail comparator with adaptive power control for low power SAR ADCs in biomedical application. In Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 1575–1578.
Guo, L., Ge, T., & Chang, J. S. (2010). A micropower comparator for high power-efficiency hearing aid class D amplifiers. In Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 1248–1251.
Jung, Y., Lee, S., Chae, J., & Temes, G. C. (2011). Low-power and low-offset comparator using latch load. Electronics Letters, 47(3), 167–168.
Huynh, A. T., Sedighi, B., Duong, H. T., Le, H. V., & Skafidas, E. (2012). A 400-\({\rm \mu }\)W 3-GHz comparator in 65-nm CMOS. In IEEE International Symposium Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), pp. 119–121.
Lu, J., & Holleman, J. (2013). A low-power high-precision comparator with time-domain bulk-tuned offset cancellation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 60(5), 1158–1167.
Babayan-Mashhadi, S., & Lotfi, R. (2014). Analysis and design of a low-voltage low-power double-tail comparator. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 22(2), 343–352.
Ahmadi, M., & Namgoong, W. (2015). Comparator power minimization analysis for SAR ADC using multiple comparators. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 62(10), 2369–2379.
Ahmadi, M., & Namgoong, W. (2015). Comparator power reduction in low-frequency SAR ADC using optimized vote allocation. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 23(11), 2384–2394.
Kong, L., Lu, Y., & Alon, E. (2011). A multi-GHz area-efficient comparator with dynamic offset cancellation. In IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), pp. 1–4.
Watanabe, H., Nakamura, S., & Takao, W. (2008). A design of HEMT comparators for ultrahigh-speed A/D conversion. IEICE Transactions on Electronics, 91(5), 688–692.
McGregor, I., & Elgaid, K. (2010). Low-power GaAs comparator and monostable. Electronics Letters, 46(17), 1214–1215.
Fiedler, H. L., Hoefflinger, B., Demmer, W., & Draheim, P. (1981). A 5-bit building block for 20 MHz A/D converters. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 16(3), 151–155.
Figueiredo, P. M., & Vital, J. C. (2006). Kickback noise reduction techniques for CMOS latched comparators. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 53(7), 541–545.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Information Science Laboratory Center of USTC for software & hardware services. They would also like to acknowledge MediaTek for USTC students and project sponsorship. And the support by the National High-tech R&D Program (863 Program) of China under Project 2015AA016801.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Diao, S. & Lin, F. An energy-efficient high-speed CMOS hybrid comparator with reduced delay time in 40-nm CMOS process. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 89, 231–238 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0811-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0811-4