Abstract
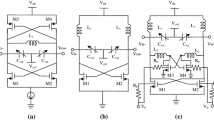
A combined low-noise amplifier and voltage-controlled oscillator (LNA–VCO) is implemented in a 0.13-µm CMOS technology. The low-power LC VCO and LNA circuits are stacked and share the same bias current. An LC filter is used between the LNA and the VCO to improve the isolation between the two functions. Based on the measurement results of the proof-of-concept prototype, the LNA achieves a gain of 18.4 dB and a noise figure (NF) of 3.8 dB at 2.4 GHz. The VCO has a center frequency of 2.45 GHz with a −5.3 dBm output power and a phase noise of −119 dBc/Hz at 1-MHz offset. The combined LNA–VCO block consumes 240 µW from a 0.8 V supply.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Song, T., H-S, Oh, Yoon, E., & Hong, S. (2007). A low-power 2.4-GHz current-reused receiver front-end and frequency source for wireless sensor network. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42(5), 1012–1022.
Taris, T., Begueret, J. B., & Deval, Y. (2011). A 60 µW LNA for 2.4 GHz wireless sensors network applications. In IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (pp. 199–202) Baltimore, USA, June 2011.
Fiorelli, R., Peralias, E. J., & Silveira, F. (2011). LC-VCO design optimization methodology based on g m /I D ratio for nanometer CMOS technologies. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 59(7), 1822–1832.
Kraimia, H., Taris, T., Begueret, J. B., & Deval, Y. (2011). A 2.4 GHz ultra-low power current-reuse bleeding mixer with resistive feedback. In IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (pp. 128–131) Beirut, Lebanon, December 2011.
Pletcher, N. M., Gambini, S., & Rabaey, J. (2009). A 52 µW wake-up receiver with 72 dBm sensitivity using an uncertain-IF architecture. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(1), 269–280.
Vidojkovic, M. (2010). A 500 μW 5 Mbps ULP super-regenerative RF front-end. In European Solid-State Circuits Conference (pp. 462–465) Sevilla, Spain, September 2010.
Han, Y., Macias-Montero, J. G., Akhnoukh, A., de Vreede, L. C. N., Long, J. R., Pekarik, J. J., & Burghartz, J. N. (2010). A 120 μW fully integrated BPSK receiver in 90 nm CMOS. In IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (pp. 277–280) Anaheim, USA, June 2010.
Abdelghany, M. A., Pokharel, R. K., Kanaya, H., & Yoshida, K. (2011). Low-voltage low-power combined LNA-single gate mixer for 5 GHz wireless systems. In IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (pp. 199–202) Baltimore, USA, June 2011.
Wang, T.-P., Chang, C.-C., Liu, R.-C., et al. (2006). A low-power oscillator mixer in 0.18-µm CMOS technology. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 54(1), 88–95.
Ortigueira, E., Fernandes, J., Silva, M., & Oliveira, L. B. (2012). An ultra compact wideband combined LNA-oscillator-mixer for biomedical applications. In IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (pp. 162–165) Boise, USA, August 2012.
Dautriche, P. (2011). Analog design trends and challenges in 28 and 20 nm CMOS technology. In The European Solid State Circuit Conference (ESSCIRC) (pp. 1–4) Helsinki, Finland, September 2011.
Mangla, A., Fadhuile, F., Taris, T., Deval, Y., & Enz, C. (2013). Design methodology for ultra low-power analog circuits using next generation BSIM6 compact model. MicroElectronic Journal, 44(7), 570–575. doi:10.1016/j.mejo.2013.02.022.
Pletcher, N., & Rabey, J. (2005). A 100 uW, 1.9 GHz oscillator with fully digital frequency tuning. In The European Solid State Circuit Conference (ESSCIRC) (pp. 387–390) Grenoble, France, September 2005.
Taris, T., Rashtian, H., Masnadi Shiraz, A. H., & Mirabbasi, S. (2013). A low-power 2.4-GHz combined LNA–VCO structure in 0.13-µm CMOS. In IEEE Northeast Workshop on Circuits and Systems (NEWCAS) (pp. 1–4) Paris, France, June 2013.
Wu, C.-Y., & Shahroury, F. R. (2006). A low voltage CMOS LNA design utilizing the technique of capacitive feedback matching network. In: IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS) (pp. 78–81) December 2006.
Lee, H., & Mohammadi, S. (2006). A 3 GHz subthreshold CMOS low noise amplifier. In IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium (pp. 545–548) San Francisco, CA, USA, June 2006.
Aaron, V., Chirn Chye, B., et al. (2008). A subthreshold low-noise amplifier optimized for ultra-low-power applications in the ISM band. IEEE Transaction on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 56(2), 286–292.
Jeong, C. J., Qu, W. et al. (2011). A 1.5 V, 140 μA CMOS ultra-low power common-gate LNA. In IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium (pp. 203–206) Baltimore, USA, June 2011.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC). Access to computer-aided design (CAD) tools, the CMOS technology design kit, and fabrication are facilitated by CMC Microsystems. The authors would like to thank Roozbeh Mehrabadi and Dr. Roberto Rosales for their CAD tool and technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work is an extended version of the following paper:
Thierry Taris, Hooman Rashtian, Amir Hossein Masnadi Shirazi, and Shahriar Mirabbasi, “A Low-Power 2.4-GHz Combined LNA–VCO Structure in 0.13-µm CMOS,” IEEE International NEWCAS Conference, Paris, France, June 2013.
This extended version includes new material as:
A specific section to further explain the inversion coefficient (IC) approach and (gm.fT/ID) metric for the design of low power RF building blocks (Section 2). The analytic expressions of the input impedance and the noise figure for the LNA part (Section 4). A new set of measurement results of the LNA–VCO chip (Section 5).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taris, T., Rashtian, H., Shirazi, A.H.M. et al. A low-power 2.4-GHz combined LNA–VCO structure in 0.13-µm CMOS. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 81, 667–675 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0439-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0439-1