Abstract
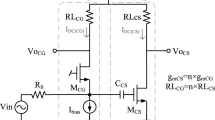
In this paper we describe a balun LNA with noise and distortion cancelling with active loads to boost the gain and reduce the noise figure (NF). Simulation and measurements results, with a 130 nm CMOS technology, show that the gain is enhanced by about 3 dB and the NF is reduced by at least 0.5 dB, with a negligible impact on the circuit linearity (IIP3 is about 0 dBm). The total power dissipation is only 4.8 mW, and the active area is less than 50 × 50 µm2.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amer, A., Hegazi, E., & Ragai, H. (2007). A low power wideband CMOS LNA for WiMax. IEEE Transactions on Circuits Systems II, 54(1), 4–8.
Bagheri, R., Mirzaei, A., Chehrazi, S., Heidari, M. E., Lee, M., Mikhemar, M., et al. (2006). An 800-MHz–6-GHz software-defined wireless receiver in 90-nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41(12), 2860–2876.
Bastos, I., Oliveira, L. B., Goes, J., & Silva, M. (2010). MOSFET-only wideband LNA with noise cancelling and gain optimization. In IEEE Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems (MIXDES) (pp. 306–311, 24–26).
Bastos, I., Oliveira, L. B., Oliveira, J., Goes, J. & Silva, M. (2012). Balun LNA with continuosly controlable gain and with noise and distortion cancellation. In IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS’12) (pp. 2143–2146). Seoul.
Bastos, I., Oliveira, L. B., Oliveira, J., Goes, J. & Silva, M. M. (2013). Double feedforward 0.6 V LNA with high gain and low noise figure. In 20th International Conference on Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems (MIXDES’13).
Blaakmeer, S., Klumperink, E., Leenaerts, D., & Nauta, B. (2008). Wideband balun-LNA with simultaneous outputs balancing, noise-canceling and distortion-canceling. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43(6), 1341–1350.
Bruccoleri, F., Klumperink, E., & Nauta, B. (2004). Wide-band CMOS low-noise amplifier exploiting thermal noise canceling. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 39(2), 275–282.
Chew, K. W., Yeo, K. S., & Chu, S. F. (2004). Effect of technology scaling on the 1/f noise of deep submicron MOS transistors. Solid-State Electronics, 48, 1101–1109.
Crols, J., & Steyaert, M. (1997). CMOS wireless transceiver design. Norwell: Kluwer.
Han, K., Zou, L., Liao, Y., Min, H., & Tang, Z. (2008). A wideband CMOS variable gain low noise amplifier based on single-to-differential stage for TV tuner applications. In IEEE Solid-State Circuits Conference, A-SSCC ‘08, (pp. 457–460), 3–5 Nov 2008.
Im, D., Nam, I., & Lee, K. (2010). A CMOS active feedback balun-LNA with high IIP2 for wideband digital TV receivers. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 58(12), 3566–3579.
Iniewski, K. (2008). VLSI circuits for biomedical applications. London: Artech House.
Lee, T. H. (2004). The design of CMOS radio frequency integrated circuits (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Mak, P.-I., & Martins, R. (2009). Design of an ESD-protected ultra-wideband LNA in nanoscale CMOS for full-band mobile TV tuners. IEEE Transactions on Circuits Systems I, 56, 933–942.
Manghisoni, M., Ratti, L., Re, V., Speziali, V., & Traversi, G. (2006). Noise characterization of 130 and 90 nm CMOS technologies for analog front-end electronics. IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference, 1, 214–218.
Razavi, B. (1998). RF Microelectronics. Bergen County: Prentice-Hall.
Xiao, J., Mehr, I., & Silva-Martinez, J. (2007). A high dynamic range CMOS variable gain amplifier for mobile DTV tuner. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42(2), 292–301.
Zhan, J.-H. C. & Taylor, S. S. (2006). A 5 GHz resistive-feedback CMOS LNA for low-cost multi-standard applications. In IEEE ISSCC 2006 Digest of Technical Papers (pp. 200–201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bastos, I., Oliveira, L.B., Goes, J. et al. A low power balun LNA with active loads for gain and noise figure optimization. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 81, 693–702 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0426-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0426-6