Abstract
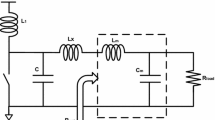
Class-E amplifiers are attractive for wireless handsets because of their high efficiency and simple implementation. However, it requires inductors in its output matching network that are inherently low Q components affecting efficiency and may require significantly large area in fully integrated implementation. In this paper a novel approach of implementing parallel circuit differential class-E amplifier is presented. Instead of using an inductor parallel to the transistor drain of each amplifier, a single capacitor at the single ended side of the balun provides the parallel inductance effect to the switching transistors. As a result, number of inductors required for circuit implementation is reduced which means reduced losses, less area and better tuning of reactance can be achieved. A test circuit is implemented in 0.13 μm CMOS process. Measurement results verify the validity of the concept. The Power Amplifier achieves 22 dBm output power at 2.4 GHz from a 2.5 V with an overall Power Added Efficiency of 38 %.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki, I., Kee, S. D., Rutledge, D. B., & Hajimiri, A. (2002). Fully integrated CMOS power amplifier design using the distributed active-transformer architecture. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 37(3), 371–383.
Yan, L., Ruili, W., Lopez, J., & Lie, D. Y. C. (2011). “A highly-efficient BiCMOS cascode class-E power amplifier using both envelope-tracking and transistor resizing for LTE-like applications,” Bipolar/BiCMOS Circuits and Technology Meeting (BCTM), 2011 IEEE, pp. 142–145, 9–11 Oct 2011.
Juntunen, E., Dawn, D., Pinel, S., & Laskar, J. (2011). A high-efficiency, high-power millimeter-wave oscillator using a Feedback Class-E Power Amplifier in 45 nm CMOS. Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, IEEE, 21(8), 430–432.
Zhang, R., Acar, M., van der Heijden, M. P., Apostolidou, M., de Vreede, L. C. N., & Leenaerts, D. M. W. (2011). “A 550–1,050 MHz + 30 dBm class-E power amplifier in 65 nm CMOS,” Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), 2011 IEEE, pp. 1–4, 5–7 June 2011.
Cripps, S. C. (2006). RF power amplifiers for wireless communications (2nd ed.). London: Artech House.
Zulinski, R. E., & Steadman, J. W. (1987). Class-E power amplifiers and frequency multipliers with finite dc feed inductance. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, CAS-34, 1074–1108.
Kumar, N., Prakash, C., Grebennikov, A., & Mediano, A. (2008). High-efficiency broadband parallel-circuit class-E RF power amplifier with reactance-compensation technique. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 56(3), 604–612.
Singhal, N., Nidhi, N., & Pamarti, S. (2010). A power amplifier with minimal efficiency degradation under back-off. In Proceedings—IEEE International symposium on circuits and systems, pp. 1851–1854.
Yoo, C., & Huang, Q. (2001). A common gate switched 0.9W class-E power amplifier with 41 % PAE in 0.25 μm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 36(5), 823–830.
Lee, O., Han, J., An, K. H., Lee, D. H., Lee, K.-S., Hong, S., et al. (2010). A charging acceleration technique for highly efficient cascode class-E CMOS power amplifiers. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 45(10), 2184–2197.
Mazzanti, A., Larcher, L., Brama, R., & Svelto, F. (2006). Analysis of reliability and power efficiency in cascode class-E PAs. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41(5), 1222–1229.
Bakalski, W., Simburger, W., Knapp, H., Wohlmuth, H.-D., & Scholtz, A. L. (2002). Lumped and distributed lattice-type LC-baluns. Microwave Symposium Digest, 2002 IEEE MTT-S International, 1, 209–212.
Singhal, N., Nidhi, N., Patel, R., & Pamarti, S. (2011). A zero-voltage-switching contour-based power amplifier with minimal efficiency degradation under back-off. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 59(6), 1589–1598.
Brama, R., Larcher, L., Mazzanti, A., & Svelto, F. (2008). A 30.5 dBm 48 % PAE CMOS Class-E PA with integrated balun for RF applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43(8), 1755–1762.
Fritzin, J., Johansson, T., & Alvandpour A. (2008). “Impedance matching techniques in 65 nm CMOS power amplifiers for 2.4 GHz 802.11n WLAN,” IEEE European Microwave Conference (EuMC), pp. 1207–1210, Amsterdam, 28–30 Oct. 2008.
Zimmermann, N., Johansson, T., & Heinen, S., (2008). “A 27.3 dBm DECT power amplifier for 2.5 V supply in 0.13 μm CMOS,” IEEE Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic Integrated Circuits in RF Systems. SiRF 2008, pp. 30–33, 23–25 Jan 2008.
Reynaert, P. (2007). A 2.45-GHz 0.13 μm CMOS PA with parallel amplification. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42(3), 551–562.
Raab, F. H. (2001). Class-E, Class-C, and Class-F power amplifiers based upon a finite number of harmonics. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 49(8), 1462–1468.
Negra, R., & Bachtold, W. (2006). Lumped-element load-network design for class-E power amplifiers. Microwave Theory and Techniques, IEEE Transactions on, 54(6), 2684–2690.
Reynaert, P., & Steyaert, M. (2006). RF power amplifiers for mobile communications. Amsterdam: Springer.
Grebennikov, A., & Sokal, N. (2007). Switch mode RF power amplifiers. Oxford: Newnes.
Walling, J. S., Lakdawala, H., Palaskas, Y., Ravi, A., Degani, O., Soumyanath, K., et al. (2009). A class-E PA with pulse-width and pulse-position modulation in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(6), 1668–1678.
Fritzin, J., &Alvandpour, A. (2009). Low Voltage Class-E Power Amplifiers for DECT and Bluetooth in 130 nm CMOS, IEEE Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic Integrated Circuits in RF Systems, SiRF '09, pp. 1–4, 19–21 Jan 2009.
Lee, O., An, K. H., Kim, H., Lee, D. H., Han, J., Yang, K. S., et al. (2010). Analysis and design of fully integrated high-power parallel-circuit class-E CMOS power amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 57(3), 725–734.
Yoon, Y., Kim, H., Cha, J., Lee, O., Kim, H. S., Kim, W., et al. (2011). Fully-integrated concurrent dual-band CMOS power amplifier with switchless matching network. Electronics Letters, 47(11), 659–661.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, H.R., Fritzin, J., Alvandpour, A. et al. A parallel circuit differential class-E power amplifier using series capacitance. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 75, 31–40 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0036-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0036-8