Abstract
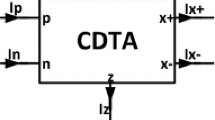
The various architectures of transceivers for current standards are firstly compared. Different possibilities to achieve multi-standard transceivers are also recalled and compared. We demonstrate that ease of realization and flexibility evolve in opposite directions. The advantages and drawbacks of reconfigurable active filters are indicated. We demonstrate that the second generation current controlled conveyor operating in current mode is perfectly suitable for the realization of frequency-agile filters. After a brief recall of the essential points of agile filters, a second order frequency agile bandpass filter operating in current mode is implemented with CCCII+ . It has four central frequencies whose values could be selected digitally. The validation results show that its tuning ratio n = f 0max/f 0min is equal to 5.1 with f 0max = 1.22 GHz.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mak, P., S-S, U., & Martins, R. P. (2007). Transceiver structure selection: Review, state-of-the-art survey and case study. IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine, 7(2), 6–25.
Behzad, R. (1997). RF Microelectronics. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall. ISBN: 978-0138875718.
Sun, Y.-R. (2006). Generalized bandpass sampling receivers for software defined radio. Doctoral thesis, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm.
Mitola, J. (1995). The software radio architecture. IEEE Communications Magazine, 33(5), 26–38.
Abidi, A. A. (2007). The path to the software-defined radio receiver. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42(5), 954–966.
Leod, J. R. M., Nesimoglu, T., Beach, M. A., & Warr, P. A. (2002). Enabling technologies for software defined radio transceivers. MILCOM 2002 Proceedings, 1(7–10), 354–358.
Maurer, L., Hueber, G., Dellsperger, T., Burger, T., Huemer, M., & Weigel, R. (2006). A frequency agile terminal receiver for wireless multi-standard applications. In: IEEE radio and wireless symposium (pp. 291–294). San Diego: IEEE.
Balwant, G. (2006). Conception of novel wideband performance-controllable RF circuits in SiGe. In Impedance matching circuit, single-ended to differential baluns, and single-ended and differential low-noise amplifiers. Doctoral thesis, IMS Laboratory, Bordeaux.
Cedric, M. (2006). Contribution a l’etude d’un Synthetiseur de Frequence pour Objets Communicants Multistandards en Technologie CMOS SO. Doctoral thesis, IMS Laboratory, Bordeaux.
Yahya, L. (2009). “Filtres à Fréquence Agile Totalement Actifs: Théorie Générale et Circuits de Validation en Technologie SiGe BiCMOS 0.25 μm”. Doctoral thesis, IMS Laboratory, Bordeaux.
Lakys, Y., Godara, B., & Fabre, A. (2009). Cognitive and encrypted communications, part 1: state of the art for frequency-agile filters. In ELECO’09 proceedings (pp. 1–16). Bursa: ELECO’09.
Koochakzadeh, M., & Tamijani, A. (2008). Multi-scale tunable filter covering a frequency range of 6.5:1. In Microwave symposium digest, 2008 IEEE MTT-S international (pp. 1023–1026). Seattle: IEEE MTT-S.
Nakaska, J. K., & Haslett, J. W. (2007). 2 GHz automatically tuned Q-enhanced CMOS bandpass filter. IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, 3–8, 1599–1602.
Pipilos, S., Tsividis, Y. P., Fenk, J., & Papananos, Y. (1996). A Si 1.8 GHz RLC filter with tunable center frequency and quality Factor. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 31(10), 1517–1525.
El Oualkadi, A. E., El Kaamouchi, M., Paillot, J.-M., Vanhoenacker-Janvier, D., & Flandre, D. (2007). Fully integrated high-Q switched capacitor bandpass filter with center frequency and bandwidth tuning. IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium, 3–5, 681–684.
Salem, S., Fakhfakh, M., Masmoudi, D., Loulou, M., Loumeau, P., & Masmoudi, N. (2006). A high performances CMOS CCII and high frequency applications. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 49(1), 71–78.
Fabre, A., Saaid, O., Wiest, F., & Boucheron, C. (1998). High frequency high-Q BiCMOS current-mode bandpass filter and mobile communication application. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 33(4), 614–625.
Dülger, F., Sánchez-Sinencio, E., & Silva-Martinez, J. (2003). A 1.3-V 5-mW fully integrated tunable bandpass filter at 2.1 GHz in 0.35-μm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(6), 918–928.
Yue, W., Shi, C., Ding, X., Ismail, M., & Olsson, H. (2002). Design of CMOS VHF/RF biquadratic filters. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 33(3), 239–248.
Yue, W., Ismail, M., & Olsson, H. (2003). RF bandpass fitler design based on CMOS active inductors. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II, 50(12), 942–949.
Gao, Z., Yu, M., Ye, Y., & Jianguo M. (2006). A CMOS bandpass filter with wide-tuning range for wireless applications. In Proceedings ISCAS 2006 (pp. 867–870). Sinchon: ISCAS.
Fabre, A., Saaid, O., Wiest, F., & Boucheron, C. (1996). High frequency applications based on a new current controlled conveyer. IEEE Transaction on Circuits and Systems, 43, 82–91.
Roberts, G.W., Sedra, A. S. (1999). All current-mode frequency selecting circuits. Electronic Letter, 27(12), 759–761.
Fabre, A. (2009). Electronique analogique rapide, Ellipses, Technosup (1st ed., p. 204). ISBN13: 978-2-7298-4386-1.
Sedra, A., & Smith, K. (1970). A second-generation current conveyor and its applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 17(1), 132–134.
Sedra, A. (1989). The current conveyor: History and progress. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 3(8–11), 1567–1571.
Fabre, A. (1983). Dual translinear voltage/current convertor. Electronics Letters, 19, 1030–1031.
Fabre, A., Saaid, O., Wiest, F., & Boucheron, C. (1997). Low power current-mode second-order bandpass IF filter. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II, 44(6), 436–446.
Multi-Projects Website (2011). http://cmp.imag.fr. Accessed 17 March 2011.
Lakys, Y., Godara, B., & Fabre, A. (2009). Cognitive and encrypted communications, part 2: A new approach to active frequency-agile filters and validation results for an agile bandpass topology in SiGe-BiCMOS. In ELECO’09 proceedings (pp. 16–29). Bursa: ELECO’09.
Lakys, Y., & Fabre, A. (2010). The shadow filter, a new family of second order filters. Electronic Letters, 46(4), 276–277.
Lakys, Y., & Fabre, A. (2010). Shadow filters, generalization to the nth class. Electronic Letters, 46(14), 985–986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakys, Y., Fabre, A. Multistandard transceivers: state of the art and a new versatile implementation for fully active frequency agile filters. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 74, 63–78 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-012-9861-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-012-9861-4