Abstract
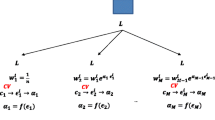
We discuss receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) for binary classification problems in clinical fields. We propose a statistical method for combining multiple feature variables, based on a boosting algorithm for maximization of the AUC. In this iterative procedure, various simple classifiers that consist of the feature variables are combined flexibly into a single strong classifier. We consider a regularization to prevent overfitting to data in the algorithm using a penalty term for nonsmoothness. This regularization method not only improves the classification performance but also helps us to get a clearer understanding about how each feature variable is related to the binary outcome variable. We demonstrate the usefulness of score plots constructed componentwise by the boosting method. We describe two simulation studies and a real data analysis in order to illustrate the utility of our method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bamber D. (1975) The area above the ordinal dominance graph and the area below the receiver operating characteristic graph. Journal of Mathematical Psychology 12: 387–415
Chambers J.M., Hastie T.J. (1992) Statistical models in S. Pacific Grove, CA, Wadsworth and Brooks
Eguchi S., Copas J. (2002) A class of logistic-type discriminant functions. Biometrika 89: 1–22
Freund Y., Schapire R.E. (1997) A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. Journal of Computer and System Sciences 55: 119–139
Friedman J., Hastie T., Tibshirani R. (2000) Additive logistic regression: A statistical view of boosting (with discussion). The Annals of Statistics 28: 337–407
Hastie T., Tibshirani R. (1986) Generalized additive models. Statistical Science 1: 297–318
Hastie T., Tibshirani R., Friedman J. (2001) The elements of statistical learning. Springer, New York
Kawakita M., Minami M., Eguchi S., Lennert-Cody C.E. (2005) An introduction to the predictive technique AdaBoost with a comparison to generalized additive models. Fisheries Research 76: 328–343
Long P.M., Servedio R.A. (2007) Boosting the area under the ROC curve. In: Platt J.C., Koller D., Singer Y., Roweis S. (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems (Vol. 20). MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 945–952
Ma S., Huang J. (2005) Regularized ROC method for disease classification and biomarker selection with microarray data. Bioinformatics 21: 4356–4362
Ma S., Huang J. (2007) Combining multiple markers for classification using ROC. Biometrics 63: 751–757
McIntosh M.W., Pepe M.S. (2002) Combining several screening tests: Optimality of the risk score. Biometrics 58: 657–664
McLachlan G.J. (2004) Discriminant analysis and statistical pattern recognition. Wiley, New York
Murata N., Takenouchi T., Kanamori T., Eguchi S. (2004) Information geometry of \({\mathcal{U}}\) -Boost and Bregman divergence. Neural Computation 16: 1437–1481
Neyman J., Pearson E.S. (1933) On the problem of the most efficient tests of statistical hypotheses. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series A 231: 289–337
Pepe M.S. (2003) The statistical evaluation of medical tests for classification and prediction. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Pepe M.S., Thompson M.L. (2000) Combining diagnostic test results to increase accuracy. Biostatistics 1: 123–140
Pepe M.S., Longton G., Anderson G.L., Schummer M. (2003) Selecting differentially expressed genes from microarray experiments. Biometrics 59: 133–142
Pepe M.S., Cai T., Longton G. (2006) Combining predictors for classification using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve. Biometrics 62: 221–229
Pepe M.S., Janes H., Longton G., Leisenring W., Newcomb P. (2004) Limitations of the odds ratio in gauging the performance of a diagnostic, prognostic, or screening marker. American Journal of Epidemiology 159: 882–890
Su J.Q., Liu J.S. (1993) Linear combinations of multiple diagnostic markers. Journal of the American Statistical Association 88: 1350–1355
Takenouchi T., Eguchi S. (2004) Robustifying AdaBoost by adding the naive error rate. Neural Computation 16: 767–787
Tutz G., Binder H. (2006) Generalized additive modeling with implicit variable selection by likelihood-based boosting. Biometrics 62: 961–971
Ueki, M., Fueda, K. (2009). Optimal tuning parameter estimation in maximum penalized likelihood method. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics. doi:10.1007/s10463-008-0186-0.
Wang Z., Chang Y.I., Ying Z., Zhu L., Yang Y. (2007) A parsimonious threshold-independent protein feature selection method through the are under receiver operating characteristic curve. Bioinformatics 23: 2788–2794
Zhang B.T., Yu B. (2005) Boosting with early stopping: Convergence and consistency. The Annals of Statistics 33: 1538–1579
Zhou X.H., Obuchowski N.A., McClish D.K. (2002) Statistical methods in diagnostic medicine. Wiley, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Komori, O. A boosting method for maximization of the area under the ROC curve. Ann Inst Stat Math 63, 961–979 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10463-009-0264-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10463-009-0264-y