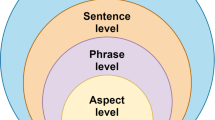
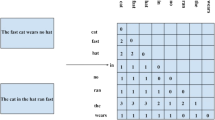
Abstract
In the field of natural language processing and text mining, sentiment analysis (SA) has received huge attention from various researchers’ across the globe. By the prevalence of Web 2.0, user’s became more vigilant to share, promote and express themselves along with any issues or challenges that are being encountered on daily activities through the Internet (social media, micro-blogs, e-commerce, etc.) Expression and opinion are a complex sequence of acts that convey a huge volume of data that pose a challenge for computational researchers to decode. Over the period of time, researchers from various segments of public and private sectors are involved in the exploration of SA with an aim to understand the behavioral perspective of various stakeholders in society. Though the efforts to positively construct SA are successful, challenges still prevail for efficiency. This article presents an organized survey of SA (also known as opinion mining) along with methodologies or algorithms. The survey classifies SA into categories based on levels, tasks, and sub-task along with various techniques used for performing them. The survey explicitly focuses on different directions in which the research was explored in the area of cross-domain opinion classification. The article is concluded with an objective to present an exclusive and exhaustive analysis in the area of opinion mining containing approaches, datasets, languages, and applications used. The observations made are expected to support researches to get a greater understanding on emerging trends and state-of-the-art methods to be applied for future exploration.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Abbasi A, Chen H, Salem A (2008) Sentiment analysis in multiple languages: feature selection for opinion classification in web forums. ACM Trans Inf Syst 26(3):1–34. https://doi.org/10.1145/1361684.1361685
Abbasi A, France S, Zhang Z, Chen H (2011) Selecting attributes for sentiment classification using feature relation networks. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 23(3):447–462
Abdelwahab O, Elmaghraby AS (2018) Deep learning based vs markov chain based text generation for cross domain adaptation for sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on information reuse and integration (IRI), pp 252–255. https://doi.org/10.1109/iri.2018.00046
Abdi A, Shamsuddin SM, Hasan S, Piran J (2019) Deep learning-based sentiment classification of evaluative text based on multi-feature fusion. Inf Process Manag 56(4):1245–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2019.02.018
Abdul-mageed M, Diab M, Kübler S (2013) SAMAR: subjectivity and sentiment analysis for Arabic social media. Comput Speech Lang 28(1):20–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csl.2013.03.001
Agarwal A, Xie B, Vovsha I, Rambow O, Passonneau R (2011) Sentiment analysis of Twitter data. In: Proceedings of the workshop on languages in social media, pp 30–38
Agrawal R, Srikant R (1994) Fast algorithms for mining association rules in large databases. In: Proceedings of the 20th international conference on very large data bases, pp 487–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02948845
Algur SP, Patil AP, Hiremath PS, Shivashankar S (2010) Conceptual level similarity measure based review spam detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on signal and image processing (ICSIP), pp 416–423
Al-Moslmi T, Omar N, Abdullah S, Albared M (2017) Approaches to cross-domain sentiment analysis: a systematic literature review. IEEE Access 5:16173–16192. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2690342
Aloufi S, Saddik AE (2013) Sentiment identification in football-specific tweets. IEEE Access 6:78609–78621. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2885117
Apache OpenNLP. https://opennlp.apache.org/. Accessed 7 May 2019
Araque O, Corcuera-Platas I, Sánchez-Rada JF, Iglesias CA (2017) Enhancing deep learning sentiment analysis with ensemble techniques in social applications. Expert Syst Appl 77:236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.02.002
Baccianella S, Esuli A, Sebastiani F (2008) SENTIWORNET 3.0: an enhanced lexical resource for sentiment analysis and opinion mining. In: Proceedings of the seventh conference on international language resources and evaluation, pp 2200–2204
Bagheri A, Saraee M, Jong FD (2013) Care more about customers: unsupervised domain-independent aspect detection for sentiment analysis of customer reviews. Knowl-Based Syst 52:201–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2013.08.011
Bai X (2011) Predicting consumer sentiments from online text. Decis Support Syst 50(4):732–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2010.08.024
Balahur A, Hermida JM, Montoyo A (2012a) Building and exploiting EmotiNet: a knowledge base for emotion detection based on the appraisal theory model. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 3(1):88–101
Balahur A, Hermida JM, Montoyo A (2012b) Detecting implicit expressions of emotion in text: a comparative analysis. Decis Support Syst 53(4):742–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.05.024
Balqisnadiah (2016) Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 image—Google Search, Web content. https://www.google.com/search?q=Web+1.0+and+Web+2.0+image&rlz=1C1CHBD_enIN807IN807&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwj6pYeG3d7iAhVEb30KHfxyDQEQ_AUIECgB&biw=1366&bih=657#imgrc=_. Accessed 10 June 2019
Banea C, Mihalcea R, Wiebe J, (2008) Multilingual subjectivity analysis using machine translation. In: Proceedings of the empirical methods in natural language processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 127–135
Banea C, Mihalcea R, Wiebe J (2013) Sense-level subjectivity in a multilingual setting. Comput Speech Lang 28(1):7–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csl.2013.03.002
Banerjee S, Chua AYK (2014) Applauses in hotel reviews: genuine or deceptive?. In: Proceedings of the science and information conference, pp 938–942
Basari ASH, Hussin B, Ananta IGP, Zeniarja J (2013) Opinion mining of movie review using hybrid method of support vector machine and particle swarm optimization. Procedia Eng 53:453–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.02.059
Bell D, Koulouri T, Lauria S, Macredie RD, Sutton J (2014) Microblogging as a mechanism for human–robot interaction. Knowl-Based Syst 69:64–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.05.009
Benamara F, Cesarano C, Picariello A, Reforgiato D, Subrahmanian V (2007) Sentiment analysis: adjectives and adverbs are better than adjectives alone. In: Proceedings of the international conference on weblogs and social media (ICWSM 2007), pp 203–206
Bird S, Klein E, Loper E (2009) Natural language processing with Python: analyzing text with the natural language toolkit. O’Reilly Media lnc, Newton
Bisio F, Gastaldo P, Peretti C, Zunino R, Cambria E (2013) Data intensive review mining for sentiment classification across heterogeneous domains. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM international conference on advances in social networks analysis and mining, pp 1061–1067
Blitzer J, Mcdonald R, Pereira F (2006) Domain adaptation with structural correspondence learning. In: Proceedings of the 2006 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 120–128
Blitzer J, Dredze M, Pereira F (2007) Biographies, bollywood, boom-boxes and blenders: domain adaptation for sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 45th annual meeting of the association of computational linguistics, pp 440–447
Boiy E, Moens M-F (2009) A machine learning approach to sentiment analysis in multilingual Web texts. Inf Retr 12(5):526–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10791-008-9070-z
Bollegala D, Mu T (2016) Cross-domain sentiment classification using sentiment sensitive embeddings. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 28(2):398–410
Bollegala D, Weir D, Carroll J (2013) Cross-domain sentiment classification using a sentiment sensitive thesaurus. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(8):1719–1731
Bollen J, Mao H, Zeng X (2011) Twitter mood predicts the stock market. J Comput Sci 2(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2010.12.007
Bosco C, Patti V, Bolioli A (2015) Developing corpora for sentiment analysis: the case of irony and senti-TUT. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 4158–4162
Bravo-marquez F, Mendoza M, Poblete B (2014) Meta-level sentiment models for big social data analysis. Knowl-Based Syst 69:86–99
Brody S, Elhadad N (2010) An unsupervised aspect-sentiment model for online reviews. In: Proceedings of the human language technologies: the 2010 annual conference of the North American chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 804–812
Cambria E (2013) An introduction to concept-level sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the Mexican international conference on artificial intelligence. Springer, Berlin, pp 478-483. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-45111-9_41
Cambria E (2016) Affective computing and sentiment analysis. IEEE Intell Syst 31(2):102–107. https://doi.org/10.1109/MIS.2016.31
Cambria E, Speer R, Havasi C, Hussain A (2010) SenticNet: a publicly available semantic resource for opinion mining. In: Proceedings of the AAAI fall symposium: common-sense knowledge, pp 14–18
Cambria E, Havasi C, Hussain A (2012) SenticNet 2: a semantic and affective resource for opinion mining and sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the twenty-fifth international florida artificial intelligence research society conference, pp 202–207
Cambria E, Schuller B, Xia Y, Havasi C (2013) New avenues in opinion mining and sentiment analysis. IEEE Intell Syst 28(2):15–21
Cambria E, Olsher D, Rajagopal D (2014) SenticNet 3: a common and common-sense knowledge base for cognition-driven sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the twenty-eighth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1515–1521
Cambria E, Gastaldo P, Bisio F, Zunino R (2015) An ELM-based model for affective analogical reasoning. Neurocomputing 149:443–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2014.01.064
Cambria E, Poria S, Bajpai R, Schuller B (2016) SenticNet 4: a semantic resource for sentiment analysis based on conceptual primitives. In: Proceedings of the 26th international conference on computational linguistics (COLING 2016), pp 2666–2677
Cambria E, Poria S, Hazarika D, Kwok K (2018) SenticNet 5: discovering conceptual primitives for sentiment analysis by means of context embeddings. In: Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1795–1802
Camp MVD, Bosch AVD (2012) The socialist network. Decis Support Syst 53(4):761–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.05.031
Carenini G, Ng R, Pauls A (2006) Multi-document summarization of evaluative text. In: Proceedings of the 11th conference of the european chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 305–312
Chakraborty R, Bhavsar M, Dandapat SK, Chandra J (2019) Tweet summarization of news articles: an objective ordering-based perspective. IEEE Trans Comput Soc Syst 6(4):761–777. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSS.2019.2926144
Chan SWK, Chong MWC (2017) Sentiment analysis in financial texts. Decis Support Syst 94:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2016.10.006
Chaturvedi I, Cambria E, Welsch RE, Herrera F (2018) Distinguishing between facts and opinions for sentiment analysis: survey and challenges. Inf Fusion 44:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2017.12.006
Che W, Li Z, Liu T (2010) LTP: a Chinese language technology platform. In: Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on computational linguistics: demonstrations, pp 13–16
Chen CC, Tseng Y (2011) Quality evaluation of product reviews using an information quality framework. Decis Support Syst 50(4):755–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2010.08.023
Chen W, Lin S, Huang S, Chung Y, Chen K (2010) E-HowNet and automatic construction of a lexical ontology. In: Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on computational linguistics: demonstrations, pp 45–48
Chen L, Liu C, Chiu H (2011) A neural network based approach for sentiment classification in the blogosphere. J Inform 5(2):313–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2011.01.003
Chen L, Qi L, Wang F (2012) Comparison of feature-level learning methods for mining online consumer reviews. Expert Syst Appl 39(10):9588–9601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.02.158
Chen F, Ji R, Su J, Cao D, Gao Y (2018) Predicting microblog sentiments via weakly supervised multimodal deep learning. IEEE Trans Multimed 20(4):997–1007. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2017.2757769
Cho H, Kim S, Lee J, Lee J (2014) Data-driven integration of multiple sentiment dictionaries for lexicon-based sentiment classification of product reviews. Knowl-Based Syst 71:61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.06.001
Costa H, Merschmann LHC, Barth F, Benevenuto F (2014) Pollution, bad-mouthing, and local marketing: the underground of location-based social networks. Inf Sci 279:123–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.03.108
Coussement K, Poel DVD (2009) Improving customer attrition prediction by integrating emotions from client/company interaction emails and evaluating multiple classifiers. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):6127–6134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.07.021
Cruz FL, Troyano JA, Enríquez F, Ortega FJ, Vallejo CG (2010) A knowledge-rich approach to feature-based opinion extraction from product reviews. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international workshop on Search and mining user-generated contents, pp 13–20
Cruz FL, Troyano JA, Enríquez F, Ortega FJ, Vallejo CG (2013) ‘Long autonomy or long delay?’ The importance of domain in opinion mining. Expert Syst Appl 40:3174–3184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.12.031
Dang Y, Zhang Y, Chen H (2010) A lexicon-enhanced method for sentiment classification: an experiment on online product reviews. IEEE Intell Syst 25(4):46–53
Dasgupta S, Ng V (2009) Mine the easy, classify the hard : a semi-supervised approach to automatic sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the joint conference of the 47th annual meeting of the ACL and the 4th international joint conference on natural language processing of the AFNLP, pp 701–709
Dashtipour K, Poria S, Hussain A, Cambria E, Hawalah AYA, Gelbukh A, Zhou Q (2016) Multilingual sentiment analysis: state of the art and independent comparison of techniques. Cogn Comput 8(4):757–771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-016-9415-7
Demirtas E (2013) Cross-lingual sentiment analysis with machine translation, utility of training corpora and sentiment lexica. Master dissertation, University of Technology
Deng Z, Luo K, Yu H (2014) A study of supervised term weighting scheme for sentiment analysis. Expert Syst Appl 41(7):3506–3513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.10.056
Derczynski L, Ritter A, Clark S, Bontcheva K (2013) Twitter part-of-speech tagging for all: overcoming sparse and noisy data. In: Proceedings of the international conference recent advances in natural language processing, pp 198–206
Deshmukh JS, Tripathy AK (2018) Entropy based classifier for cross-domain opinion mining. Appl Comput Inform 14(1):55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aci.2017.03.001
Desmet B, Hoste V (2013) Emotion detection in suicide notes. Expert Syst Appl 40(16):6351–6358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.05.050
Dey A, Jenamani M, Thakkar JJ (2018) Senti-N-Gram: an n-gram lexicon for sentiment analysis. Expert Syst Appl 103:92–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.03.004
Ding X, Liu B, Zhang L (2009) Entity discovery and assignment for opinion mining applications. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 1125–1134
Du J, Xu H, Huang X (2014) Box office prediction based on microblog. Expert Syst Appl 41(4):1680–1689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.08.065
Duh K, Fujino A, Nagata M (2011) Is machine translation ripe for cross-lingual sentiment classification ? In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: short papers, pp 429–433
Duric A, Song F (2012) Feature selection for sentiment analysis based on content and syntax models. Decis Support Syst 53(4):704–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.05.023
Eirinaki M, Pisal S, Singh J (2012) Sciences feature-based opinion mining and ranking. J Comput Syst Sci 78(4):1175–1184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcss.2011.10.007
Fan T, Chang C (2011) Blogger-centric contextual advertising. Expert Syst Appl 38:2010–2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.07.105
Fang Y, Tan H, Zhang J (2018) Multi-strategy sentiment analysis of consumer reviews based on semantic fuzziness. IEEE Access 6:20625–20631. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2820025
Farra N, Challita E, Assi RA, Hajj H (2010) Sentence-level and document-level sentiment mining for Arabic texts. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on data mining workshops sentence-level (IEEE Computer Society), pp 1114–1119. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDMW.2010.95
Feizollah A, Ainin S, Anuar NB, Abdullah ANB, Hazim M (2019) Halal products on Twitter: data extraction and sentiment analysis using stack of deep learning algorithms. IEEE Access 7:83354–83362. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2923275
Feldman R (2013) Techniques and applications for sentiment analysis. Commun ACM 56(4):82–89
Franco-salvador M, Cruz FL, Troyano JA, Rosso P (2015) Cross-domain polarity classification using a knowledge-enhanced meta-classifier. Knowl-Based Syst 86:46–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2015.05.020
Fu X, Yang J, Li J, Fang M, Wang H (2018) Lexicon-enhanced LSTM with attention for general sentiment analysis. IEEE Access Spec Sect Artif Intell Cogn Comput Commun Netw 6:71884–71891. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2878425
Fu X, Zhang S, Chen J, Ouyang T, Wu J (2019) A sentiment-aware trading volume prediction model for P2P market using LSTM. IEEE Access 7:81934–81944. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2923637
Fusilier DH, Montes-y-gómez M, Rosso P, Cabrera RG (2015) Detecting positive and negative deceptive opinions using PU-learning. Inf Process Manag 51(4):433–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2014.11.001
García-moya L, Anaya-sánchez H, Berlanga-llavori R (2013) Retrieving product features and opinions from customer reviews. IEEE Intell Syst 3:19–27
Gerani S, Mehdad Y, Carenini G, Ng RT, Nejat B (2014) Abstractive summarization of product reviews using discourse structure. In: Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP), pp 1602–1613
Geva T, Zahavi J (2014) Empirical evaluation of an automated intraday stock recommendation system incorporating both market data and textual news. Decis Support Syst 57:212–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2013.09.013
Ghiassi M, Skinner J, Zimbra D (2013) Twitter brand sentiment analysis: a hybrid system using n-gram analysis and dynamic artificial neural network. Expert Syst Appl 40(16):6266–6282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.05.057
Ghose A, Ipeirotis PG (2011) Estimating the helpfulness and economic impact of product reviews: mining text and reviewer characteristics. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 23(10):1498–1512
Ghulam H, Zeng F, Li W, Xiao Y (2019) Deep learning-based sentiment analysis for roman Urdu text. Procedia Comput Sci 147:131–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.01.202
Gimpel K et al (2011) Part-of-speech tagging for Twitter: annotation, features, and experiments. In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: short papers, pp 42–47
Gindl S, Weichselbraun A, Scharl A (2013) Rule-based opinion target and aspect extraction to acquire affective knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 22nd international conference on World Wide Web (IW3C2), pp 557–563
Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y (2011) Domain adaptation for large-scale sentiment classification: a deep learning approach. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on machine learning, pp 513–520
Go A, Bhayani R, Huang L (2009) Twitter sentiment classification using distant supervision. CS224N project report, Stanford University 1(12), pp 1–6
Gruber TR (1995) Toward principles for the design of ontologies used for knowledge sharing. Int J Hum Comput Stud 43:907–928
Gui L, Xu R, Lu Q, Xu J, Xu J, Liu B, Wang X (2014) Cross-lingual opinion analysis via negative transfer detection. In: Proceedings of the 52nd annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (short papers), pp 860–865
Hai Z, Chang K, Kim J, Yang CC (2014) Identifying features in opinion mining via intrinsic and extrinsic domain relevance. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26(3):623–634
Harakawa R, Ogawa T, Haseyama M (2017) Extracting hierarchical structure of web video groups based on sentiment-aware signed network analysis. IEEE Access 5:16963–16973. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2741098
Hassan A, Radev D (2010) Identifying text polarity using random walks. In: Proceedings of the 48th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 395–403
He Y, Lin C, Alani H (2011) Automatically extracting polarity-bearing topics for cross-domain sentiment classification conference item. In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: human language technologies, pp 123–131
He Y, Lin C, Gao W, Wong KF (2013) Dynamic joint sentiment-topic model. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol 5(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1145/2542182.2542188
Hiroshi K, Tetsuya N, Hideo W (2004) Deeper sentiment analysis using machine translation technology. In: Proceedings of the 20th international conference on computational linguistics (COLING’04), pp 494–500
Hu M, Liu B (2004) Mining and summarizing customer reviews. In: Proceedings of the tenth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 168–177
Hu N, Bose I, Gao Y, Liu L (2011a) Manipulation in digital word-of-mouth: a reality check for book reviews. Decis Support Syst 50(3):627–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2010.08.013
Hu N, Liu L, Sambamurthy V (2011b) Fraud detection in online consumer reviews. Decis Support Syst 50(3):614–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2010.08.012
Hu Y, Chen Y, Chou H (2017) Opinion mining from online hotel reviews—a text summarization approach. Inf Process Manag 53:436–449
Huang AH, Yen DC (2013) Predicting the helpfulness of online reviews—a replication. Int J Hum-Comput Interact 29:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2012.694791
Hung C, Lin H (2013) Using objective words in SentiWordNet to mouth sentiment classification. IEEE Intell Syst 2:47–54
Hussein DMEDM (2016) A survey on sentiment analysis challenges. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 30(4):330–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2016.04.002
Jiang L, Yu M, Zhou M, Liu X, Zhao T (2011) Target-dependent Twitter sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 151–160
Jimenez SM, Martin-valdivia MT, Molina-gonzalez MD, Urena-Lopez LA (2016) Domain adaptation of polarity lexicon combining term frequency and bootstrapping. In: Proceedings of the 7th workshop on computational approaches to subjectivity, sentiment and social media analysis, pp 137–146
Jindal N, Liu B (2008) Opinion spam and analysis. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on web search and data mining, pp 219–230
Jo Y, Oh A (2011) Aspect and sentiment unification model for online review analysis. In: Proceedings of the fourth ACM international conference on Web search and data mining. ACM, pp 815–824
Jung JJ (2012) Online named entity recognition method for micro texts in social networking services: a case study of twitter. Expert Syst Appl 39(9):8066–8070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.01.136
Justo R, Corcoran T, Lukin SM, Walker M, Torres MI (2014) Extracting relevant knowledge for the detection of sarcasm and nastiness in the social web. Knowl-Based Syst 69:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.05.021
Kanayama H, Nasukawa T (2014) Fully automatic lexicon expansion for domain-oriented sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP 2006) Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 355–363. https://doi.org/10.3115/1610075.1610125
Kang D, Park Y (2014) Review-based measurement of customer satisfaction in mobile service: sentiment analysis and VIKOR approach. Expert Syst Appl 41(4):1041–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.07.101
Kang H, Yoo SJ, Han D (2012) Senti-lexicon and improved Naïve Bayes algorithms for sentiment analysis of restaurant reviews. Expert Syst Appl 39(5):6000–6010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.11.107
Kennedy A, Inkpen D (2006) Sentiment classification of movie reviews using contextual valence shifters. Comput Intell 22:100–125
Kevin Atkinson (2006) GNU Aspell, Gnu Aspell 0.60.4. http://aspell.net/. Accessed 5 May 2019
Khan FH, Bashir S, Qamar U (2014) TOM: twitter opinion mining framework using hybrid classification scheme. Decis Support Syst 57:245–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2013.09.004
Kim S, Hovy E (2004) Determining the sentiment of opinions. In: Proceedings of the 20th international conference on computational linguistics, pp 1367–1373
Kim S, Zhang J, Chen Z, Oh A, Liu S (2013) A hierarchical aspect-sentiment model for online reviews. In: Proceedings of the twenty-seventh AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 526–533
Kong L, Schneider N, Swayamdipta S, Bhatia A, Dyer C, Smith NA (2014) A dependency parser for Tweets. In: Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 1001–1012
Kontopoulos E, Berberidis C, Dergiades T, Bassiliades N (2013) Ontology-based sentiment analysis of twitter posts. Expert Syst Appl 40(10):4065–4074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.01.001
Kouloumpis E, Wilson T, Moore J (2011) Twitter sentiment analysis: the good the bad and the OMG !. In: Proceedings of the fifth international AAAI conference on weblogs and social media, pp 538–541
Krishnamoorthy S (2015) Linguistic features for review helpfulness prediction. Expert Syst Appl 42(7):3751–3759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.12.044
Ku L, Chen H (2007) Mining opinions from the Web: beyond relevance retrieval. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 58(12):1838–1850. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi
Lambert P (2015) Aspect-level cross-lingual sentiment classification with constrained SMT. In: Proceedings of the 53rd annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th international joint conference on natural language processing, pp 781–787
Lane PCR, Clarke D, Hender P (2012) On developing robust models for favourability analysis: model choice, feature sets and imbalanced data. Decis Support Syst 53(4):712–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.05.028
Lang K (1995) NewsWeeder: learning to filter Netnews. In: Proceedings of the twelfth international conference on machine learning. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, pp 331–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-55860-377-6.50048-7
Lau RYK, Li C, Liao SSY (2014) Social analytics: learning fuzzy product ontologies for aspect-oriented sentiment analysis. Decis Support Syst 65:80–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2014.05.005
Lazaridou A, Titov I, Sporleder C (2013) A Bayesian model for joint unsupervised induction of sentiment, aspect and discourse representations. In: Proceedings of the 51st annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 1630–1639
Lee S, Choeh JY (2014) Predicting the helpfulness of online reviews using multilayer perceptron neural networks. Expert Syst Appl 41(6):3041–3046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.10.034
Lee P, Hu Y, Lu K (2018) Assessing the helpfulness of online hotel reviews: a classification-based approach. Telemat Inform 35:436–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2018.01.001
Lerman K, Blair-goldensohn S, Mcdonald R (2009) Sentiment summarization: evaluating and learning user preferences. In: Proceedings of the 12th conference of the European chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 514–522
Li Y, Li T (2013) Deriving market intelligence from microblogs. Decis Support Syst 55(1):206–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2013.01.023
Li Y, Shiu Y (2012) A diffusion mechanism for social advertising over microblogs. Decis Support Syst 54(1):9–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.02.012
Li ST, Tsai FC (2013) A fuzzy conceptualization model for text mining with application in opinion polarity classification. Knowl-Based Syst 39:23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2012.10.005
Li N, Wu DD (2010) Using text mining and sentiment analysis for online forums hotspot detection and forecast. Decis Support Syst 48(2):354–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2009.09.003
Li W, Xu H (2013) Text-based emotion classification using emotion cause extraction. Expert Syst Appl 41:1742–1749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.08.073
Li F, Huang M, Zhu X (2007) Sentiment analysis with global topics and local dependency. In: Proceedings of the twenty-fourth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1371–1376
Li F, Huang M, Yang Y, Zhu X (2011) Learning to identify review spam. In: Proceedings of the twenty-second international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 2488–2493
Li S, Guan Z, Tang L-Y, Chen Z (2012) Exploiting consumer reviews for product feature ranking. J Comput Sci Technol 27(3):635–649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-012-1250-z
Li S, Xue Y, Wang Z, Zhou G (2013) Active learning for cross-domain sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the twenty-third international joint conference on artificial intelligence active, pp 2127–2133
Li X, Xie H, Chen L, Wang J, Deng X (2014) News impact on stock price return via sentiment analysis. Knowl-Based Syst 69:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.04.022
Li H, Chen Z, Mukherjee A, Liu B, Shao J (2015) Analyzing and detecting opinion spam on a large-scale dataset via temporal and spatial patterns. In: Proceedings of the ninth international association for the advancement of artificial intelligence conference on web and social media analyzing, pp 634–637
Li S, Zhou L, Li Y (2015b) Improving aspect extraction by augmenting a frequency-based method with web-based similarity measures. Inf Process Manag 51(1):58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2014.08.005
Li Y, Pan Q, Yang T, Wang S, Tang J, Cambria E (2017) Learning word representations for sentiment analysis. Cogn Comput 9(6):843–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-017-9492-2
Liang J, Zhang K, Zhou X, Hu Y, Tan J, Bai S (2016) Leveraging latent sentiment constraint in probabilistic matrix factorization for cross-domain sentiment classification. Procedia Comput Sci 80:366–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2016.05.353
Lin C, He Y (2009) Joint sentiment/topic model for sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM conference on information and knowledge management, pp 375–384
Lin C, He Y, Everson R, Ruger S (2012) Weakly supervised joint sentiment-topic detection from text. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 24(6):1134–1145
Lin C, Lee Y, Yu C, Chen H (2014) Exploring ensemble of models in taxonomy-based cross-domain sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM international conference on conference on information and knowledge management—CIKM’14, pp 1279–1288
Liu B (2012) Sentiment analysis and opinion mining. Morgan and Claypool publishers
Liu L, Nie X, Wang H (2012) Toward a fuzzy domain sentiment ontology tree for sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 5th international congress on image and signal processing (CISP 2012), pp 1620–1624
Liu H, He J, Wang T, Song W, Du X (2013a) Electronic commerce research and applications combining user preferences and user opinions for accurate recommendation. Electron Commer Res Appl 12(1):14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elerap.2012.05.002
Liu Y, Jin J, Ji P, Harding JA, Fung RYK (2013b) Computer-aided design identifying helpful online reviews: a product designer’ s perspective. Comput Aided Des 45(2):180–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2012.07.008
Lo SL, Cambria E, Chiong R, Cornforth D (2017) Multilingual sentiment analysis: from formal to informal and scarce resource languages. Artif Intell Rev 48(4):499–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-016-9508-4
Long M, Wang J, Cao Y, Sun J, Yu PS (2016) Deep learning of transferable representation for scalable domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 28(8):2027–2040. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2016.2554549
Lu Y, Kong X, Quan X, Liu W, Xu Y (2010) Exploring the sentiment strength of user reviews. In: Proceedings of the international conference on Web-age information management (WAIM 2010), pp 471–482
Lubis FF, Rosmansyah Y, Supangkat SH (2017) Improving course review helpfulness prediction through sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the international conference on ICT for smart society (ICISS), pp 1-5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTSS.2017.8288877
Ma Y, Peng H, Cambria E (2018) Targeted aspect-based sentiment analysis via embedding commonsense knowledge into an attentive LSTM. In: Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI conference on artificial intelligence AAAI 2018, pp 5876–5883
Maas AL et al (2014) Learning word vectors for sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 142–150
Majumder N, Poria S, Peng H, Chhaya N, Cambria E, Gelbukh A (2019) Sentiment and sarcasm classification with multitask learning. IEEE Intell Syst 34(3):38–43
Maks I, Vossen P (2012) A lexicon model for deep sentiment analysis and opinion mining applications. Decis Support Syst 53(4):680–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.05.025
Manning CD, Surdeanu M, Bauer J, Finkel J, Bethard SJ, McClosky D (2014) The Stanford corenlp natural language processing toolkit. In: Proceedings of the 52nd annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: system demonstrations, pp 55–60
Manshu T, Bing W (2019) Adding prior knowledge in hierarchical attention neural network for cross-domain sentiment classification. IEEE Access 7:32578–32588. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2901929
Marcacini RM, Rossi RG, Matsuno IP, Rezende SO (2018) Cross-domain aspect extraction for sentiment analysis: a transductive learning approach. Decis Support Syst 114:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2018.08.009
Martín-Valdivia M-T, Martínez-cámara E, Perea-Ortega JM, Ureña-lópez LA (2013) Sentiment polarity detection in Spanish reviews combining supervised and unsupervised approaches. Expert Syst Appl 40:3934–3942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.12.084
Mcauley J, Leskovec J (2013) Hidden factors and hidden topics: understanding rating dimensions with review text. In: Proceeding of the 7th ACM conference on recommender systems, pp 165–172. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/2507157.2507163
McAuley J, Pandey R, Leskovec J (2015) Inferring networks of substitutable and complementary products. In: Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 785–794. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/2783258.2783381
Mcdonald R, Hannan K, Neylon T, Wells M, Reynar J (2007) Structured models for fine-to-coarse sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 45th annual meeting of the association of computational linguistics, 432-439
Medhat W, Hassan A, Korashy H (2014) Sentiment analysis algorithms and applications: a survey. Ain Shams Eng J Electr Eng 5(4):1093–1113
Miao Q, Li Q, Dai R (2009) AMAZING: a sentiment mining and retrieval system. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):7192–7198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.09.035
Mihalcea R, Banea C, Wiebe J (2007) Learning multilingual subjective language via cross-lingual projections. In: Proceedings of the 45th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 976–983
Min H, Park JC (2012) Identifying helpful reviews based on customer’s mentions about experiences. Expert Syst Appl 39(15):11830–11838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.01.116
Moghaddam S, Ester M (2013) The FLDA Model for aspect-based opinion mining: addressing the cold start problem categories and subject descriptors. In: Proceedings of the international World Wide Web conferences steering committee, pp 909–918
Moghaddam S, Jamali M, Ester M (2012) ETF: extended tensor factorization model for personalizing prediction of review helpfulness categories and subject descriptors. In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM international conference on web search and data mining, pp 163–172
Mohammad SM (2012) From once upon a time to happily ever after: tracking emotions in mail and books. Decis Support Syst 53(4):730–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.05.030
Molina-González MD, Martínez-Cámara E, Martín-Valdivia M-T, Perea-Ortega JM (2013) Semantic orientation for polarity classification in Spanish reviews. Expert Syst Appl 40(18):7250–7257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.06.076
Montejo-Raez A, Diıaz-Galiano MC, Urena-Lopez LA (2014) Crowd explicit sentiment analysis. Knowl-Based Syst 69:134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.05.007
Montoyo A, Martínez-barco P, Balahur A (2012) Subjectivity and sentiment analysis: an overview of the current state of the area and envisaged developments. Decis Support Syst 53(4):675–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.05.022
Moraes R, Valiati JF, Neto WPG (2013) Document-level sentiment classification: an empirical comparison between SVM and ANN. Expert Syst Appl 40(2):621–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.07.059
Moreo A, Romero M, Castro JL, Zurita JM (2012) Lexicon-based comments-oriented news sentiment analyzer system. Expert Syst Appl 39(10):9166–9180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.02.057
Mostafa MM (2013) More than words: social networks text mining for consumer brand sentiments. Expert Syst Appl 40(10):4241–4251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.01.019
Mudambi SM, Schuff D (2010) what makes a helpful online review? A study of customer reviews on amazon.com. MIS Q 34(1):185–200. https://doi.org/10.2307/20721420
Mukherjee S, Joshi S (2013) Sentiment aggregation using conceptnet ontology. In: Proceedings of the sixth international joint conference on natural language processing, pp 570–578
Mukherjee S, Joshi S (2014) Author-specific sentiment aggregation for polarity prediction of reviews. In: Proceedings of the 9th edition of the language resources and evaluation conference (LREC 2014), pp 3092–3099
Mukherjee A, Liu B, Glance N (2012) Spotting fake reviewer groups in consumer reviews. In: Proceedings of the 21st international conference on World Wide Web (IW3C2), pp 191–200
Mukherjee A, Kumar A, Liu B, Wang J, Hsu M, Castellanos M (2013) Spotting opinion spammers using behavioral footprints. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 632–640
Mullen T, Collier N (2004) Sentiment analysis using support vector machines with diverse information sources. In: Proceedings of the 9th conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP-04), pp 412–418
Nakayama Y, Fujii A (2015) Extracting condition-opinion relations toward fine-grained opinion mining. In: Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 622–631
Narayanan R, Liu B, Choudhary A (2009) Sentiment analysis of conditional sentences. In: Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 180–189
Nassirtoussi AK, Aghabozorgi S, Wah TY, Ngo DCL (2015) Text mining of news-headlines for FOREX market prediction: a multi-layer dimension reduction algorithm with semantics and sentiment. Expert Syst Appl 42:306–324
Nasukawa T, Yi J (2003) Sentiment analysis capturing favorability using natural language processing. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on knowledge capture. ACM, pp 70–77. https://doi.org/10.1145/945645.945658
Navigli R, Ponzetto SP (2012) BabelNet: the automatic construction, evaluation and application of a wide-coverage multilingual semantic network. Artif Intell 193:217–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artint.2012.07.001
Neri F, Aliprandi C, Capeci F, Cuadros M, By T (2012) Sentiment analysis on social media. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/ACM international conference on advances in social networks analysis and mining (ASONAM 2012), pp 951–958. https://doi.org/10.1109/ASONAM.2012.164
Neviarouskaya A, Prendinger H, Ishizuka M (2011) SentiFul: a lexicon for sentiment analysis. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 2(1):22–36
Ngo-Ye TL, Sinha AP (2014) The influence of reviewer engagement characteristics on online review helpfulness: a text regression model. Decis Support Syst 61(1):47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2014.01.011
Nguyen HT, Le Nguyen M (2018) Multilingual opinion mining on YouTube—a convolutional N-gram BiLSTM word embedding. Inf Process Manag 54:451–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2018.02.001
Nielsen FA (2011) A new ANEW: evaluation of a word list for sentiment analysis in microblogs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1103.2903
Nishikawa H, Hasegawa T, Matsuo Y, Kikui G (2010) Opinion summarization with integer linear programming formulation for sentence extraction and ordering. In: Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on computational linguistics, pp 910–918
Nozza D, Fersini E, Messina E (2016) Deep learning and ensemble methods for domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 28th international conference on tools with artificial intelligence (ICTAI), pp 184–189. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTAI.2016.0037
O’Connor B, Krieger M, Ahn D (2010) TweetMotif: exploratory search and topic summarization for Twitter. In: Proceedings of the fourth international AAAI conference on weblogs and social media, pp 384–385
O’Leary DE (2011) Blog mining-review and extensions: “from each according to his opinion”. Decis Support Syst 51(4):821–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2011.01.016
Ohana B, Delany SJ, Tierney B (2012) A Case-based approach to cross-domain sentiment classification. In: proceedings of the international conference on case-based reasoning, pp 284–296
Ortigosa A, Martín JM, Carro RM (2013) Computers in human behavior sentiment analysis in Facebook and its application to e-learning. Comput Hum Behav 31:527–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.05.024
Ott M, Choi Y, Cardie C, Hancock JT (2011) Finding deceptive opinion spam by any stretch of the imagination. In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 309–319
Ott M, Cardie C, Hancock JT (2013) Negative deceptive opinion spam. In: Proceedings of the NAACL-HLT. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 497–501
Pan SJ, Ni X, Sun J, Yang Q, Chen Z (2010) Cross-domain sentiment classification via spectral feature alignment. In: Proceedings of the 19th international conference on World Wide Web—WWW’10, pp 751–760
Pang B, Lee L (2004) A sentimental education: sentiment analysis using subjectivity summarization based on minimum. In: Proceedings of the 42nd annual meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 271–278
Pang B, Lee L (2005) Seeing stars: Exploiting class relationships for sentiment categorization with respect to rating scales. arXiv preprint arXiv:cs/0506075
Pang B, Lee L (2008) Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Found Trends Inf Retr 2(1–2):1–135
Pang B, Lee L, Vaithyanathan S (2002) Thumbs up? Sentiment classification using machine learning techniques. In: Proceedings of the ACL-02 conference on Empirical methods in natural language processing, vol 10, pp 79–86
Patodkar VN, Sheikh IR (2016) Twitter as a corpus for sentiment analysis and opinion mining. Int J Adv Res Comput Commun Eng 5(12):320–322. https://doi.org/10.17148/IJARCCE.2016.51274
Peñalver-martinez I et al (2014) Feature-based opinion mining through ontologies. Expert Syst Appl 41(13):5995–6008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.03.022
Pennebaker JW, Boyd RL, Jordan K, Blackburn K (2015) The development and psychometric properties of in LIWC2015. University of Texas at Austin, Austin
Pessutto LRC, Vargas DS, Moreira VP (2019) Multilingual aspect clustering for sentiment analysis. Knowl-Based Syst 192:105339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.105339
Ponomareva N, Thelwall M (2012) Biographies or blenders: which resource is best for cross-domain sentiment analysis? In: Proceedings of the international conference on intelligent text processing and computational linguistics, pp 488–499
Ponomareva N, Thelwall M (2012) Do neighbours help? An exploration of graph-based algorithms for cross-domain sentiment classification. In Proceedings of the 2012 joint conference on empirical methods in natural language processing and computational natural language learning, pp 655–665
Ponomareva N, Thelwall M (2013) Semi-supervised vs. cross-domain graphs for sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of recent advances in natural language processing, pp 571–578
Popescu A, Etzioni O (2005) Extracting product features and opinions from reviews. In: Proceedings of human language technology conference and conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (HLT/EMNLP), pp 339–346
Popescu O, Strapparava C (2014) Time corpora: epochs, opinions and changes. Knowl-Based Syst 69:3–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.04.029
Poria S, Gelbukh A, Hussain A, Howard N, Das D, Bandyopadhay S (2013) Enhanced SenticNet with affective labels for concept-based opinion mining. IEEE Intell Syst 28(2):31–38
Poria S, Cambria E, Winterstein G, Huang G (2014a) Sentic patterns: dependency-based rules for concept-level sentiment analysis. Knowl-Based Syst 69(1):45–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.05.005
Poria S, Gelbukh A, Cambria E, Hussain A, Huang G (2014b) EmoSenticSpace: a novel framework for affective common-sense reasoning. Knowl-Based Syst 69:108–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.06.011
Poria S, Cambria E, Gelbukh A (2016a) Aspect extraction for opinion mining with a deep convolutional neural network. Knowl-Based Syst 108:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2016.06.009
Poria S, Cambria E, Hazarika D, Vij P (2016) A deeper look into sarcastic tweets using deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 26th international conference on computational linguistics (COLING 2016), pp 1601–1612
MF Porter (2001) Snowball: a language for stemming algorithms. http://snowball.tartarus.org/texts/introduction.html. Accessed 5 May 2019
Prabowo R, Thelwall M (2009) Sentiment analysis: a combined approach. J Inform 3:143–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2009.01.003
Ptáček T, Habernal I, Hong J (2014) Sarcasm detection on czech and english twitter. In: Proceedings of the COLING 2014, the 25th international conference on computational linguistics: technical papers, pp 213–223
Purnawirawan N, Pelsmacker PD, Dens N (2012) Balance and sequence in online reviews: how perceived usefulness affects attitudes and intentions. J Interact Mark 26(4):244–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intmar.2012.04.002
Qiu G, Liu B, Bu J, Chen C (2009) Expanding domain sentiment lexicon through double propagation. In: Proceedings of the 21st international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1199–1204
Qiu G, He X, Zhang F, Shi Y, Bu J, Chen C (2010) DASA: dissatisfaction-oriented advertising based on sentiment analysis. Expert Syst Appl 37(9):6182–6191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.02.109
Qiu L, Rui H, Whinston A (2013a) Social network-embedded prediction markets: the effects of information acquisition and communication on predictions. Decis Support Syst 55(4):978–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2013.01.007
Qiu X, Zhang Q, Huang X (2013) FudanNLP: a Toolkit for Chinese natural language processing. In: Proceedings of the 51st annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 49–54
Quan C, Ren F (2014) Unsupervised product feature extraction for feature-oriented opinion determination. Inf Sci 272:16–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.02.063
Rabelo JCB, Prudêncio RBC, Barros FA (2012) Using link structure to infer opinions in social networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics (SMC), pp 681–685
Racherla P, Friske W (2012) Perceived ‘usefulness’ of online consumer reviews: an exploratory investigation across three services categories. Electron Commer Res Appl 11(6):548–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elerap.2012.06.003
Radev DR et al (2003) Evaluation challenges in large-scale document summarization. In: Proceedings of the 41st annual meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 375–382
Rastogi A, Mehrotra M (2018) Impact of behavioral and textual features on opinion spam detection. In: Proceedings of the second international conference on intelligent computing and control systems (ICICCS 2018) IEEE, pp 852–857
Ravi K, Ravi V (2015) A survey on opinion mining and sentiment analysis: tasks, approaches. Knowl-Based Syst 89:14–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2015.06.015
Rehurek R, Sojka P (2010) Software framework for topic modelling with large corpora. In: Proceedings of the LREC 2010 workshop on new challenges for NLP frameworks, pp 45–50
Remus R (2012) Domain adaptation using domain similarity- and domain complexity-based instance selection for cross-domain sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 12th international conference on data mining workshops domain, IEEE computer society, pp 717–723. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDMW.2012.46
Reyes A, Rosso P (2012) Making objective decisions from subjective data: detecting irony in customer reviews. Decis Support Syst 53(4):754–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.05.027
Rida-e-fatima S et al (2019) A multi-layer dual attention deep learning model with refined word embeddings for aspect-based sentiment analysis. IEEE Access 7:114795–114807. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2927281
Rill S, Reinel D, Scheidt J, Zicari RV (2014) PoliTwi: early detection of emerging political topics on twitter and the impact on concept-level sentiment analysis. Knowl-Based Syst 69:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.05.008
Roy SD, Mei T, Zeng W, Li S (2012) SocialTransfer: cross-domain transfer learning from social streams for media applications. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 649–658
Rui H, Liu Y, Whinston A (2013) Whose and what chatter matters? The effect of tweets on movie sales. Decis Support Syst 55(4):863–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.12.022
Saeed RMK, Rady S, Gharib TF (2019) An ensemble approach for spam detection in Arabic opinion texts. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2019.10.002
Saleh MR, Martin-valdivia MT, Montejo-Raez A, Urena-Lopez LA (2011) Experiments with SVM to classify opinions in different domains. Expert Syst Appl 38(12):14799–14804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.05.070
Sanju P, Mirnalinee TT (2014) Construction of enhanced sentiment sensitive thesaurus for cross domain sentiment classification using Wiktionary. In: Proceedings of the third international conference on soft computing for problem solving, pp 195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-1768-8
Satapathy R, Guerreiro C, Chaturvedi I, Cambria E (2017) Phonetic-based microtext normalization for Twitter sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on data mining workshops (ICDMW), pp 407–413. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDMW.2017.59
Satapathy R, Li Y, Cavallari S, Cambria E (2019) Seq2Seq deep learning models for microtext normalization. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on neural networks, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2019.8851895
Satapathy R, Singh A, Cambria E (2019) PhonSenticNet: a cognitive approach to microtext normalization for concept-level sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the international conference on computational data and social networks, pp 177–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34980-6_20
Satapathy R, Cambria E, Nanetti A, Hussain A (2020) A review of shorthand systems: from brachygraphy to microtext and beyond. Cogn Comput
Seki Y, Kando N, Aono M (2009) Multilingual opinion holder identification using author and authority viewpoints. Inf Process Manag 45(2):189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2008.11.004
Shuang K, Guo H, Zhang Z, Loo J (2018) A sentiment information collector–extractor architecture based neural network for sentiment analysis. Inf Sci 467:549–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.08.026
Sindhu I, Muhammad Daudpota S, Badar K, Bakhtyar M, Baber J, Nurunnabi (2019) Aspect-based opinion mining on student’s feedback for faculty teaching performance evaluation. IEEE Access 7:108729–108741. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2928872
Sindhwani V, Melville P (2008) Document-word co-regularization for semi-supervised sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the eighth IEEE international conference on data mining, pp 1025–1030. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2008.113
Singh SK, Sachan MK (2019) SentiVerb system: classification of social media text using sentiment analysis. Multimed Tools Appl 78(22):32109–32136
Sobkowicz P, Kaschesky M, Bouchard G (2012) Opinion mining in social media: modeling, simulating, and forecasting political opinions in the web. Govern Inf Q 29(4):470–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2012.06.005
Socher R, et al (2013) Recursive deep models for semantic compositionality over a sentiment treebank. In: Proceedings of the 2013 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 1631–1642
Spina D, Gonzalo J, Amigó E (2013) Discovering filter keywords for company name disambiguation in twitter. Expert Syst Appl 40(12):4986–5003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.03.001
Stanik C, Haering M, Maalej W (2019) Classifying multilingual user feedback using traditional machine learning and deep learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 27th international requirements engineering conference workshops (REW 2019). IEEE, pp 220–226. https://doi.org/10.1109/REW.2019.00046
Stone PJ, Dunphy DC, Smith MS (1966) The general inquirer: a computer approach to content analysis
Sun S, Luo C, Chen J (2017) A review of natural language processing techniques for opinion mining systems. Inf Fusion 36:10–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2016.10.004
Taboada M, Grieve J (2004) Analyzing appraisal automatically classifying sentiment. In: Proceedings of the AAAI spring symposium on exploring attitude and affect in text Stanford, pp 158–161
Taboada M, Brooke J, Tofilosk M, Voll K, Stede M (2011) Lexicon-based methods for sentiment analysis. Comput Linguist 37(2):267–307
Tackstrom O, Mcdonald R (2008) Semi-supervised latent variable models for sentence-level sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: human language technologies, pp 569–574
Taddy M (2013) Measuring political sentiment on Twitter: factor optimal design for multinomial inverse regression. Technometrics 55(4):37–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.2013.778791
Tan S, Cheng X, Wang Y, Xu H (2009) Adapting Naive Bayes to domain adaptation for sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the European conference on information retrieval in advances in information retrieval, pp 337–349
Tan C, Lee L, Tang J, Jiang L, Zhou M, Li P (2011) User-level sentiment analysis incorporating social networks. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining (KDD-11), pp 1397–1405
Tan LK, Na J, Theng Y-L, Chang K (2012) Phrase-level sentiment polarity classification using rule-based typed dependencies and additional complex phrases consideration. J Comput Sci Technol 27(3):650–666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-012-1251-y
Tang H, Tan S, Cheng X (2009) A survey on sentiment detection of reviews. Expert Syst Appl 36(7):10760–10773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.02.063
Tang D, Wei F, Qin B, Zhou M, Liu T (2014) Building large-scale Twitter-specific sentiment lexicon: a representation learning approach. In: Proceedings of COLING 2014, the 25th international conference on computational linguistics: technical papers, pp 172–182
Tang D, Qin B, Wei F, Dong L, Liu T, Zhou M (2015) A joint segmentation and classification framework for sentence level sentiment classification. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 23(11):1750–1761
Tartir S, Abdul-Nabi I (2017) Semantic sentiment analysis in Arabic social media. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci 29(2):229–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2016.11.011
Thelwall M, Buckley K (2013) Topic-based sentiment analysis for the social web: the role of mood and issue-related words. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 64(8):1608–1617. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22872
Thelwall M, Buckley K, Paltoglou G, Cai D (2010) Sentiment strength detection in short informal text. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 61(12):2544–2558
Thelwall M, Buckley K, Paltoglou G (2011) Sentiment in Twitter events. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 62(2):406–418. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.21462
Thelwall M, Buckley K, Paltoglou G (2012) Sentiment strength detection for the social web 1. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 63(1):163–173
Thet TT, Na J, Khoo CSG (2010) Aspect-based sentiment analysis of movie reviews on discussion boards. J Inf Sci 36(5):823–848. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165551510388123
Toutanova K, Klein D, Manning CD, Singer Y (2003) Feature-rich part-of-speech tagging with a cyclic dependency network. In: Proceedings of the conference of the North American chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics on human language technology, vol 1. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 173–180
Trainor KJ, Andzulis J, Rapp A, Agnihotri R (2013) Social media technology usage and customer relationship performance: a capabilities-based examination of social CRM. J Bus Res 67(6):1201–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2013.05.002
Tsai AC, Wu C, Tsai RT, Hsu JY (2013) Building a concept-level sentiment on commonsense knowledge. IEEE Intell Syst 28(2):22–30
Tsai Y-L, Tsai RT-H, Chueh C-H, Chang S-C (2014) Cross-domain opinion word identification with query-by-committee active learning. In: Proceedings of the international conference on technologies and applications of artificial intelligence. Springer, Cham, pp 334–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-13987-6_31
Tsakalidis A, Papadopoulos S, Kompatsiaris I (2014) An ensemble model for cross-domain polarity classification on Twitter. In: Proceedings of the international conference on web information systems engineering, pp 168–177
Tsytsarau M, Palpanas T (2012) Survey on mining subjective data on the web. Data Min Knowl Disc 24(3):478–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-011-0238-6
Turney PD (2002) Thumbs up or thumbs down? Semantic orientation applied to unsupervised classification of reviews. In: Proceedings of the 40th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pp 417–424
Velikovich L, Blair-goldensohn S, Hannan K, McDonald R (2010) The viability of web-derived polarity lexicons. In: Proceedings of the human language technologies: the 2010 annual conference of the North American chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 777–785
Vilares D, Peng H, Satapathy R, Cambria E (2018) BabelSenticNet: a commonsense reasoning framework for multilingual sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE symposium series on computational intelligence (SSCI 2018), pp 1292–1298. https://doi.org/10.1109/SSCI.2018.8628718
Vinodhini G, Chandrasekaran RM (2014) Opinion mining using principal component analysis based ensemble model for e-commerce application. CSI Trans ICT 2(3):169–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-014-0055-3
Virmani D, Arora P, Kulkarni PS (2017) Cross domain analyzer to acquire review proficiency in big data. ICT Express 3(3):128–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2017.04.004
Walker MA, Anand P, Tree JEF, Abbott R, King J (2012) A corpus for research on deliberation and debate. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on language resources and evaluation (LREC-2012), pp 812–817
Wan X (2008) Using bilingual knowledge and ensemble techniques for unsupervised Chinese sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 553–561
Wang J, Lee C (2011) Unsupervised opinion phrase extraction and rating in Chinese blog posts. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on privacy, security, risk, and trust, and IEEE international conference on social computing, pp 820–823
Wang S, Manning CD (2012) Baselines and bigrams: simple, good sentiment and topic classification. In: Proceedings of the 50th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 90–94
Wang H, Lu Y, Zhai C (2010) Latent aspect rating analysis on review text data: a rating regression approach. In: Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGKDD conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (KDD’2010), pp 783–792
Wang G, Xie S, Liu B, Yu PS (2011) Review graph based online store review spammer detection. In: Proceedings of the 11th IEEE international conference on data mining review (IEEE Computer Society), pp 1242–1247. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2011.124
Wang S, Li D, Song X, Wei Y, Li H (2011b) A feature selection method based on improved fisher’s discriminant ratio for text sentiment classification. Expert Syst Appl 38(7):8696–8702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.01.077
Wang G, Sun J, Ma J, Xu K, Gu J (2013a) Sentiment classification: the contribution of ensemble learning. Decis Support Syst 57:77–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2013.08.002
Wang H, Yin P, Zheng L, Liu JNK (2013b) Sentiment classification of online reviews: using sentence-based language model. J Exp Theor Artif Intell 26(1):13–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/0952813X.2013.782352
Wang T et al (2014) Product aspect extraction supervised with online domain knowledge. Knowl-Based Syst 71:86–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.05.018
Wang L, Liu K, Cao Z, Zhao J, Melo GD (2015) Sentiment-aspect extraction based on restricted Boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 53rd annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th international joint conference on natural language processing, pp 616–625
Wang J, Peng B, Zhang X (2018a) Using a stacked residual LSTM model for sentiment intensity prediction. Neurocomputing 322:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.09.049
Wang L, Niu J, Song H, Atiquzzaman M (2018b) SentiRelated: a cross-domain sentiment classification algorithm for short texts through sentiment related index. J Netw Comput Appl 101:111–119
Wei B, Pal C (2010) Cross lingual adaptation: an experiment on sentiment classifications. In: Proceedings of the 48th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 258–262
Weichselbraun A, Gindl S, Scharl A (2014) Enriching semantic knowledge bases for opinion mining in big data applications. Knowl-Based Syst 69:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.04.039
Whissell CM (1989) The dictionary of affect in language. In: The measurement of emotions, Academic Press, pp 113–131
Whitelaw C, Garg N, Argamon S (2005) Using appraisal groups for sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM international conference on information and knowledge management. ACM, pp 625–631
Wiebe J, Wilson T, Cardie C (2005) Annotating expressions of opinions and emotions in language. Lang Resour Eval 39:165–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10579-005-7880-9
Wilson T, Wiebe J, Hoffmann P (2005) Recognizing contextual polarity in phrase-level sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the human language technology conference and conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (HLT/EMNLP), pp 347–354
Wu Q, Tan S (2011) A two-stage framework for cross-domain sentiment classification. Expert Syst Appl 38(11):14269–14275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.04.240
Wu C, Tsai RT (2014) Using relation selection to improve value propagation in a ConceptNet-based sentiment dictionary. Knowl-Based Syst 69:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.04.043
Wu P, Li X, Shen S, He D (2019a) Social media opinion summarization using emotion cognition and convolutional neural networks. Int J Inf Manag 51:101978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.07.004
Wu S, Wu F, Chang Y, Wu C, Huang Y (2019b) Automatic construction of target-specific sentiment lexicon. Expert Syst Appl 116:285–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.09.024
Xia R, Zong C, Li S (2011) Ensemble of feature sets and classification algorithms for sentiment classification. Inf Sci 181(6):1138–1152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2010.11.023
Xia R, Zong C, Hu X, Cambria E (2013) Feature ensemble plus sample selection: domain adaptation classification. IEEE Intell Syst 28(3):10–18
Xie J, Chen B, Gu X, Liang F, Xu X (2019) Self-attention-based BiLSTM model for short text fine-grained sentiment classification. IEEE Access 7:180558–180570. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2957510
Xu K, Liao SS, Li J, Song Y (2011) Mining comparative opinions from customer reviews for competitive intelligence. Decis Support Syst 50(4):743–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2010.08.021
Xu H, Zhang F, Wang W (2015) Implicit feature identification in Chinese reviews using explicit topic mining model. Knowl-Based Syst 76:166–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.12.012
Xuan HNT, Le AC, Nguyen LM (2012) Linguistic features for subjectivity classification. In: Proceedings of the international conference on asian language processing (IALP), pp 17–20. https://doi.org/10.1109/IALP.2012.47
Xueke X, Xueqi C, Songbo T, Yue L, Huawei S (2013) Aspect-level opinion mining of online customer reviews. China Commun 10(3):25–41
Yan Z, Xing M, Zhang D, Ma B (2015) EXPRS: an extended PageRank method for product feature extraction from online consumer reviews. Inf Manag 52(7):850–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2015.02.002
Yang B, Cardie C (2014) Context-aware learning for sentence-level sentiment analysis with posterior regularization. In: Proceedings of the 52nd annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 325–335
Yang P, Gao W, Tan Q, Wong K (2013) A link-bridged topic model for cross-domain document classification. Inf Process Manag 49(6):1181–1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2013.05.002
Yessenalina A, Yue Y, Cardie C (2010) Multi-level structured models for document-level sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 1046–1056
Young T, Hazarika D, Poria S, Cambria E (2018) Recent trends in deep learning based natural language processing. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 13(3):55–75. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCI.2018.2840738
Yu H, Hatzivassiloglou V (2003) Towards answering opinion questions : separating facts from opinions and identifying the polarity of opinion sentences. In: Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 129–136
Yu J, Jiang J (2016) Learning sentence embeddings with auxiliary tasks for cross-domain sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 236–246
Yu X, Liu Y, Huang JX (2012) Mining online reviews for predicting sales performance: a case study in the movie domain. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 24(4):720–734. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2010.269
Yu L, Wu J, Chang P, Chu H (2013a) Using a contextual entropy model to expand emotion words and their intensity for the sentiment classification of stock market news. Knowl-Based Syst 41:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2013.01.001
Yu Y, Duan W, Cao Q (2013b) The impact of social and conventional media on firm equity value: a sentiment analysis approach. Decis Support Syst 55(4):919–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.12.028
Zhai Z, Liu B, Xu H, Jia P (2011) Clustering product features for opinion mining. In: Proceedings of the 4th ACM international conference on web search and data mining, pp 347–354
Zhai Z, Xu H, Kang B, Jia P (2011b) Exploiting effective features for Chinese sentiment classification. Expert Syst Appl 38(8):9139–9146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.01.047
Zhai Z, Liu B, Wang J, Xu H, Jia P (2012) Product feature grouping for opinion mining. IEEE Intell Syst 27(4):37–44
Zhan J, Loh HT, Liu Y (2009) Gather customer concerns from online product reviews—a text summarization approach. Expert Syst Appl 36(2):2107–2115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2007.12.039
Zhang Z (2008) Weighing stars: aggregating online product. IEEE Intell Syst 23(5):42–49
Zhang Z, Ye Q, Zhang Z, Li Y (2011) Sentiment classification of Internet restaurant reviews written in Cantonese. Expert Syst Appl 38(6):7674–7682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.12.147
Zhang K, Xie Y, Yang Y, Sun A, Liu H, Choudhary A (2014) Incorporating conditional random fields and active learning to improve sentiment identification. Neural Netw 58:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.04.005
Zhang Y, Hu X, Li P, Li L, Wu X (2015) Cross-domain sentiment classification-feature divergence, polarity divergence or both? Pattern Recogn Lett 65:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2015.07.006
Zhang RUI, Wang Z, Yin KAI, Huang Z (2019) Emotional text generation based on cross-domain sentiment transfer. IEEE Access 7:100081–100089
Zhao R, Mao K (2014) Supervised adaptive-transfer PLSA for cross-domain text classification. In: Procceedings of the IEEE international conference on data mining workshop, pp 259–266. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDMW.2014.163
Zhao W, Guan Z, Chen L, He X, Cai D, Wang B, Wang Q (2018) Weakly-supervised deep embedding for product review sentiment analysis. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 30(1):185–197. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2017.2756658
Zhao W, Peng H, Eger S, Cambria E, Yang M (2019) Towards scalable and reliable capsule networks for challenging NLP applications. In: Proceedings of the 57th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 1549–1559. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P19-1150
Zheng X, Lin Z, Wang X, Lin K, Song M (2014) Incorporating appraisal expression patterns into topic modeling for aspect and sentiment word identification. Knowl-Based Syst 61:29–47
Zhou L, Chaovalit P (2008) Ontology-supported polarity mining. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 59(1):98–110. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.20735
Zhou H, Song F (2012) Aspect-level sentiment analysis based on a generalized probabilistic topic and syntax model. In: Proceedings of the twenty-eighth international Florida artificial intelligence research society conference, pp 241–244
Zhou G, Zhou Y, Guo X, Tu X, He T (2015) Cross-domain sentiment classification via topical correspondence transfer. Neurocomputing 159:298–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2014.12.006
Zhu Z, Dai D, Ding Y, Qian J, Li S (2013) Employing emotion keywords to improve cross-domain sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the workshop on Chinese lexical semantics, pp 64–71
Zhu X, Ghahramani Z (2002) Learning from labeled and unlabeled data with label propagation
Zhu J, Wang Q (2015) NiuParser: a Chinese syntactic and semantic parsing toolkit. In: Proceedings of the 53rd annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th international joint conference on natural language processing: system demonstrations, pp 145–150
Zhu J, Wang H, Zhu M, Tsou BK, Ma M (2011) Aspect-based opinion polling from customer reviews. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 2(1):37–49
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R.K., Sachan, M.K. & Patel, R.B. 360 degree view of cross-domain opinion classification: a survey. Artif Intell Rev 54, 1385–1506 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09884-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09884-9