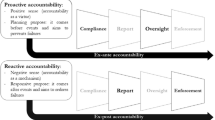
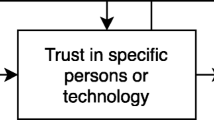
Abstract
The notion of Multi-Agent System environment is currently considered as a mediating entity, functioning as enabler but possibly also as a manager and constrainer of agent actions, perceptions, and interactions. In this paper, we analyze how the environment could be a first class abstraction to support the building, the development and the management of Agreements in decentralized and open systems between autonomous agents. To this aim we analyze the synergies between the environment and the foundational dimensions of agreement technologies such as semantics, norms, organizations, argumentation & negotiation, trust.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
see (Weyns et al. 2007) for comprehensive surveys.
Agreement Technologies refer to computer systems in which autonomous software agents negotiate with each other, typically on behalf of humans, in order to come to mutually acceptable agreements.
Memorandum of Understanding of the Agreement Technologies COST Action IC0801, http://w3.cost.eu/fileadmin/domain_files/ICT/Action_IC0801/mou/IC0801-e.pdf last accessed 27th September 2012.
References
Arcos JL, Noriega P, Rodriguez-Aguilar JA, Sierra C (2007) E4mas through electronic institutions. In: Weyns D, Parunak H, Michel F (eds), Environments for multi-agent systems III., number 4389 in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 184–202. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 08/05/2006
Bandini S, Manzoni S, Vizzari G (2009) Agent based modeling and simulation: an informatics perspective. J Artif Soc Soc Simul 12(4):4
Beun R-J, Eijk R (2004) A co-operative dialogue game for resolving ontological discrepancies. In: Dignum F (ed) Advances in agent communication, LNAI 2922. Springer, Berlin pp 349–363
Bromuri S, Stathis K (2008) Situating cognitive agents in GOLEM. In: Weyns D, Brueckner S, Demazeau Y (eds) Engineering environment-mediated multi-agent systems, vol. 5049., of LNCSSSpringer Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 115–134
Bromuri S, Stathis K (2009) Distributed agent environments in the ambient event calculus. In: Proceedings of the third ACM international conference on distributed event-based systems, DEBS ’09, pp 12:1–12:12, New York, NY, USA, ACM
da Silva VT, Choren R, Lucena CD (2008) MAS-ML: a multi-agent system modeling language. Int J Agent-Oriented Softw Eng 2(4):381–421
da Silva Figueiredo K, Torres da Silva V, de Oliveira Braga C (2011) Modeling norms in multi-agent systems with normml. In: De Vos M, Fornara N, Pitt J, Vouros G (eds) Coordination, organizations, institutions, and norms in agent systems VI, vol. 6541., of Lecture Notes in Computer ScienceSpringer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 39–57
Dignum V (2009) Handbook of research on multi-agent systems : semantics and dynamics of organizational models, chapter the role of organization in agent systems, pp 1–16. Information Science Reference Publisher, ISBN 978-1-60566-256-5, doi:10.4018/978-1-60566-256-5.ch001
d’Inverno M, Luck M, Noriega P, Rodriguez-Aguilar JA, Sierra C (2012) Communicating open systems. Artif Intell 186:38–94
dos Santos CT, Quaresma P, Vieira R, Isaac A (2009) Comparing argumentation frameworks for composite ontology matching. In: McBurney P, Rahwan I, Parsons S, Maudet N (eds), ArgMAS, vol. 6057 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, pp 305–320
Esparcia S, Argente E, Centeno R, Hermoso R (2011) Enhancing MAS environments with organizational mechanisms. Int J Artif Intell Tools (IJAIT) 20(4):663–690
Esparcia S, Centeno R, Hermoso R, Argente E (2011) Artifacting and regulating the environment of a virtual organization. In: 23rd IEEE international conference on tools with artificial intelligence (ICTAI 2011). IEEE
Ferber J, Michel F, Baez J (2005) AGRE: integrating environments with organizations. In: Environments for multi-agent systems, vol. 3374 of LNCS, pp 48–56. Springer
Fornara N, Colombetti M (2009) Specifying and enforcing norms in artificial institutions. In: Baldoni M, Son T, van Riemsdijk M, Winikoff M (eds) Declarative agent languages and technologies VI, vol. 5397. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–17
Fornara N, Tampitsikas C (2012) Using OWL artificial institutions for dynamically creating open spaces of interaction. In: Proceedings of the AT 2012 first international conference on agreement technologies, October 15–16, 2012 in Dubrovnik, Croatia., page to appear
Garca-Camino A, Noriega P, Rodrguez-Aguilar JA (2005) Implementing norms in electronic institutions. In: Proceedings of the 4th international joint conference on autonomous agents and multiagent systems (AAMAS ’05, (ed) Michal Pechoucek ST, Steinernald. Utrecht, NL, ACM Press, pp 667–673
Gordon TF, Karacapilidis N (1997) The zeno argumentation framework. In: Proceedings sixth international conference on AI and law, pp 10–18, New York, ACM Press
Hodge BJ, Anthony W, Gales L (2002) Organization theory: a strategic approach. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Hübner J, Boissier O, Kitio R, Ricci A (2010) Instrumenting multi-agent organisations with organisational artifacts and agents. Auton Agents Multi-Agent Syst 20:369–400
Hulstijn J, Dastani M, van der Torre L (2000) Negotiation protocols and dialogue games. In: Proceedings Belgian-Dutch AI conference (BNAIC-2000), Kaatsheuvel
Karunatillake NC (2006) Argumentation-based negotiation in a social context. Phd, School of electronics and Computer Science, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK
Koster A, Schorlemmer WM, Sabater-Mir J (2012) Engineering trust alignment: theory, method and experimentation. Int J Hum-Comput Stud 70(6):450–473
Kraus S, Sycara K, Evenchik A (1998) Reaching agreement through argumentation: a logical model and implementation. Artif Intell 104:1–69
Krummenacher R, Simperl EPB, Cerizza D, Valle ED, Nixon LJB, Foxvog D (2009) Enabling the European patient summary through triplespaces. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 95(2–S1):33–43
Kullerkupp R (2012) Analysis and preliminary design of a social networking system for supporting information exchange about medicines. Master’s thesis. Department of Informatics, Tallinn University of Technology, Estonia
Locatelli MP, Vizzari G (2007) Awareness in collaborative ubiquitous environments: the multilayered multi-agent situated system approach. TAAS 2(4)
McBurney P, Parsons S (2009) Dialogue games for agent argumentation. In: Rahwan I, Simari G (eds) Argumentation in artificial intelligence, chapter 13. Springer, Berlin, pp 261–280
Miller T, McBurney P (2011) Propositional dynamic logic for reasoning about first-class agent interaction protocols. Comput Intell 27(3):422–457
Miller T, McBurney P (2008) Annotation and matching of first-class agent interaction protocols. In: Proceedings seventh international joint conference on autonomous agents and multi-agent systems (AAMAS 2008, (ed) Padgham L, Parkes D, Mueller JP, Parsons S. NY, SA, ACM Press, New York
Miller T, McBurney P (2010) Characterising and matching iterative and recursive agent interaction protocols. In: Proceedings ninth international conference on autonomous agents and multi-agent systems (AAMAS 2010, (ed) van der Hoek W, Kaminka G, Luck M, Sen S. Toronto, Canada, IFAAMAS, ACM Press, pp 1207–1214
Odell J, Parunak HVD, Fleischer M, Brueckner S (2003) Modeling agents and their environment. In: Agent-oriented software engineering III, vol. 2585 of LNCS, pp 16–31. Springer, Berlin
Okuyama FY, Bordini RH, da Rocha Costa AC (2008) A distributed normative infrastructure for situated multi-agent organisations. In: Proceedings of the 7th international joint conference on autonomous agents and multiagent systems - vol. 3, AAMAS ’08. Richland, SC, International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, pp 1501–1504
Oliva E, McBurney P, Omicini A (2007) Co-argumentation artifact for agent societies. In: Rahwan I, Reed C, Parsons S, (eds), Proceedings fourth international workshop on argumentation in multi-agent systems (ArgMAS 2007), pp. 115–130, AAMAS (2007) Honolulu. Hawai’i, USA
Omicini A, Ricci A, Viroli M (2008) Artifacts in the A &A meta-model for multi-agent systems. Auton Agents Multi-Agent Syst 17(3):432–456
Oren N, Norman T, Preece A, Chalmers S (2004) Policing virtual organizations. In: Proceedings second european conference on multi-agent systems (EUMAS 2004, (ed) Ghidini C, Giorgini P, Hoek W. Barcelona, Spain, EUMAS, pp 499–508
Pinyol I, Sabater-Mir J (2012) Computational trust and reputation models for open multi-agent systems: a review. Artif Intell Rev, pp 1–25
Piunti M, Ricci A, Boissier O, Hübner JF (2009) Embodied organisations in MAS environments. In: Proceedings of the 7th German conference on multiagent system technologies MATES’09, vol. 5774 of LNAI, pp 115–127. Springer
Reed C, Norman TJ, Jennings NR (2002) Negotiating the semantics of agent communications languages. Comput Intell 18(2):229–252
Ricci A, Piunti M, Viroli M, Omicini A (2009) Environment programming in cartago. In: Bordini RH, Dastani M, Dix J, El Fallah-Seghrouchni A (eds) Multi-agent programming: languages, platforms and applications, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 259–288
Ricci A, Piunti M, Viroli M (2011) Environment programming in multi-agent systems: an artifact-based perspective. Auton Agents Multi-Agent Syst 23(2):158–192
Sarrasin JJ, Schumacher M, Hay C, Richard P (June 2010) Health-identity: mobile services for consumers of medicines. In: Special topic conference “Seamless care - safe care: the challenges of interoperability”
Searle JR (1995) The construction of social reality. Free Press, NY
Sensoy M, Norman TJ, Vasconcelos WW, Sycara KP (2012) Owl-polar: a framework for semantic policy representation and reasoning. J Web Sem 12:148–160
Sterling L, Taveter K (2009) The art of agent-oriented modeling. The MIT Press, Massachusetts
Tampitsikas C, Bromuri S, Fornara N, Schumacher MI (2012) Interdependent artificial institutions in agent environments. Appl Artif Intell 26(4):398–427
Tinnemeier N, Dastani M, Meyer J-J (2010) Programming norm change. In: Proceedings of the 9th international conference on autonomous agents and multiagent systems: vol. 1, AAMAS ’10. Richland, SC, ACM, pp 957–964
Wagner J, Hollenbeck J (2001) Organizational behavior. South-Western Pub
Weyns D, Holvoet T (2004) Formal model for situated multiagent systems. Fundam Inform 63(2–3):125–158
Weyns D, Omicini A, Odell JJ (2007) Environment as a first-class abstraction in multi-agent systems. Auton Agents Multi-Agent Syst 14(1):5–30
Weyns D, Parunak HVD (eds) (2007) Special issue on environments for multi-agent systems, vol, 14 (1) of autonomous agents and multi-agent systems. Springer Netherlands
Weyns D, Parunak HVD, Michel F, Holvoet T, Ferber J (2005) Environments for multiagent systems: state-of-the-art and research challenges. In: Weyns D, Parunak HVD, Michel F, Holvoet T, Ferber J (eds) Environment for multi-agent systems, vol. 3374. Springer, Berlin pp 1–47
Weyns D, Schelfthout K, Holvoet T, Lefever T (2005) Decentralized control of E’GV transportation systems. In: Pechoucek M, Steiner D, Thompson SG (eds) AAMAS industrial applications, pp 67–74. ACM
Acknowledgments
This paper is the synthesis of the discussions from the workshop and panel about Environment in Agreement Technologies, held during the COST Action IC0801 Agreement Technologies meeting June 1 and 2, 2012, organized by O. Boissier, C. Carrascosa, A. Ricci, M. Schumacher. We would like to thank the COST Action IC0801 for the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Argente, E., Boissier, O., Carrascosa, C. et al. The role of the environment in agreement technologies. Artif Intell Rev 39, 21–38 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-012-9388-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-012-9388-1