Abstract
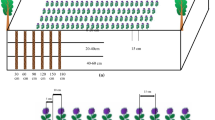
Silvopastoral systems have been a way to address issues related to land use and desertification on the fringe of cities, particularly in northwest China where fast-growing urban population and threat of desertification have become serious problems. A field experiment conducted in northwest China evaluated the root distribution and interspecific interaction between the poplar (Populus L.) and alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) in a silvopastoral system. Roots were sampled once every 15 d using an auger sampling method in a seven-year-old poplar tree + three-year-old alfalfa silvopastoral system, a three-year-old sole alfalfa, and a seven-year-old sole poplar. The results showed that intercropping had a negative effect on the root length density (RLD) of alfalfa and reduced the average root diameter (ARD) of alfalfa at 20–60 cm soil depth. The specific root length (SRL) of alfalfa in silvopastoral system was higher compared to sole cropping. In contrast, intercropping with alfalfa had a positive effect on the RLD and ARD of poplar at the alfalfa grown areas at 0–20 cm soil depth, but less effect on the SRL of poplar. Intercropping caused the reduction of alfalfa yield, but had not significant effect on the yield of stem wood volume of poplar. Calculating the land equivalent ratio in a poplar tree + alfalfa silvopastoral system, it showed that this system was advantageous in the utilization of resources and had a higher productivity compared with sole cropping. In conclusion, root competition and interactions between two intercropped species affects yield of alfalfa and the root distribution of intercropped species in a poplar + alfalfa silvopastoral system.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avice JC, Ourry A, Lemaire G, Volenec JJ, Boucaud J (1997) Root protein and vegetative storage protein are key organic nutrients for alfalfa shoot regrowth. Crop Sci 37:1187–1193. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1997.0011183X003700040027x
Chen G, Kong X, Gan Y, Zhang R, Feng F, Yu A, Cai Z, Wan S, Qiang C (2018) Enhancing the systems productivity and water use efficiency through coordinated soil water sharing and compensation in strip-intercropping. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28612-6
Cralle HT (1981) Nitrogen fixation and vegetative regrowth of alfalfa and birdsfoot trefoil after successive harvests or floral debudding. Plant Physiol 67:898–905. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.67.5.898
Dhima KV, Lithourgidis AS, Vasilakoglou IB, Dordas CA (2007) Competition indices of common vetch and cereal intercrops in two seeding ratio. Field Crop Res 100:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2006.07.008
Eissenstat DM, Yanai RD (1997) The ecology of root lifespan. Adv Ecol Res 27:1–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60005-7
Fortier J, Gagnon D, Truax B, Lambert F (2010) Biomass and volume yield after 6 years in multiclonal hybrid poplar riparian buffer strips. Biomass Bioenerg 34:1028–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2010.02.011
Francaviglia R, Benedetti A, Doro L, Madrau S, Ledda L (2014) Influence of land use on soil quality and stratification ratios under agro-silvo-pastoral Mediterranean management systems. Agric Ecosyst Environ 183:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2013.10.026
Gabriel EP, Atangana AR, Khasa DP (2017) Tree planting in urban and peri-urban of Kinshasa: survey of factors facilitating agroforestry adoption. Urban For Urban Green 30:12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2017.12.015
Gakis S, Mantzanas K, Alifragis D, Papanastasis VP, Papaioannou A, Seilopoulos D, Platis P (2004) Effects of understorey vegetation on tree establishment and growth in a silvopastoral system in northern Greece. Agrofor Syst 60:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:agfo.0000013275.30617.ad
Gautam MK, Mead DJ, Frampton CM, Clinton PW, Chang SX (2003) Pinus radiata in a sub-humid temperate silvopastoral system: modelling of seasonal root growth. For Ecol Manag 182:303–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(03)00065-3
Holdo RM, Brocato ER (2015) Tree–grass competition varies across select savanna tree species: a potential role for rooting depth. Plant Ecol 216:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-015-0460-1
Isaac ME, Anglaaere LCN, Borden K, Adu-Bredu S (2014) Intraspecific root plasticity in agroforestry systems across edaphic conditions. Agr Ecosyst Environ 185:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2013.12.004
Jose S, Gillespie AR, Pallardy SG (2004) Interspecific interactions in temperate agroforestry. Agrofor Syst 61–62:237–255. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:agfo.0000029002.85273.9b
Livesley SJ, Gregory PJ, Buresh RJ (2004) Competition in tree row agroforestry systems. 3. Soil water distribution and dynamics. Plant Soil 264:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:plso.0000047750.80654.d5
Loreau M, Hector A (2001) Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments. Nature 412:72–76. https://doi.org/10.1038/35083573
Ma YH, Fu SL, Zhang XP, Zhao K, Chen HYH (2017) Intercropping improves soil nutrient availability, soil enzyme activity and tea quantity and quality. Appl Soil Ecol 119:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.06.028
Mcintyre BD, Riha SJ, Ong CK (1997) Competition for water in a hedge-intercrop system. Field Crops Res 52:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(96)01062-3
Menezes RSC, Salcedo IH, Elliott ET (2002) Microclimate and nutrient dynamics in a silvopastoral system of semiarid northeastern Brazil. Agrofor Syst 56:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021172530939
Paulo MJ, Stein A, Tomé M (2002) A spatial statistical analysis of cork oak competition in two Portugue. Can J For Res 32:598–599. https://doi.org/10.1139/x02-107
Plaza-Bonilla D, Álvaro-Fuentes J, Hansen NC, Lampurlanés J, Cantero-Martínez C (2014) Winter cereal root growth and aboveground–belowground biomass ratios as affected by site and tillage system in dryland Mediterranean conditions. Plant Soil 374:925–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1926-3
Priyadarshini KVR, Prins HHT, Bie S, Heitkönig IMA, Woodborne S, Gort G, Kirkman K, Ludwig F, Dawson TE, Kroon H (2016) Seasonality of hydraulic redistribution by trees to grasses and changes in their water–source use that change tree–grass interactions. Ecohydrology 9:218–228. https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.1624
Querné A, Battie-Laclau P, Dufour L, Wery J, Dupraz C (2017) Effects of walnut trees on biological nitrogen fixation and yield of intercropped alfalfa in a Mediterranean agroforestry system. Eur J Agron 84:35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2016.12.001
Rivest D, Rolo V, López-Díaz L, Moreno G (2011) Shrub encroachment in Mediterranean silvopastoral systems: Retama sphaerocarpa and Cistus ladanifer induce contrasting effects on pasture and Quercus ilex production. Agric Ecosyst Environ 141:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.04.018
Schroth G, Zech W (1995) Root length dynamics in agroforestry with Gliricidia sepium as compared to sole cropping in the semi-deciduous rainforest zone of West Africa. Plant Soil 170:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00010482
Tedder M, Kirkman K, Morris C, Fynn R (2014) Tree–grass competition along a catenal gradient in a mesic grassland, South Africa. Grassl Sci. 60:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/grs.12034
Thompson DJ, Newman RF, Hope G, Broersma K, Quinton DA (2000) Nitrogen cycling in silvopastoral systems in the Pacific Northwest: a review. Can J Plant Sci 80:21–28. https://doi.org/10.4141/P99-045
Upson MA, Burgess PJ (2013) Soil organic carbon and root distribution in a temperate arable agroforestry system. Plant Soil 373:43–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1733-x
Wang BJ, Zhang W, Ahanbieke P, Gan YW, Xu WL, Li LH, Christie P, Li L (2014) Interspecific interactions alter root length density, root diameter and specific root length in jujube/wheat agroforestry systems. Agrofor Syst 88:835–850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-014-9729-y
Yu Y, Stomph TJ, Makowski D, Werf WVD (2015) Temporal niche differentiation increases the land equivalent ratio of annual intercrops: a meta-analysis. Field Crop Res 184:133–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2015.09.010
Zhang G, Yang Z, Dong S (2011) Interspecific competitiveness affects the total biomass yield in an alfalfa and corn intercropping system. Field Crop Res 124:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2011.06.006
Zhang W, Ahanbieke P, Wang BJ, Gan YW, Li LH, Christie P, Li L (2015) Temporal and spatial distribution of roots as affected by interspecific interactions in a young walnut/wheat alley cropping system in northwest China. Agrofor Syst 89:327–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-014-9770-x
Zhang W, Wang BJ, Gan YW, Duan ZP, Hao XD, Xu WL, Lv X, Li LH (2017) Competitive interaction in a jujube tree/wheat agroforestry system in northwest China’s Xinjiang Province. Agrofor Syst 91:881–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-017-0153-y
Zhao C, Feng Z, Chen G (2004) Soil water balance simulation of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) in the semiarid Chinese Loess Plateau. Agr Water Manage. 69:101–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2004.04.006
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 31460335 and 31560376), by the National Forage Industry Technical system of China (CARS-34), by a project funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Project No. 2015M582737), by the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology (Project No. 2009BADA4B03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, T., Zhu, Y., Duan, Z.P. et al. Root distribution and productivity in a poplar tree + alfalfa silvopastoral system in northwest China’s Xinjiang Province. Agroforest Syst 94, 997–1010 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-019-00466-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-019-00466-5