Abstract
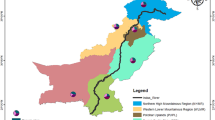
Many causes are suspected to explain the decline of medicinal plant species. This study aims to understand the threats on Zanthoxylum zanthoxyloïdes and Morinda lucida in Benin in order to plan sound conservation strategies. A total of 247 respondents of the Southern and Central Zones of Benin were interviewed based on the uses of each target species, their perceptions about species availability in the natural vegetation and the farming operations (clearing and uprooting) that destroy plant species. In the field, 130 plots were established in various habitats where at least one plant of the two species was found, to assess the abundance of each targeted species. Traditional medicinal uses were recognized by respondents as the most important and preferred use of the target species based on the cultural importance index (1.86–2.50) within each zone. Zanthoxylum zanthoxyloïdes and M. lucida were both available in Southern Benin but were threatened by farming operations in this zone. The findings indicate that the ecological impacts of medicinal uses of the two tree species are minor compared to the effects of pineapple production. The findings also suggest the need for conservation actions and further researches in this area of pineapple production in Southern Benin to reconcile the issue of pineapple production with the need for biodiversity conservation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adomou AC, Sinsin B, van der Maesen LJG (2006) Phytosociological and chorological approaches to phytogeography: a meso-scale study in Benin. Syst Geogr Plants 76:155–178
Adomou AC, Agbani OP, Sinsin B (2011) Plants. In: Neuenschwander PS, Sinsin B, Goergen G (eds) Protection de la Nature en Afrique de l’Ouest: Une Liste Rouge pour le Bénin. Nature Conservation in West Africa: Red List for Benin. International Institute of Tropical Agriculture, Ibadan, Nigeria
Allabi AC, Busia K, Ekanmian V, Bakiono F (2012) The use of medicinal plants in self-care in the Agonlin region of Benin. J Ethnopharmacol 133:234–243
Azando EVB, Hounzangbé-Adoté MS, Olounladé PA, Brunet S, Fabre N, Valentin A, Hoste H (2011) Involvement of tannins and flavonoids in the in vitro effects of Newbouldia laevis and Zanthoxylum zanthoxyloïdes extracts on the exsheathment of third-stage infective larvae of gastrointestinal nematodes. Vet Parasitol 180:292–297
Bajwa AA (2014) Sustainable weed management in conservation agriculture. Crop Prot 65:105–113
Botha J, Witkowski ETF, Shackleton CM (2007) Factors influencing prices of medicinal plants traded in the Lowveld, South Africa. Int J Sustain Dev World 14:450–469
Cunningham AB (1996) People, park and plant use: recommendations for multiple-use zones and development alternatives around Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, Uganda. People and Plants Working Paper 4. UNESCO, Paris
Deleke Koko KI, Djego J, Gbenou J, Hounzangbe-Adote MS, Sinsin B (2011) Etude phytochimique des principales plantes galactogènes et emménagogues utilisées dans les terroirs riverains de la Zone cynégétique de la Pendjari. Int J Biol Chem Sci 5:618–633
Delvaux C, Sinsin B, Darchambeau F, Van Damme P (2009) Recovery from bark harvesting of 12 medicinal tree species in Benin, West Africa. J Appl Ecol 46:703–712
Matu EN (2011) Zanthoxylum zanthoxyloides (Lam.) Zepern. & Timler. In: Schmelzer GH, Gurib-Fakim A (eds) PROTA (plant resources of Tropical Africa / Ressources végétales de l’Afrique tropicale), Wageningen, Pays Bas
Djego J, Djego-Djossou S, Cakpo Y, Agnani P, Sinsin B (2011) Evaluation du potentiel ethnobotanique des populations rurales au Sud et au centre du Bénin. Int J Biol Chem Sci 5:1432–1447
Friedman J, Yaniv Z, Dafni A, Palewitch D (1986) A preliminary classification of the healing potential of medicinal plants, based on a rational analysis of an ethno pharmacological field survey among Bedouins in the Negev Desert, Israel. J Ethnopharmacol 16:275–287
Gaoue OG, Ticktin T (2007) Patterns of harvesting foliage and bark from the multipurpose tree Khaya senegalensis in Benin: variation across ecological regions and its impacts on population structure. Biol Conserv 137:424–436
Höft M, Barik SK, Lykke AM (1999) Quantitative ethnobotany. Applications of multivariate and statistical analysis in ethnobotany. People and Plants Working Paper 6. Paris, UNESCO, p 44
Houehanou TD, Assogbadjo AE, Glèlè Kakaï R, Houinato M, Sinsin B (2011) Valuation of local preferred uses and traditional ecological knowledge in relation to three multipurpose tree species in Bénin (West Africa). For Policy Econ 13:554–562
Houehanou TD, GlèlèKakaï R, Assogbadjo AE, Kindomihou VM, Houinato M, Wittig R, Sinsin B (2013) Change in the woody floristic composition, diversity and structure from protected to unprotected savannas. Afr J Ecol 51:358–365
Hounzangbé-Adoté MS, Paolini V, Fouraste I, Moutairou K, Hoste H (2005a) In vitro effects of four tropical plants on three life-cycle stages of the parasitic nematode, Haemonchus contortus. Res Vet Sci 78:155–160
Hounzangbé-Adoté MS, Zinsou FE, Hounpke V, Moutairou K, Hoste H (2005b) In vivo effects of Fagara leaves on sheep infected with gastrointestinal nematodes. Trop Anim Health Prod 37:205–214
Jusu A, Sanchez AC (2013) Economic importance of the medicinal plant trade in Sierra Leone. Econ Bot 67:299–312
MAEP (2015) Statistiques agricoles. DPP/MAEP, Cotonou
Maunder M (2013) Plant conservation. Encycl Biodivers 6:76–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-384719-5.00280-X
Miko Gohoun F (2013) Amélioration de la production de la culture d’ananas (Ananas comosus) (L.) MERR dans la Commune d’Allada au Bénin. Mémoire de fin de formation. Ecole Polytechnique d’Abomey-Calavi, Abomey-Calavi, p 36
Mueller-Dombois D, Ellenberg H (1974) Aims and methods of vegetation ecology. Wiley, New York, p 547
Olounladé PA, Azando EV, Hounzangbé-Adoté MS, Ha TB, Leroy E, Moulis C, Fabre N, Magnaval JF, Hoste H, Valentin A (2012) In vitro anthelmintic activity of the essential oils of Zanthoxylum zanthoxyloides and Newbouldia laevis against Strongyloides ratti. Parasitol Res 4:1427–1433
Quiroz D, Towns A, Legba SI, Swier J, Brière S, Sosef M, van Andel T (2014) Quantifying the domestic market in herbal medicine in Benin, West Africa. J Ethnopharmacol 151:1100–1108
Sulieman HM, Buchroithner MF, Elhag MM (2012) Use of local knowledge for assessing vegetation changes in the Southern Gadarif Region, Sudan. Afr J Ecol 50:233–242
Vodouhè FG, Coulibaly O, Assogbadjo AE, Sinsin B (2008) Medicinal plant commercialization in Benin: an analysis of profit distribution equity across supply chain actors and its effect on the sustainable use of harvested species. J Med Plants Res 2:331–340
White F (1983) The vegetation of Africa. UNESCO, Paris
Yetein MH, Houessou LG, Lougbégnon TO, Teka O, Tente B (2013) Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used for the treatment of malaria in plateau of Allada, Benin (West Africa). J Ethnopharmacol 146:154–163
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the West Africa Agricultural Productivity Program (WAAPP) Benin for granting M. Alain Sèakpo YAOITCHA a PhD scholarship to conduct these scientific researches. We also thank the competitive funding program for research of the University of Abomey-Calavi (PFCR/UAC) for its contribution to data collection through the VPMAS project. The involvement of interviewers and people has been a great success of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yaoitcha, A.S., Vodouhe, F.G., Azihou, A.F. et al. Vulnerability assessment of medicinal tree species in Benin (West Africa): Zanthoxylum zanthoxyloïdes (Lam.) and Morinda lucida Benth. Agroforest Syst 93, 2267–2279 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-019-00349-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-019-00349-9