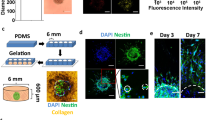
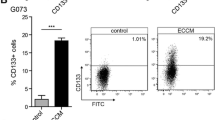
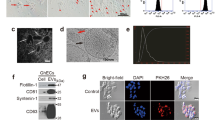
Abstract
Glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) reside close to blood vessels (BVs) but vascular cues contributing to GSC stemness and the nature of GSC-BVs cross talk are not fully understood. Here, we dissected vascular cues influencing GSC gene expression and function to perfusion-based vascular cues, as well as to those requiring direct GSC-endothelial cell (EC) contacts. In light of our previous finding that perivascular tumor cells are metabolically different from tumor cells residing further downstream, cancer cells residing within a narrow, < 60 µm wide perivascular niche were isolated and confirmed to possess a superior tumor-initiation potential compared with those residing further downstream. To circumvent reliance on marker expression, perivascular GSCs were isolated from the respective locales based on their relative state of quiescence. Combined use of these procedures uncovered a large number of previously unrecognized differentially expressed GSC genes. We show that the unique metabolic milieu of the perivascular niche dominated by the highly restricted zone of mTOR activity is conducive for acquisition of GSC properties, primarily in the regulation of genes implicated in cell cycle control. A complementary role of vascular cues including those requiring direct glioma/EC contacts was revealed using glioma/EC co-cultures. Outstanding in the group of glioma cells impacted by nearby ECs were multiple genes responsible for maintaining GSCs in an undifferentiated state, a large fraction of which also relied on Notch-mediated signaling. Glioma-EC communication was found to be bidirectional, evidenced by extensive Notch-mediated EC reprogramming by contacting tumor cells, primarily metabolic EC reprogramming.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tykocki T, Eltayeb M (2018) Ten-year survival in glioblastoma A systematic review. J Clin Neurosci 54:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2018.05.002
Batchelor TT, Reardon DA, de Groot JF, Wick W, Weller M (2014) Antiangiogenic therapy for glioblastoma: current status and future prospects. Clin Cancer Res 20(22):5612–5619. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0834
Lathia JD, Mack SC, Mulkearns-Hubert EE, Valentim CL, Rich JN (2015) Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Genes Dev 29(12):1203–1217. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.261982.115
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA, Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman RM, Cusimano MD, Dirks PB (2004) Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 432(7015):396–401. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03128
Meacham CE, Morrison SJ (2013) Tumour heterogeneity and cancer cell plasticity. Nature 501(7467):328–337. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12624
Magee JA, Piskounova E, Morrison SJ (2012) Cancer stem cells: impact, heterogeneity, and uncertainty. Cancer Cell 21(3):283–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.03.003
Thankamony AP, Saxena K, Murali R, Jolly MK, Nair R (2020) Cancer stem cell plasticity—a deadly deal. Front Mol Biosci 7:79. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2020.00079
Poli V, Fagnocchi L, Zippo A (2018) Tumorigenic cell reprogramming and cancer plasticity: interplay between signaling, microenvironment, and epigenetics. Stem Cells Int 2018:4598195. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4598195
Dirkse A, Golebiewska A, Buder T, Nazarov PV, Muller A, Poovathingal S, Brons NHC, Leite S, Sauvageot N, Sarkisjan D, Seyfrid M, Fritah S, Stieber D, Michelucci A, Hertel F, Herold-Mende C, Azuaje F, Skupin A, Bjerkvig R, Deutsch A, Voss-Bohme A, Niclou SP (2019) Stem cell-associated heterogeneity in Glioblastoma results from intrinsic tumor plasticity shaped by the microenvironment. Nat Commun 10(1):1787. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09853-z
Calabrese C, Poppleton H, Kocak M, Hogg TL, Fuller C, Hamner B, Oh EY, Gaber MW, Finklestein D, Allen M, Frank A, Bayazitov IT, Zakharenko SS, Gajjar A, Davidoff A, Gilbertson RJ (2007) A perivascular niche for brain tumor stem cells. Cancer Cell 11(1):69–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2006.11.020
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature 359(6398):843–845. https://doi.org/10.1038/359843a0
Cao Z, Ding BS, Guo P, Lee SB, Butler JM, Casey SC, Simons M, Tam W, Felsher DW, Shido K, Rafii A, Scandura JM, Rafii S (2014) Angiocrine factors deployed by tumor vascular niche induce B cell lymphoma invasiveness and chemoresistance. Cancer Cell 25(3):350–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.02.005
Pasquier J, Ghiabi P, Chouchane L, Razzouk K, Rafii S, Rafii A (2020) Angiocrine endothelium: from physiology to cancer. J Transl Med 18(1):52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-020-02244-9
Kumar S, Sharife H, Kreisel T, Mogilevsky M, Bar-Lev L, Grunewald M, Aizenshtein E, Karni R, Paldor I, Shlomi T, Keshet E (2019) Intra-Tumoral Metabolic Zonation and Resultant Phenotypic Diversification Are Dictated by Blood Vessel Proximity. Cell Metab 30(1):201-211e206
Rafii S, Butler JM, Ding BS (2016) Angiocrine functions of organ-specific endothelial cells. Nature 529(7586):316–325. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17040
Weber JM, Calvi LM (2010) Notch signaling and the bone marrow hematopoietic stem cell niche. Bone 46(2):281–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2009.08.007
Brooks LJ, Parrinello S (2017) Vascular regulation of glioma stem-like cells: a balancing act. Curr Opin Neurobiol 47:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2017.06.008
Matsumoto K, Arao T, Tanaka K, Kaneda H, Kudo K, Fujita Y, Tamura D, Aomatsu K, Tamura T, Yamada Y, Saijo N, Nishio K (2009) mTOR signal and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha regulate CD133 expression in cancer cells. Cancer Res 69(18):7160–7164. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1289
Yan GN, Yang L, Lv YF, Shi Y, Shen LL, Yao XH, Guo QN, Zhang P, Cui YH, Zhang X, Bian XW, Guo DY (2014) Endothelial cells promote stem-like phenotype of glioma cells through activating the Hedgehog pathway. J Pathol 234(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4349
Fessler E, Borovski T, Medema JP (2015) Endothelial cells induce cancer stem cell features in differentiated glioblastoma cells via bFGF. Mol Cancer 14:157. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0420-3
Anido J, Saez-Borderias A, Gonzalez-Junca A, Rodon L, Folch G, Carmona MA, Prieto-Sanchez RM, Barba I, Martinez-Saez E, Prudkin L, Cuartas I, Raventos C, Martinez-Ricarte F, Poca MA, Garcia-Dorado D, Lahn MM, Yingling JM, Rodon J, Sahuquillo J, Baselga J, Seoane J (2010) TGF-beta receptor inhibitors target the CD44(high)/Id1(high) glioma-initiating cell population in human glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 18(6):655–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.10.023
Zhu TS, Costello MA, Talsma CE, Flack CG, Crowley JG, Hamm LL, He X, Hervey-Jumper SL, Heth JA, Muraszko KM, DiMeco F, Vescovi AL, Fan X (2011) Endothelial cells create a stem cell niche in glioblastoma by providing NOTCH ligands that nurture self-renewal of cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Res 71(18):6061–6072. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4269
Hovinga KE, Shimizu F, Wang R, Panagiotakos G, Van Der Heijden M, Moayedpardazi H, Correia AS, Soulet D, Major T, Menon J, Tabar V (2010) Inhibition of notch signaling in glioblastoma targets cancer stem cells via an endothelial cell intermediate. Stem Cells 28(6):1019–1029. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.429
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW, Kleihues P (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114(2):97–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4
Kumar S, Sharife H, Kreisel T, Bar-Lev L, Grunewald M, Keshet E (2020) Isolation of tumor cells based on their distance from blood vessels. Bio-Protocol. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.3628
Hu Y, Smyth GK (2009) ELDA: extreme limiting dilution analysis for comparing depleted and enriched populations in stem cell and other assays. J Immunol Methods 347(1–2):70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2009.06.008
Trapnell C, Hendrickson DG, Sauvageau M, Goff L, Rinn JL, Pachter L (2013) Differential analysis of gene regulation at transcript resolution with RNA-seq. Nat Biotechnol 31(1):46–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2450
Hashimshony T, Senderovich N, Avital G, Klochendler A, de Leeuw Y, Anavy L, Gennert D, Li S, Livak KJ, Rozenblatt-Rosen O, Dor Y, Regev A, Yanai I (2016) CEL-Seq2: sensitive highly-multiplexed single-cell RNA-Seq. Genome Biol 17:77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-0938-8
Taverna F, Goveia J, Karakach TK, Khan S, Rohlenova K, Treps L, Subramanian A, Schoonjans L, Dewerchin M, Eelen G, Carmeliet P (2020) BIOMEX: an interactive workflow for (single cell) omics data interpretation and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res 48(W1):W385–W394. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa332
Kim WT, Ryu CJ (2017) Cancer stem cell surface markers on normal stem cells. BMB Rep 50(6):285–298. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.6.039
Richichi C, Brescia P, Alberizzi V, Fornasari L, Pelicci G (2013) Marker-independent method for isolating slow-dividing cancer stem cells in human glioblastoma. Neoplasia 15(7):840–847. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.13662
Civenni G, Walter A, Kobert N, Mihic-Probst D, Zipser M, Belloni B, Seifert B, Moch H, Dummer R, van den Broek M, Sommer L (2011) Human CD271-positive melanoma stem cells associated with metastasis establish tumor heterogeneity and long-term growth. Cancer Res 71(8):3098–3109. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3997
Boiko AD, Razorenova OV, van de Rijn M, Swetter SM, Johnson DL, Ly DP, Butler PD, Yang GP, Joshua B, Kaplan MJ, Longaker MT, Weissman IL (2010) Human melanoma-initiating cells express neural crest nerve growth factor receptor CD271. Nature 466(7302):133–137. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09161
Imai T, Tamai K, Oizumi S, Oyama K, Yamaguchi K, Sato I, Satoh K, Matsuura K, Saijo S, Sugamura K, Tanaka N (2013) CD271 defines a stem cell-like population in hypopharyngeal cancer. PLoS ONE 8(4):e62002. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0062002
Abbas T, Dutta A (2009) p21 in cancer: intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat Rev Cancer 9(6):400–414. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2657
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1999) CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 13(12):1501–1512. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.13.12.1501
Engeland K (2018) Cell cycle arrest through indirect transcriptional repression by p53: I have a DREAM. Cell Death Differ 25(1):114–132. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.172
Alshehri MM, Robbins SM, Senger DL (2017) The role of neurotrophin signaling in gliomagenesis: a focus on the p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75(NTR)/CD271). Vitam Horm 104:367–404
Johnston AL, Lun X, Rahn JJ, Liacini A, Wang L, Hamilton MG, Parney IF, Hempstead BL, Robbins SM, Forsyth PA, Senger DL (2007) The p75 neurotrophin receptor is a central regulator of glioma invasion. PLoS Biol 5(8):e212. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0050212
Kahn J, Hayman TJ, Jamal M, Rath BH, Kramp T, Camphausen K, Tofilon PJ (2014) The mTORC1/mTORC2 inhibitor AZD2014 enhances the radiosensitivity of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Neuro Oncol 16(1):29–37. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/not139
Sunayama J, Matsuda K, Sato A, Tachibana K, Suzuki K, Narita Y, Shibui S, Sakurada K, Kayama T, Tomiyama A, Kitanaka C (2010) Crosstalk between the PI3K/mTOR and MEK/ERK pathways involved in the maintenance of self-renewal and tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Stem Cells 28(11):1930–1939. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.521
Sunayama J, Sato A, Matsuda K, Tachibana K, Suzuki K, Narita Y, Shibui S, Sakurada K, Kayama T, Tomiyama A, Kitanaka C (2010) Dual blocking of mTor and PI3K elicits a prodifferentiation effect on glioblastoma stem-like cells. Neuro Oncol 12(12):1205–1219. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noq103
O’Brien C, Cavet G, Pandita A, Hu X, Haydu L, Mohan S, Toy K, Rivers CS, Modrusan Z, Amler LC, Lackner MR (2008) Functional genomics identifies ABCC3 as a mediator of taxane resistance in HER2-amplified breast cancer. Cancer Res 68(13):5380–5389. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0234
Calatozzolo C, Gelati M, Ciusani E, Sciacca FL, Pollo B, Cajola L, Marras C, Silvani A, Vitellaro-Zuccarello L, Croci D, Boiardi A, Salmaggi A (2005) Expression of drug resistance proteins Pgp, MRP1, MRP3, MRP5 and GST-pi in human glioma. J Neurooncol 74(2):113–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-6152-7
Yin S, Xu L, Bonfil RD, Banerjee S, Sarkar FH, Sethi S, Reddy KB (2013) Tumor-initiating cells and FZD8 play a major role in drug resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 12(4):491–498. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-1090
Ferrari-Toninelli G, Bonini SA, Uberti D, Buizza L, Bettinsoli P, Poliani PL, Facchetti F, Memo M (2010) Targeting notch pathway induces growth inhibition and differentiation of neuroblastoma cells. Neuro Oncol 12(12):1231–1243. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noq101
Ottone C, Krusche B, Whitby A, Clements M, Quadrato G, Pitulescu ME, Adams RH, Parrinello S (2014) Direct cell-cell contact with the vascular niche maintains quiescent neural stem cells. Nat Cell Biol 16(11):1045–1056. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3045
Sestan N, Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rakic P (1999) Contact-dependent inhibition of cortical neurite growth mediated by notch signaling. Science 286(5440):741–746
Purow BW, Haque RM, Noel MW, Su Q, Burdick MJ, Lee J, Sundaresan T, Pastorino S, Park JK, Mikolaenko I, Maric D, Eberhart CG, Fine HA (2005) Expression of notch-1 and its ligands, delta-like-1 and Jagged-1, is critical for glioma cell survival and proliferation. Cancer Res 65(6):2353–2363
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, Campbell LL, Polyak K, Brisken C, Yang J, Weinberg RA (2008) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 133(4):704–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.027
Polyak K, Weinberg RA (2009) Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer 9(4):265–273. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2620
Teodorczyk M, Schmidt MHH (2014) Notching on cancer’s door: notch signaling in brain tumors. Front Oncol 4:341. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2014.00341
Chen J, Kesari S, Rooney C, Strack PR, Chen J, Shen H, Wu L, Griffin JD (2010) Inhibition of notch signaling blocks growth of glioblastoma cell lines and tumor neurospheres. Genes Cancer 1(8):822–835. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601910383564
Fan X, Khaki L, Zhu TS, Soules ME, Talsma CE, Gul N, Koh C, Zhang J, Li YM, Maciaczyk J, Nikkhah G, Dimeco F, Piccirillo S, Vescovi AL, Eberhart CG (2010) NOTCH pathway blockade depletes CD133-positive glioblastoma cells and inhibits growth of tumor neurospheres and xenografts. Stem Cells 28(1):5–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.254
Xie Q, Wu Q, Kim L, Miller TE, Liau BB, Mack SC, Yang K, Factor DC, Fang X, Huang Z, Zhou W, Alazem K, Wang X, Bernstein BE, Bao S, Rich JN (2016) RBPJ maintains brain tumor-initiating cells through CDK9-mediated transcriptional elongation. J Clin Invest 126(7):2757–2772. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI86114
Schreck KC, Taylor P, Marchionni L, Gopalakrishnan V, Bar EE, Gaiano N, Eberhart CG (2010) The Notch target Hes1 directly modulates Gli1 expression and Hedgehog signaling: a potential mechanism of therapeutic resistance. Clin Cancer Res 16(24):6060–6070. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1624
Bazzoni R, Bentivegna A (2019) Role of notch signaling pathway in glioblastoma pathogenesis. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030292
Bayin NS, Frenster JD, Sen R, Si S, Modrek AS, Galifianakis N, Dolgalev I, Ortenzi V, Illa-Bochaca I, Khahera A, Serrano J, Chiriboga L, Zagzag D, Golfinos JG, Doyle W, Tsirigos A, Heguy A, Chesler M, Barcellos-Hoff MH, Snuderl M, Placantonakis DG (2017) Notch signaling regulates metabolic heterogeneity in glioblastoma stem cells. Oncotarget 8(39):64932–64953. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18117
Helms HC, Abbott NJ, Burek M, Cecchelli R, Couraud PO, Deli MA, Forster C, Galla HJ, Romero IA, Shusta EV, Stebbins MJ, Vandenhaute E, Weksler B, Brodin B (2016) In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier: an overview of commonly used brain endothelial cell culture models and guidelines for their use. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36(5):862–890. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X16630991
Man S, Ubogu EE, Williams KA, Tucky B, Callahan MK, Ransohoff RM (2008) Human brain microvascular endothelial cells and umbilical vein endothelial cells differentially facilitate leukocyte recruitment and utilize chemokines for T cell migration. Clin Dev Immunol 2008:384982. https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/384982
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi B, Varambally S (2017) UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia 19(8):649–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr.Sharona Elgavish and the Info-Core Bioinformatics unit of the Hebrew University faculty of Medicine for bioinformatics analysis, all the members of the Keshet lab for their inputs and Dr. Aparna Anand for proof reading the manuscript. This work was supported by the Cooperation Program in Cancer Research of the Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum (DKFZ), the Israeli Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) to EK (CA-178) and New Faculty Grant from Indian Institute of Technology Delhi to SK (MI00148).
Disclosure
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SK conceived, designed, and performed experiments. LB performed in vitro co-culture experiments and data analysis. MM, HS, MG, and TL assisted in animal studies. FT, JG, and PC analyzed transcriptomics/metabolomics data of co-culture experiments. EK conceived and supervised the study. SK and EK wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 17918 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Bar-Lev, L., Sharife, H. et al. Identification of vascular cues contributing to cancer cell stemness and function. Angiogenesis 25, 355–371 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-022-09830-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-022-09830-z