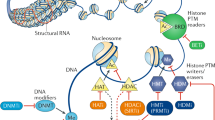
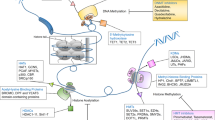
Abstract
Cancer cells are often dependent on epigenetic pathways for their survival. Consequently, drugs that target the epigenome, rather than the underlying DNA sequence, are currently attracting considerable attention. In recent years, the first epigenetic drugs have been approved for cancer chemotherapy, mainly for hematological applications. Limitations in single-drug efficacies have thus far limited their application in the treatment of solid tumors. Nevertheless, promising activity for these compounds has been suggested when combined with other, distinctly targeted agents. In this review, we discuss the anti-angiogenic activity of histone deacetylase and DNA methyltransferase inhibitors and their combinations with other targeted (anti-angiogenic) therapeutics in treatment of solid tumors. The role that these inhibitors play in the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis, particularly in combination with other targeted agents, and the advantages they present over broad acting anticancer agents, are critically discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 5FD:
-
5-Fluoro-2′-deoxycytidine
- Ang-2:
-
Angiopoietin2
- AML:
-
Acute myeloid leukemia
- AZA:
-
Azacitidine, 5-AZA-CR, 5-azacytidine
- bFGF:
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- FGFR:
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor
- CAM:
-
Chorioallantoic membrane of the chicken embryo
- CTCL:
-
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma
- CYR61:
-
Cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61
- DAC:
-
Decitabine, 5-AZA-2′-deoxycytidine, 5-AZA-CdR
- DNMT:
-
DNA methyltransferase
- E-cadherin:
-
Epithelial cadherin
- EC:
-
Endothelial cells
- EGCG:
-
Epigallocatechin gallate
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)
- FAO:
-
Fatty acid oxidation
- FSC:
-
Feedback system control
- HAT:
-
Acetyltransferase
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha
- HUVEC:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- HYD:
-
Hydralazine
- IC50 :
-
The half maximal inhibitory concentration
- IGF1:
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- KP1019:
-
trans-[Tetrachlorobis(1H-indazole)ruthenate(III)
- miRNA:
-
Noncoding microRNA
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- MTA1:
-
Metastasis-associated protein 1
- mTOR:
-
Mechanistic target of rapamycin
- MVD:
-
Microvessel density
- NAMI-A:
-
trans-[Tetrachloro(dimethylsulfoxide)(imidazole)ruthenate(III)]
- NOX4:
-
NADPH oxidase 4
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- NuRD:
-
Nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- p300-HAT:
-
p300 histone acetyltransferase
- PBA:
-
Phenylbutyrate
- PDGF-B:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor subunit B
- PDGFR-B:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor subunit B receptor
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- PVRL2:
-
Poliovirus receptor-related 2
- RAPTA-C:
-
Ru(η6-p-cymene)(pta)Cl2
- RAPTA-T:
-
Ru(η6-toluene)(pta)Cl2
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- SAHA:
-
Vorinostat
- SAM:
-
S-adenosyl methionine
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- SIRT:
-
Histone deacetylase sirtuins
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor beta
- TIMP3:
-
Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase 3
- Tie-2:
-
Angiopoietin 1 receptor
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- TSA:
-
Trichostatin A
- TSG:
-
Tumor suppressor gene
- TSP-1:
-
Thrombospondin 1
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFR:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
- VE-cadherin:
-
Vascular endothelial cadherin
- VHL:
-
Von Hippel–Lindau
- VPA:
-
Valproic acid
- WIF-1:
-
Wnt inhibitory factor 1
- ZEB:
-
Zebularine
References
Rodríguez-Paredes M, Esteller M (2011) Cancer epigenetics reaches mainstream oncology. Nat Med 17(3):330–339
Russo VEA, Martienssen RA, Riggs AD (1996) Epigenetic mechanisms of gene regulation. Cold Spring Harbor, New york
Viré E, Brenner C, Deplus R, Blanchon L, Fraga M, Didelot C, Morey L, Van Eynde A, Bernard D, Vanderwinden J-M, Bollen M, Esteller M, Di Croce L, de Launoit Y, Fuks F (2006) The Polycomb group protein EZH2 directly controls DNA methylation. Nature 439(7078):871–874
Bird A (2002) DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev 16(1):6–21
Peserico A, Simone C (2011) Physical and functional HAT/HDAC interplay regulates protein acetylation balance. J Biomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1155/2011/371832
Whittaker SJ, Demierre MF, Kim EJ, Rook AH, Lerner A, Duvic M, Scarisbrick J, Reddy S, Robak T, Becker JC, Samtsov A, McCulloch W, Kim YH (2010) Final results from a multicenter, international, pivotal study of romidepsin in refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 28(29):4485–4491
Santini V, Melnick A, Maciejewski JP, Duprez E, Nervi C, Cocco L, Ford KG, Mufti G (2013) Epigenetics in focus: pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndromes and the role of hypomethylating agents. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 88(2):231–245
Nervi C, De Marinis E, Codacci-Pisanelli G (2015) Epigenetic treatment of solid tumours: a review of clinical trials. Clin Epigenet 7(1):127
Mann J (2002) Natural products in cancer chemotherapy: past, present and future. Nat Rev Cancer 2(2):143–148
Rajesh E, Sankari LS, Malathi L, Krupaa JR (2015) Naturally occurring products in cancer therapy. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 7(Suppl 1):S181–S183
Cherblanc FL, Davidson RWM, Di Fruscia P, Srimongkolpithak N, Fuchter MJ (2013) Perspectives on natural product epigenetic modulators in chemical biology and medicine. Nat Prod Rep 30(5):605
Suzuki T, Miyata N (2006) Epigenetic control using natural products and synthetic molecules. Curr Med Chem 13(8):935–958
Herman JG, Baylin SB (2003) Gene silencing in cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med 349(21):2042–2054
Esteller M (2007) Cancer epigenomics: DNA methylomes and histone-modification maps. Nat Rev Genet 8(4):286–298
Boehm T, Folkman J, Browder T, O’Reilly MS (1997) Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature 390(6658):404–407
Griffioen AW, Molema G (2000) Angiogenesis: potentials for pharmacologic intervention in the treatment of cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and chronic inflammation. Pharmacol Rev 52(2):237–268
Bergers G, Hanahan D (2008) Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 8(8):592–603
van Beijnum JR, Nowak-Sliwinska P, Huijbers EJM, Thijssen VL, Griffioen AW (2015) The great escape; the hallmarks of resistance to antiangiogenic therapy. Pharmacol Rev 67(2):441–461
Huijbers EJM, van Beijnum JR, Thijssen VL, Sabrkhany S, Nowak-Sliwinska P, Griffioen AW (2016) Role of the tumor stroma in resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Drug Resist Updates 25:26–37
Bani MR, Decio A, Giavazzi R, Ghilardi C (2017) Contribution of tumor endothelial cells to drug resistance: anti-angiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitors act as p-glycoprotein antagonists. Angiogenesis. doi:10.1007/s10456-017-9549-6
Chun P (2015) Histone deacetylase inhibitors in hematological malignancies and solid tumors. Arch Pharm Res 38(6):933–949
Hellebrekers DMEI, Melotte V, Viré E, Langenkamp E, Molema G, Fuks F, Herman JG, Van Criekinge W, Griffioen AW, Van Engeland M (2007) Identification of epigenetically silenced genes in tumor endothelial cells. Cancer Res 67(9):4138–4148
Pazin MJ, Kadonaga JT (1997) What’s up and down with histone deacetylation and transcription? Cell 89(3):325–328
Gu W, Roeder RG (1997) Activation of p53 sequence-specific DNA binding by acetylation of the p53 C-terminal domain. Cell 90(4):595–606
Zhang W, Bieker JJ (1998) Acetylation and modulation of erythroid Kruppel-like factor (EKLF) activity by interaction with histone acetyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(17):9855–9860
Dokmanovic M, Clarke C, Marks PA (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: overview and perspectives. Mol Cancer Res 5(10):981–989
Mottet D, Bellahcène A, Pirotte S, Waltregny D, Deroanne C, Lamour V, Lidereau R, Castronovo V (2007) Histone deacetylase 7 silencing alters endothelial cell migration, a key step in angiogenesis. Circ Res 101(12):1237–1246
Gallinari P, Di Marco S, Jones P, Pallaoro M, Steinkühler C (2007) HDACs, histone deacetylation and gene transcription: from molecular biology to cancer therapeutics. Cell Res 17(3):195–211
Fath DM, Kong X, Liang D, Lin Z, Chou A, Jiang Y, Fang J, Caro J, Sang N (2006) Histone deacetylase inhibitors repress the transactivation potential of hypoxia-inducible factors independently of direct acetylation of HIF-alpha. J Biol Chem 281(19):13612–13619
Semenza GL (2010) Defining the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics. Oncogene 29(5):625–634
Verheul HMW, Salumbides B, Van Erp K, Hammers H, Qian DZ, Sanni T, Atadja P, Pili R (2008) Combination strategy targeting the hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha with mammalian target of rapamycin and histone deacetylase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 14(11):3589–3597
Kim DH, Kim M, Kwon HJ (2003) Histone deacetylase in carcinogenesis and its inhibitors as anti-cancer agents. J Biochem Mol Biol 36(1):110–119
Kim MS, Kwon HJ, Lee YM, Baek JH, Jang JE, Lee SWK, Moon EJ, Kim HS, Lee SWK, Chung HY, Kim CW, Kim KW (2001) Histone deacetylases induce angiogenesis by negative regulation of tumor suppressor genes. Nat Med 7(4):437–443
Michaelis M, Suhan T, Cinatl J, Driever PH, Cinatl J (2004) Valproic acid and interferon-alpha synergistically inhibit neuroblastoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol 25(6):1795–1799
Michaelis M, Michaelis UR, Fleming I, Suhan T, Cinatl JJ, Blaheta RA, Hoffmann K, Kotchetkov R, Busse R, Nau H, Cinatl JJ (2004) Valproic acid inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Mol Pharmacol 65(3):520–527
Ellis L, Hammers H, Pili R (2009) Targeting tumor angiogenesis with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Lett 280(2):145–153
Kong X, Lin Z, Liang D, Fath D (2006) Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce VHL and ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Mol Cell Biol 26(6):2019–2028
Hellebrekers DMEI et al (2006) Epigenetic regulation of tumor endothelial cell anergy: silencing of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 by histone modifications. Cancer Res 66(22):10770–10777
Srivastava RK, Kurzrock R, Shankar S (2010) MS-275 sensitizes TRAIL-resistant breast cancer cells, inhibits angiogenesis and metastasis, and reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 9(12):3254–3266
Mie Lee Y, Kim S-H, Kim H-S, Jin Son M, Nakajima H, Jeong Kwon H, Kim K-W (2003) Inhibition of hypoxia-induced angiogenesis by FK228, a specific histone deacetylase inhibitor, via suppression of HIF-1alpha activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 300(1):241–246
Vieira-Coimbra M, Henrique R, Jeronimo C (2015) New insights on chromatin modifiers and histone post-translational modifications in renal cell tumours. Eur J Clin Invest 45:16–24
Chang S, Young BD, Li S, Qi X, Richardson JA, Olson EN (2006) Histone deacetylase 7 maintains vascular integrity by repressing matrix metalloproteinase 10. Cell 126(2):321–334
Kato H, Tamamizu-Kato S, Shibasaki F (2004) Histone deacetylase 7 associates with hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and increases transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 279(40):41966–41974
Kaluza D, Kroll J, Gesierich S, Manavski Y, Boeckel J-N, Doebele C, Zelent A, Rossig L, Zeiher AM, Augustin HG, Urbich C, Dimmeler S (2013) Histone deacetylase 9 promotes angiogenesis by targeting the antiangiogenic microRNA-17-92 cluster in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(3):533–543
Kaluza D, Kroll J, Gesierich S, Yao T-P, Boon RA, Hergenreider E, Tjwa M, Rossig L, Seto E, Augustin HG, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S, Urbich C (2011) Class IIb HDAC6 regulates endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis by deacetylation of cortactin. EMBO J 30(20):4142–4156
Hrgovic I, Doll M, Pinter A, Kaufmann R, Kippenberger S, Meissner M (2017) Histone deacetylase inhibitors interfere with angiogenesis by decreasing endothelial VEGFR-2 protein half-life in part via a VE-cadherin-dependent mechanism. Exp Dermatol 26(2):194–201
Calera MR, Venkatakrishnan A, Kazlauskas A (2004) VE-cadherin increases the half-life of VEGF receptor 2. Exp Cell Res 300(1):248–256
Hakami NY, Dusting GJ, Peshavariya HM (2016) Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor suppresses NADPH Oxidase 4-Derived Redox Signalling and Angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med 20(10):1932–1944
Deroanne CF, Bonjean K, Servotte S, Devy L, Colige A, Clausse N, Blacher S, Verdin E, Foidart J-M, Nusgens BV, Castronovo V (2002) Histone deacetylases inhibitors as anti-angiogenic agents altering vascular endothelial growth factor signaling. Oncogene 21(3):427–436
Qian DZ, Wang X, Kachhap SK, Kato Y, Wei Y, Zhang L, Atadja P, Pili R (2004) The histone deacetylase inhibitor NVP-LAQ824 Inhibits angiogenesis and has a greater antitumor effect in combination with the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584. Cancer Res 64(18):6626–6634
Potente M, Dimmeler S (2008) Emerging roles of SIRT1 in vascular endothelial homeostasis. Cell Cycle 7(14):2117–2122
Saunders LR, Verdin E (2007) Sirtuins: critical regulators at the crossroads between cancer and aging. Oncogene 26(37):5489–5504
Lappas M (2012) Anti-inflammatory properties of sirtuin 6 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mediat Inflamm 2012:597514
Zhang Q-J, Wang Z, Chen H-Z, Zhou S, Zheng W, Liu G, Wei Y-S, Cai H, Liu D-P, Liang C-C (2008) Endothelium-specific overexpression of class III deacetylase SIRT1 decreases atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Cardiovasc Res 80(2):191–199
Safe S, Kasiappan R (2016) Natural products as mechanism-based anticancer agents: Sp transcription factors as targets. Phyther Res 30(11):1723–1732
Gerhauser C (2013) Cancer chemoprevention and nutri-epigenetics: state of the art and future challenges. Top Curr Chem 11(1):73–132
Sagar SM, Yance D, Wong RK (2006) Natural health products that inhibit angiogenesis: a potential source for investigational new agents to treat cancer—part 2. Curr Oncol 13(3):14–26
Dhar S, Kumar A, Li K, Tzivion G, Levenson AS (2015) Resveratrol regulates PTEN/Akt pathway through inhibition of MTA1/HDAC unit of the NuRD complex in prostate cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1853(2):265–275
Saenglee S, Jogloy S, Patanothai A, Leid M, Senawong T (2016) Cytotoxic effects of peanut phenolics possessing histone deacetylase inhibitory activity in breast and cervical cancer cell lines. Pharmacol Rep 68(6):1102–1110
Tseng SH, Lin SM, Chen JC, Su YH, Huang HY, Chen CK, Lin PY, Chen Y (2004) Resveratrol suppresses the angiogenesis and tumor growth of gliomas in rats. Clin Cancer Res 10(6):2190–2202
Raina K, Kumar S, Dhar D, Agarwal R (2016) Silibinin and colorectal cancer chemoprevention: a comprehensive review on mechanisms and efficacy. J Biomed Res 30(6):452–465
Deep G, Kumar R, Nambiar DK, Jain AK, Ramteke AM, Serkova NJ, Agarwal C, Agarwal R (2016) Silibinin inhibits hypoxia-induced HIF-1α–mediated signaling, angiogenesis and lipogenesis in prostate cancer cells: in vitro evidence and in vivo functional imaging and metabolomics. Mol Carcinog 56(3):833–848
Jiang C, Agarwal R, Lü J (2000) Anti-angiogenic potential of a cancer chemopreventive flavonoid antioxidant, silymarin: inhibition of key attributes of vascular endothelial cells and angiogenic cytokine secretion by cancer epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 276(1):371–378
Singh RP, Sharma G, Dhanalakshmi S, Agarwal C, Agarwal R (2003) Suppression of advanced human prostate tumor growth in athymic mice by silibinin feeding is associated with reduced cell proliferation, increased apoptosis, and inhibition of angiogenesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 12(9):933–939
Singh T, Prasad R, Katiyar SK (2016) Therapeutic intervention of silymarin on the migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells is associated with the axis of multiple molecular targets including class 1 HDACs, ZEB1 expression, and restoration of miR-203 and E-cadherin expression. Am J Cancer Res 6(6):1287–1301
Laird PW, Jaenisch R (1996) The role of DNA methylation in cancer genetics and epigenetics. Annu Rev Genet 30(1):441–464
Watt F, Molloy PL (1988) Cytosine methylation prevents binding to DNA of a HeLa cell transcription factor required for optimal expression of the adenovirus major late promoter. Genes Dev 2(9):1136–1143
Hendrich B, Bird A (1998) Identification and characterization of a family of mammalian methyl-CpG binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol 18(11):6538–6547
Boyes J, Bird A (1991) DNA methylation inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein. Cell 64(6):1123–1134
Bird A, Nan X, Ng H-H, Johnson CA, Laherty CD, Turner BM, Eisenman RN (1998) Transcriptional repression by the methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 involves a histone deacetylase complex. Nature 393(6683):386–389
Okano M, Xie S, Li E (1998) Cloning and characterization of a family of novel mammalian DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferases. Nat Am Inc 19(3):219–220
Okano M, Bell DW, Haber DA, Li E (1999) DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell 99(3):247–257
Beard C, Li E, Jaenisch R (1995) Loss of methylation activates Xist in somatic but not in embryonic cells. Genes Dev 9(19):2325–2334
Bestor TH (1992) Activation of mammalian DNA methyltransferase by cleavage of a Zn binding regulatory domain. EMBO J 11(7):2611–2617
Li E, Bestor TH, Jaenisch R (1992) Targeted mutation of the DNA methyltransferase gene results in embryonic lethality. Cell 69(6):915–926
Matouk CC, Marsden PA (2008) Epigenetic regulation of vascular endothelial gene expression. Circ Res 102(8):873–878
Şahin M, Şahin E, Gümüşlü S, Erdoǧan A, Gültekin M (2010) DNA methylation or histone modification status in metastasis and angiogenesis-related genes: a new hypothesis on usage of DNMT inhibitors and S-adenosylmethionine for genome stability. Cancer Metastasis Rev 29(4):655–676
Guo W, Dong Z, He M, Guo Y, Guo J, Chen Z, Yang Z, Kuang G (2010) Aberrant methylation of thrombospondin-1 and its association with reduced expression in gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. J Biomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1155/2010/721485
Zhang Y, Wang X, Xu B, Wang B, Wang Z, Liang Y, Zhou J, Hu J, Jiang B (2013) Epigenetic silencing of miR-126 contributes to tumor invasion and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 30(4):1976–1984
Chan SL, Cui Y, van Hasselt A, Li H, Srivastava G, Jin H, Ng KM, Wang Y, Lee KY, Tsao GSW, Zhong S, Robertson KD, Rha SY, Chan ATC, Tao Q (2007) The tumor suppressor Wnt inhibitory factor 1 is frequently methylated in nasopharyngeal and esophageal carcinomas. Lab Investig 87(7):644–650
Bo BL, Eun JL, Eun HJ, Chun HK, Dong KC, Sang YS, Park J, Kim DH (2009) Aberrant methylation of APC, MGMT, RASSF2A, and Wif-1 genes in plasma as a biomarker for early detection of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15(19):6185–6191
Veeck J, Wild PJ, Fuchs T, Schüffler PJ, Hartmann A, Knüchel R, Dahl E (2009) Prognostic relevance of Wnt-inhibitory factor-1 (WIF1) and Dickkopf-3 (DKK3) promoter methylation in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-217
Lee SM, Park JY, Kim DS (2013) Wif1 hypermethylation as unfavorable prognosis of non-small cell lung cancers with EGFR mutation. Mol Cells 36(1):69–73
Lambiv WL, Vassallo I, Delorenzi M, Shay T, Diserens AC, Misra A, Feuerstein B, Murat A, Migliavacca E, Hamou MF, Sciuscio D, Burger R, Domany E, Stupp R, Hegi ME (2011) The Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF1) is targeted in glioblastoma and has a tumor suppressing function potentially by induction of senescence. Neuro Oncol 13(7):736–747
Skurk C, Maatz H, Rocnik E, Bialik A, Force T, Walsh K (2005) Glycogen-synthase kinase3beta/beta-catenin axis promotes angiogenesis through activation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in endothelial cells. Circ Res 96(3):308–318
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 473(7347):298–307
Ramachandran I, Thavathiru E, Ramalingam S, Natarajan G, Mills WK, Benbrook DM, Zuna R, Lightfoot S, Reis A, Anant S, Queimado L (2012) Wnt inhibitory factor 1 induces apoptosis and inhibits cervical cancer growth, invasion and angiogenesis in vivo. Oncogene 31(22):2725–2737
Saito Y, Friedman JM, Chihara Y, Egger G, Chuang JC, Liang G (2009) Epigenetic therapy upregulates the tumor suppressor microRNA-126 and its host gene EGFL7 in human cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379(3):726–731
van Beijnum JR, Giovannetti E, Poel D, Nowak-Sliwinska P, Griffioen AW (2017) miRNAs: micro-managers of anti-cancer combination therapies. Angiogenesis. doi:10.1007/s10456-017-9545-x
Lindner DJ, Wu Y, Haney R, Jacobs BS, Fruehauf JP, Tuthill R, Borden EC (2013) Thrombospondin-1 expression in melanoma is blocked by methylation and targeted reversal by 5-Aza-deoxycytidine suppresses angiogenesis. Matrix Biol 32(2):123–132
Mirochnik Y, Kwiatek A, Volpert O (2008) Thrombospondin and apoptosis: molecular mechanisms and use for design of complementation treatments. Curr Drug Targets 9(10):851–862
Jueliger S, Lyons J, Cannito S, Pata I, Pata P, Shkolnaya M, Lo Re O, Peyrou M, Villarroya F, Pazienza V, Rappa F, Cappello F, Azab M, Taverna P, Vinciguerra M (2016) Efficacy and epigenetic interactions of novel DNA hypomethylating agent guadecitabine (SGI-110) in preclinical models of hepatocellular carcinoma. Epigenetics 11(10):709–720
Shih YP, Liao YC, Lin Y, Lo SH (2010) DLC1 negatively regulates angiogenesis in a paracrine fashion. Cancer Res 70(21):8270–8275
Griffioen AW (2008) Anti-angiogenesis: making the tumor vulnerable to the immune system. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57(10):1553–1558
Hellebrekers DMEI, Jair K-W, Viré E, Eguchi S, Hoebers NTH, Fraga MF, Esteller M, Fuks F, Baylin SB, van Engeland M, Griffioen AW (2006) Angiostatic activity of DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther 5(2):467–475
Alexius-Lindgren M, Andersson E, Lindstedt I, Engström W (2014) The RECK gene and biological malignancy-its significance in angiogenesis and inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases. Anticancer Res 34(8):3867–3874
Shian S-G, Kao Y-R, Wu FY-H, Wu C-W (2003) Inhibition of invasion and angiogenesis by zinc-chelating agent disulfiram. Mol Pharmacol 64(5):1076–1084
Murai R, Yoshida Y, Muraguchi T, Nishimoto E, Morioka Y, Kitayama H, Kondoh S, Kawazoe Y, Hiraoka M, Uesugi M, Noda M (2010) A novel screen using the Reck tumor suppressor gene promoter detects both conventional and metastasis-suppressing anticancer drugs. Oncotarget 1(4):252–264
Graça I, Sousa EJ, Costa-Pinheiro P, Vieira FQ, Torres-Ferreira J, Martins MG, Henrique R, Jerónimo C (2014) Anti-neoplastic properties of hydralazine in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 5(15):5950–5964
Chavez-Blanco A, Perez-Plasencia C, Perez-Cardenas E, Carrasco-Legleu C, Rangel-Lopez E, Segura-Pacheco B, Taja-Chayeb L, Trejo-Becerril C, Gonzalez-Fierro A, Candelaria M, Cabrera G, Duenas-Gonzalez A (2006) Antineoplastic effects of the DNA methylation inhibitor hydralazine and the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid in cancer cell lines. Cancer Cell Int. doi:10.1186/1475-2867-6-2
Zhang Q, Lin Z, Yin X, Tang L, Luo H, Li H, Zhang Y, Luo W (2016) In vitro and in vivo study of hydralazine, a potential anti-angiogenic agent. Eur J Pharmacol 779:138–146
Li X, Feng Y, Liu J, Feng X, Zhou K, Tang X (2013) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits IGF-I-stimulated lung cancer angiogenesis through downregulation of HIF-1α and VEGF expression. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenom 6(3):169–178
Sakamoto Y, Terashita N, Muraguchi T, Fukusato T, Kubota S (2013) Effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on A549 lung cancer tumor growth and angiogenesis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77(9):1799–1803
Gu J, Makey KL, Tucker KB, Chinchar E, Mao X, Pei I, Thomas EY, Miele L (2013) EGCG, a major green tea catechin suppresses breast tumor angiogenesis and growth via inhibiting the activation of HIF-1alpha and NFkappaB, and VEGF expression. Vasc Cell 5(1):9
Kato K, Long NK, Makita H, Toida M, Yamashita T, Hatakeyama D, Hara A, Mori H, Shibata T (2008) Effects of green tea polyphenol on methylation status of RECK gene and cancer cell invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer 99(4):647–654
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P, Aggarwal BB (2008) Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett 269(2):199–225
Arbiser JL, Klauber N, Rohan R, van Leeuwen R, Huang MT, Fisher C, Flynn E, Byers HR (1998) Curcumin is an in vivo inhibitor of angiogenesis. Mol Med 4(6):376–383
Du L, Xie Z, Wu LC, Chiu M, Lin J, Chan KK, Liu S, Liu Z (2012) Reactivation of RASSF1A in breast cancer cells by curcumin. Nutr Cancer Int J 64(8):1228–1235
Mirza S, Sharma G, Parshad R, Gupta SD, Pandya P, Ralhan R (2013) Expression of DNA methyltransferases in breast cancer patients and to analyze the effect of natural compounds on DNA methyltransferases and associated proteins. J Breast Cancer 16(1):23–31
Teiten MH, Dicato M, Diederich M (2013) Curcumin as a regulator of epigenetic events. Mol Nutr Food Res 57(9):1619–1629
Alexandrow MG, Song LJ, Altiok S, Gray J, Haura EB, Kumar NB (2012) Curcumin: a novel Stat3 pathway inhibitor for chemoprevention of lung cancer. Eur J Cancer Prev 21(5):407–412
Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, Song L, Haura E, Turkson J, Zhang S, Wang T, Sinibaldi D, Coppola D, Heller R, Ellis LM, Karras J, Bromberg J, Pardoll D, Jove R, Yu H (2002) Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 21(13):2000–2008
Wei D, Le X, Zheng L, Wang L, Frey JA, Gao AC, Peng Z, Huang S, Xiong HQ, Abbruzzese JL, Xie K (2003) Stat3 activation regulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and human pancreatic cancer angiogenesis and metastasis. Oncogene 22(3):319–329
Lee H, Zhang P, Herrmann A, Yang C, Xin H, Wang Z, Hoon DSB, Forman SJ, Jove R, Riggs AD, Yu H (2012) Acetylated STAT3 is crucial for methylation of tumor-suppressor gene promoters and inhibition by resveratrol results in demethylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(20):7765–7769
Huang L, Hu B, Ni J, Wu J, Jiang W, Chen C, Yang L, Zeng Y, Wan R, Hu G, Wang X (2016) Transcriptional repression of SOCS3 mediated by IL-6/STAT3 signaling via DNMT1 promotes pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35(1):27
Stahl A, Joyal JS, Chen J, Sapieha P, Juan AM, Hatton CJ, Pei DT, Hurst CG, Seaward MR, Krah NM, Dennison RJ, Greene ER, Boscolo E, Panigrahy D, Smith LEH (2012) SOCS3 is an endogenous inhibitor of pathologic angiogenesis. Blood 120(14):2925–2929
Dhillon N, Aggarwal BB, Newman RA, Wolff RA, Kunnumakkara AB, Abbruzzese JL, Ng CS, Badmaev V, Kurzrock R (2008) Phase II trial of curcumin in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(14):4491–4499
Licona C, Spaety M-E, Capuozzo A, Ali M, Santamaria R, Armant O, Delalande F, Van Dorsselaer A, Cianferani S, Spencer J, Pfeffer M, Mellitzer G, Gaiddon C (2017) A ruthenium anticancer compound interacts with histones and impacts differently on epigenetic and death pathways compared to cisplatin. Oncotarget 8(2):2568–2584
Nazarov AA, Baquié M, Nowak-Sliwinska P, Zava O, van Beijnum JR, Groessl M, Chisholm DM, Ahmadi Z, McIndoe JS, Griffioen AW, van den Bergh H, Dyson PJ (2013) Synthesis and characterization of a new class of anti-angiogenic agents based on ruthenium clusters. Sci Rep 3:1485
Clavel CM, Păunescu E, Nowak-Sliwinska P, Griffioen AW, Scopelliti R, Dyson PJ (2014) Discovery of a highly tumor-selective organometallic ruthenium(II)-arene complex. J Med Chem 57(8):3546–3558
Allardyce CS, Dyson PJ (2016) Metal-based drugs that break the rules. Dalton Trans 45(8):3201–3209
Singh V, Azad GK, Mandal P, Amarendar Reddy M, Tomar RS (2014) Anti-cancer drug KP1019 modulates epigenetics and induces DNA damage response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 588(6):1044–1052
Leijen S, Burgers SA, Baas P, Pluim D, Tibben M, Van Werkhoven E, Alessio E, Sava G, Beijnen JH, Schellens JHM (2015) Phase I/II study with ruthenium compound NAMI-A and gemcitabine in patients with non-small cell lung cancer after first line therapy. Investig New Drugs 33(1):201–214
Rademaker-Lakhai JM, Van Den Bongard D, Pluim D, Beijnen JH, Schellens JHM (2004) A phase I and pharmacological study with imidazolium-trans-DMSO-imidazole-tetrachlororuthenate, a novel ruthenium anticancer agent. Clin Cancer Res 10:3717–3727
Hartinger CG, Jakupec MA, Zorbas-Seifried S, Groessl M, Egger A, Berger W, Zorbas H, Dyson PJ, Keppler BK (2008) KP1019, a new redox-active anticancer agent—preclinical development and results of a clinical phase I study in tumor patients. Chem Biodivers 5(10):2140–2155
Trondl R, Heffeter P, Kowol CR, Jakupec MA, Berger W, Keppler BK (2014) NKP-1339, the first ruthenium-based anticancer drug on the edge to clinical application. Chem Sci 5(8):2925
Morbidelli L, Donnini S, Filippi S, Messori L, Piccioli F, Orioli P, Sava G, Ziche M (2003) Antiangiogenic properties of selected ruthenium(III) complexes that are nitric oxide scavengers. Br J Cancer 88(9):1484–1491
Pintus G, Tadolini B, Posadino AM, Sanna B, Debidda M, Bennardini F, Sava G, Ventura C (2002) Inhibition of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway by the novel antimetastatic agent NAMI-A down regulates c-myc gene expression and endothelial cell proliferation. Eur J Biochem 269(23):5861–5870
Vacca A, Bruno M, Boccarelli A, Coluccia M, Ribatti D, Bergamo A, Garbisa S, Sartor L, Sava G (2002) Inhibition of endothelial cell functions and of angiogenesis by the metastasis inhibitor NAMI-A. Br J Cancer 86(6):993–998
Hartinger CG, Dyson PJ (2009) Bioorganometallic chemistry–from teaching paradigms to medicinal applications. Chem Soc Rev 38(2):391–401
Smith GS, Therrien B (2011) Targeted and multifunctional arene ruthenium chemotherapeutics. Dalton Trans 40(41):10793
Süss-Fink G (2014) Water-soluble arene ruthenium complexes: from serendipity to catalysis and drug design. J Organomet Chem 751:2–19
Murray BS, Babak MV, Hartinger CG, Dyson PJ (2016) The development of RAPTA compounds for the treatment of tumors. Coord Chem Rev 306:86–114
Scolaro C, Bergamo A, Brescacin L, Delfino R, Cocchietto M, Laurenczy G, Geldbach TJ, Sava G, Dyson PJ (2005) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ruthenium(II)-arene PTA complexes. J Med Chem 48:4161–4171
Weiss A, Berndsen RH, Dubois M, Müller C, Schibli R, Griffioen AW, Dyson PJ, Nowak-Sliwinska P (2014) In vivo anti-tumor activity of the organometallic ruthenium(II)-arene complex [Ru(η6-p-cymene)Cl2 (pta)] (RAPTA-C) in human ovarian and colorectal carcinomas. Chem Sci 5(12):4742–4748
Nowak-Sliwinska P, Van Beijnum JR, Casini A, Nazarov AA, Wagnieres G, Van Den Bergh H, Dyson PJ, Griffioen AW (2011) Organometallic ruthenium(II) arene compounds with antiangiogenic activity. J Med Chem 54(11):3895–3902
Shoemaker RH (2006) The NCI60 human tumour cell line anticancer drug screen. Nat Rev Cancer 6(10):813–823
Adhireksan Z, Davey GE, Campomanes P, Groessl M, Clavel CM, Yu H, Nazarov AA, Yeo CHF, Ang WH, Dröge P, Rothlisberger U, Dyson PJ, Davey CA (2014) Ligand substitutions between ruthenium-cymene compounds can control protein versus DNA targeting and anticancer activity. Nat Commun 5:3462
Nowak-Sliwinska P, Segura T, Iruela-Arispe ML (2014) The chicken chorioallantoic membrane model in biology, medicine and bioengineering. Angiogenesis 4:779–804
Lee RFS, Escrig S, Croisier M, Clerc-Rosset S, Knott GW, Meibom A, Davey CA, Johnsson K, Dyson PJ (2015) NanoSIMS analysis of an isotopically labelled organometallic ruthenium(II) drug to probe its distribution and state in vitro. Chem Commun (Camb) 51(92):16486–16489
Wu B, Ong MS, Groessl M, Adhireksan Z, Hartinger CG, Dyson PJ, Davey CA (2011) A ruthenium antimetastasis agent forms specific histone protein adducts in the nucleosome core. Chemistry 17(13):3562–3566
Adhireksan Z, Palermo G, Riedel T, Ma Z, Muhammad R, Röthlisberger U, Dyson PJ, Davey CA (2017) Allosteric cross-talk in chromatin can mediate drug-drug synergy. Nat Commun. doi:10.1038/ncomms14860
Weiss A, Nowak-Sliwinska P (2016) Current trends in multidrug optimization. J Lab Autom. doi:10.1177/2211068216682338
Nowak-Sliwinska P, Weiss A, Ding X, Dyson PJ, van den Bergh H, Griffioen AW, Ho C-M (2016) Optimization of drug combinations using feedback system control. Nat Protoc 11(2):302–315. doi:10.1177/2472630316682338
Weiss A, Ding X, van Beijnum JR, Wong I, Wong TJ, Berndsen RH, Dormond O, Dallinga M, Shen L, Schlingemann RO, Pili R, Ho C-M, Dyson PJ, van den Bergh H, Griffioen AW, Nowak-Sliwinska P (2015) Rapid optimization of drug combinations for the optimal angiostatic treatment of cancer. Angiogenesis 18(3):233–244
Oronsky BT, Oronsky AL, Lybeck M, Oronsky NC, Scicinski JJ, Carter C, Day RM, Rodriguez Orengo JF, Rodriguez-Torres M, Fanger GF, Reid TR (2015) Episensitization: defying time’s arrow. Front Oncol. doi:10.3389/fonc.2015.00134
Spencer J, Amin J, Wang M, Packham G, Alwi SSS, Tizzard GJ, Coles SJ, Paranal RM, Bradner JE, Heightman TD (2011) Synthesis and biological evaluation of JAHAs: ferrocene-based histone deacetylase inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett 2(5):358–362
Librizzi M, Longo A, Chiarelli R, Amin J, Spencer J, Luparello C (2012) Cytotoxic effects of Jay Amin hydroxamic acid (JAHA), a ferrocene-based class i histone deacetylase inhibitor, on triple-negative MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells. Chem Res Toxicol 25(11):2608–2616
Beisel C, Paro R (2011) Silencing chromatin: comparing modes and mechanisms. Nat Rev Genet 12(2):123–135
Robertson KD, Ait-Si-Ali S, Yokochi T, Wade PA, Jones PL, Wolffe AP (2000) DNMT1 forms a complex with Rb, E2F1 and HDAC1 and represses transcription from E2F-responsive promoters. Nat Genet 25(3):338–342
Rountree MR, Bachman KE, Baylin SB (2000) DNMT1 binds HDAC2 and a new co-repressor, DMAP1, to form a complex at replication foci. Nat Genet 25(3):269–277
Shiva Shankar TV, Willems L (2014) Epigenetic modulators mitigate angiogenesis through a complex transcriptomic network. Vasc Pharmacol 60(2):57–66
Chen WY, Townes TM (2000) Molecular mechanism for silencing virally transduced genes involves histone deacetylation and chromatin condensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(1):377–382
Liu X, Luo M, Wu K (2012) Epigenetic interplay of histone modifications and DNA methylation mediated by HDA6. Plant Signal Behav 7(6):633–635
Bachman KE, Park BH, Rhee I, Rajagopalan H, Herman JG, Baylin SB, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (2003) Histone modifications and silencing prior to DNA methylation of a tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Cell 3(1):89–95
Selker EU (1998) Trichostatin A causes selective loss of DNA methylation in Neurospora. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(16):9430–9435
Zhou Q, Agoston AT, Atadja P, Nelson WG, Davidson NE (2008) Inhibition of histone deacetylases promotes ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of DNA methyltransferase 1 in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 6(5):873–883
Vaissière T, Sawan C, Herceg Z (2008) Epigenetic interplay between histone modifications and DNA methylation in gene silencing. Mutat Res 659(1–2):40–48
Cedar H, Bergman Y (2009) Linking DNA methylation and histone modification: patterns and paradigms. Nat Rev Genet 10(5):295–304
Lyu T, Jia N, Wang J, Yan X, Yu Y, Lu Z, Bast RC, Hua K, Feng W (2013) Expression and epigenetic regulation of angiogenesis-related factors during dormancy and recurrent growth of ovarian carcinoma. Epigenetics 8(12):1330–1346
Gros C, Fahy J, Halby L, Dufau I, Erdmann A, Gregoire JM, Ausseil F, Vispé S, Arimondo PB (2012) DNA methylation inhibitors in cancer: recent and future approaches. Biochimie 94(11):2280–2296
Cameron EE, Bachman KE, Myohanen S, Herman JG, Baylin SB (1999) Synergy of demethylation and histone deacetylase inhibition in the re-expression of genes silenced in cancer. Nat Genet 21(1):103–107
Zhang J, Lu A, Li L, Yue J, Lu Y (2010) p16 Modulates VEGF expression via its interaction with HIF-1alpha in breast cancer cells. Cancer Invest 28(6):588–597
Miki K, Shimizu E, Yano S, Tani K, Sone S (2001) Demethylation by 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-azadC) of p16INK4A gene results in downregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human lung cancer cell lines. Oncol Res 12(8):335–342
Anand-Apte B, Bao L, Smith R, Iwata K, Olsen BR, Zetter B, Apte SS (1996) A review of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP-3) and experimental analysis of its effect on primary tumor growth. Biochem Cell Biol 74(6):853–862
Qi JH, Ebrahem Q, Moore N, Murphy G, Claesson-Welsh L, Bond M, Baker A, Anand-Apte B (2003) A novel function for tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP3): inhibition of angiogenesis by blockage of VEGF binding to VEGF receptor-2. Nat Med 9(4):407–415
Suzuki M, Shinohara F, Rikiishi H (2008) Zebularine-induced reduction in VEGF secretion by HIF-1α degradation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep 1(4):465–471
Cecconi D, Donadelli M, Pozza ED, Rinalducci S, Zolla L, Scupoli MT, Righetti PG, Scarpa A, Palmieri M (2009) Synergistic effect of trichostatin A and 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine on growth inhibition of pancreatic endocrine tumour cell lines: a proteomic study. Proteomics 9(7):1952–1966
Shaker S, Bernstein M, Momparler LF, Momparler RL (2003) Preclinical evaluation of antineoplastic activity of inhibitors of DNA methylation (5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine) and histone deacetylation (trichostatin A, depsipeptide) in combination against myeloid leukemic cells. Leuk Res 27(5):437–444
Griffiths EA, Gore SD (2008) DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes. Semin Hematol 45(1):23–30
Kirschbaum MH, Foon KA, Frankel P, Ruel C, Pulone B, Tuscano JM, Newman EM (2014) A phase 2 study of belinostat (PXD101) in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia or patients over the age of 60 with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia: a California Cancer Consortium Study. Leuk Lymphoma 55(10):2301–2304
Gore SD et al (2006) Combined DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibition in the treatment of myeloid neoplasms. Cancer Res 66(12):6361–6369
Voso MT et al (2009) Valproic acid at therapeutic plasma levels may increase 5-azacytidine efficacy in higher risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Clin Cancer Res 15(15):5002–5007
Fandy TE et al (2009) Early epigenetic changes and DNA damage do not predict clinical response in an overlapping schedule of 5-azacytidine and entinostat in patients with myeloid malignancies. Blood 114(13):2764–2773
Gryder BE, Sodji QH, Oyelere Adegboyega K (2012) Targeted cancer therapy: giving histone deacetylase inhibitors all they need to succeed. Futur Med Chem 4(4):505–524
Kato Y, Yoshimura K, Shin T, Verheul H, Hammers H, Sanni TB, Salumbides BC, Van Erp K, Schulick R, Pili R (2007) Synergistic in vivo antitumor effect of the histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 in combination with interleukin 2 in a murine model of renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13(15):4538–4546
Shen L, Ciesielski M, Ramakrishnan S, Miles KM, Ellis L, Sotomayor P, Shrikant P, Fenstermaker R, Pili R (2012) Class I histone deacetylase inhibitor entinostat suppresses regulatory T cells and enhances immunotherapies in renal and prostate cancer models. PLoS ONE 7(1):e30815
Pili R, Salumbides B, Zhao M, Altiok S, Qian D, Zwiebel J, Carducci MA, Rudek MA (2012) Phase I study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor entinostat in combination with 13-cis retinoic acid in patients with solid tumours. Br J Cancer 106(1):77–84
Smits KM, Melotte V, Niessen HEC, Dubois L, Oberije C, Troost EGC, Starmans MHW, Boutros PC, Vooijs M, van Engeland M, Lambin P (2014) Epigenetics in radiotherapy: where are we heading? Radiother Oncol 111(2):168–177
Wachowska M, Muchowicz A, Golab J (2015) Targeting epigenetic processes in photodynamic therapy-induced anticancer immunity. Front Oncol 5:176
Wang Z et al (2015) Broad targeting of angiogenesis for cancer prevention and therapy. Semin Cancer Biol 35(Suppl):S224–S243
Kuusk T, Grivas N, Bex A (2017) Antiangiogenic therapy combined with immune checkpoint blockade in renal cancer: a review. Angiogenesis. doi:10.1007/s10456-017-9550-0
Ramjiawan RR, Griffioen AW, Duda DG (2017) Anti-angiogenesis for cancer revisited: Is there a role for combinations with immunotherapy? Angiogenesis. doi:10.1007/s10456-017-9552-y
Hamming LC, Slotman BJ, Verheul HMW, Thijssen V (2017) The clinical application of angiostatic therapy in combination with radiotherapy: past, present, future. Angiogenesis. doi:10.1007/s10456-017-9546-9
Dameron KM, Volpert OV, Tainsky MA, Bouck N (1994) Control of angiogenesis in fibroblasts by p53 regulation of thrombospondin-1. Science 265(5178):1582–1584
Volpert OV, Tolsma SS, Pellerin S, Feige JJ, Chen H, Mosher DF, Bouck N (1995) Inhibition of angiogenesis by thrombospondin-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 217:326–332
Benjamin D, Colombi M, Moroni C, Hall MN (2011) Rapamycin passes the torch: a new generation of mTOR inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10(11):868–880
Heffeter P, Atil B, Kryeziu K, Groza D, Koellensperger G, Korner W, Jungwirth U, Mohr T, Keppler BK, Berger W (2013) The ruthenium compound KP1339 potentiates the anticancer activity of sorafenib in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Cancer 49:3366–3375
Kassouf E, Tehfe MA, Florescu M, Soulieres D, Lemieux B, Ayoub J-PM, Charpentier D, Yelle L, Daigneault L, Colin P, Momparler RL, Plante I, Lassonde G, Charbonneau MR, Raynal NJ-M, Blais N (2015) Phase I and II studies of the decitabine–genistein drug combination in advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 33(15_suppl):e13556
Puduvalli VK, Wu J, Yuan Y, Armstrong TS, Groves MD, Raizer JJ, Giglio P, Colman H, Peereboom DM, Walbert T, Avgeropoulos NG, Iwamoto FM, Chamberlain MC, Paleologos N, Gilbert MR (2015). Brain tumor trials collaborative bayesian adaptive Adaptive randomized phase II trial of bevacizumab plus vorinostat versus bevacizumab alone in adults with recurrent glioblastoma (BTTC-1102). J Clin Oncol 33:1
Stimson L, La Thangue NB (2009) Biomarkers for predicting clinical responses to HDAC inhibitors. Cancer Lett 280(2):177–183
Wheler JJ, Janku F, Falchook GS, Jackson TL, Fu S, Naing A, Tsimberidou AM, Moulder SL, Hong DS, Yang H, Piha-Paul SA, Atkins JT, Garcia-Manero G, Kurzrock R (2014) Phase I study of anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody bevacizumab and histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid in patients with advanced cancers. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73(3):495–501
Plumb JA, Strathdee G, Sludden J, Kaye SB, Brown R (2000) Reversal of drug resistance in human tumor xenografts by 2′-deoxy-5-azacytidine-induced demethylation of the hMLH1 gene promoter. Cancer Res 60(21):6039–6044
Wang L, Li H, Ren Y, Zou S, Fang W, Jiang X, Jia L, Li M, Liu X, Yuan X, Chen G, Yang J, Wu C (2016) Targeting HDAC with a novel inhibitor effectively reverses paclitaxel resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via multiple mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.328
Berndsen RH, Weiss A, Abdul UK, Wong TJ, Meraldi P, Griffioen AW, Dyson PJ, Nowak-Sliwinska P (2017) Combination of ruthenium(II)-arene complex [Ru(eta6-p-cymene)Cl2(pta)] (RAPTA-C) and the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib results in efficient angiostatic and antitumor activity. Sci Rep. doi:10.1038/srep43005
Yu C, Friday BB, Lai J-P, McCollum A, Atadja P, Roberts LR, Adjei AA (2007) Abrogation of MAPK and Akt signaling by AEE788 synergistically potentiates histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen species generation. Clin Cancer Res 13(4):1140–1148
Witta SE, Gemmill RM, Hirsch FR, Coldren CD, Hedman K, Ravdel L, Helfrich B, Dziadziuszko R, Chan DC, Sugita M, Chan Z, Baron A, Franklin W, Drabkin HA, Girard L, Gazdar AF, Minna JD, Bunn PA (2006) Restoring E-cadherin expression increases sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 66(2):944–950
Derksen PWB, Liu X, Saridin F, van der Gulden H, Zevenhoven J, Evers B, van Beijnum JR, Griffioen AW, Vink J, Krimpenfort P, Peterse JL, Cardiff RD, Berns A, Jonkers J (2006) Somatic inactivation of E-cadherin and p53 in mice leads to metastatic lobular mammary carcinoma through induction of anoikis resistance and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 10(5):437–449
Peinado H, Marin F, Cubillo E, Stark H-J, Fusenig N, Nieto MA, Cano A (2004) Snail and E47 repressors of E-cadherin induce distinct invasive and angiogenic properties in vivo. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 13):2827–2839
Chen M-C, Chen C-H, Wang J-C, Tsai A-C, Liou J-P, Pan S-L, Teng C-M (2013) The HDAC inhibitor, MPT0E028, enhances erlotinib-induced cell death in EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC cells. Cell Death Dis 4:e810
Lee T-G, Jeong E-H, Kim SY, Kim H-R, Kim CH (2015) The combination of irreversible EGFR TKIs and SAHA induces apoptosis and autophagy-mediated cell death to overcome acquired resistance in EGFR T790M-mutated lung cancer. Int J Cancer 136(11):2717–2729
Witta SE, Jotte RM, Konduri K, Neubauer MA, Spira AI, Ruxer RL, Varella-Garcia M, Bunn PA, Hirsch FR (2012) Randomized phase II trial of erlotinib with and without entinostat in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer who progressed on prior chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 30(18):2248–2255
Gray JE, Haura E, Chiappori A, Tanvetyanon T, Williams CC, Pinder-Schenck M, Kish JA, Kreahling J, Lush R, Neuger A, Tetteh L, Akar A, Zhao X, Schell MJ, Bepler G, Altiok S (2014) A phase i, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of panobinostat, an HDAC inhibitor, combined with erlotinib in patients with advanced aerodigestive tract tumors. Clin Cancer Res 20(6):1644–1655
Loges S, Schmidt T, Carmeliet P (2010) Mechanisms of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy and development of third-generation anti-angiogenic drug candidates. Genes Cancer 1(1):12–25
Wang Z et al (2015) Broad targeting of angiogenesis for cancer prevention and therapy. Semin Cancer Biol 35(Suppl):S224–S243
Ding X, Liu W, Weiss A, Li Y, Wong I, Griffioen AW, van den Bergh H, Xu H, Nowak-Sliwinska P, Ho C-M (2014) Discovery of a low order drug-cell response surface for applications in personalized medicine. Phys Biol 11(6):65003
Treps L, Conradi L-C, Harjes U, Carmeliet P (2016) Manipulating angiogenesis by targeting endothelial metabolism: hitting the engine rather than the drivers—a new perspective? Pharmacol Rev 68(3):872–887
Weiss A, Berndsen RH, Ding X, Ho C-M, Dyson PJ, van den Bergh H, Griffioen AW, Nowak-Sliwinska P (2015) A streamlined search technology for identification of synergistic drug combinations. Sci Rep 5:14508
Yang Q, Tian Y, Liu S, Zeine R, Chlenski A, Salwen HR, Henkin J, Cohn SL (2007) Thrombospondin-1 peptide ABT-510 combined with valproic acid is an effective antiangiogenesis strategy in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 67(4):1716–1724
Pili R, Kruszewski MP, Hager BW, Lantz J, Carducci MA (2001) Combination of phenylbutyrate and 13-cis retinoic acid inhibits prostate tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 61(4):1477–1485
Wang H, Zhou H, Zou Y, Liu Q, Guo C, Gao G, Shao C, Gong Y (2010) Resveratrol modulates angiogenesis through the GSK3β/β-catenin/TCF-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol 80(9):1386–1395
Acknowledgements
We thank the European Research Council (ERC-StG-2015-680209 to PNS) and the Dutch Cancer Society (VU2014-7234 to AWG and PNS) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berndsen, R.H., Abdul, U.K., Weiss, A. et al. Epigenetic approach for angiostatic therapy: promising combinations for cancer treatment. Angiogenesis 20, 245–267 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9551-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9551-z