Abstract
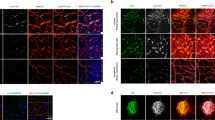
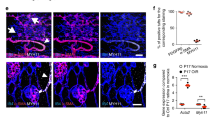
Apart from tumor-driven neovascularization, a less-appreciated consequence of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is the hyperproliferation of vascular mural cells (pericytes). This study aims at establishing a role for pericytes in NF1, and determining whether interference with the function of a key pericyte component (NG2 proteoglycan) inhibits NF1 tumor neovascularization. Neovascularization in NF1 was studied in Nf+/+(control), Nf1+/−, and Nf1−/−embryos at E-10, ischemia-induced retinal angiogenesis model in 24 eyes of Nf1+/−, Nf1+/+mice, and in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs) derived from NF1 patients (ST88-14, NMS-2PC) orthotopically grown in nude mice (Crl: nu/nu). The anti-angiogenic effect of intracorneal polymer pellets containing anti-NG2 neutralizing antibody was quantified in the nude-mouse corneal angiogenesis model in which angiogenesis was induced by xenografting NMS-2PC tumor into the corneal stroma of 22 eyes. By using confocal microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and BrdU proliferation assay, the pericyte/endothelium ratios and proliferation rates were measured. Activated pericytes were present at the leading tip of the angiogenic sprouts. Pericytes showed continuous investment of endothelium in both NMS-2PC and ST88-14 MPNST tumor xenografts. Mean corneal angiogenesis induced by NMS-2PC tumor grafts in NG2-antibody treated eyes was 1.491 and 3.186 mm 2 in isotype-matched non-immunoglobulin treated eyes (control) (P=0.0002). A total of 193.8 vascular nuclei (a measure of ischemia-induced retinal angiogenesis) was present in angiogenic retinal tufts in Nf1+/− mice compared to 89.23 in Nf1+/+ mice (control) (P < 0.0001). Mean pericyte/endothelium investment ratios were 1.015, 1.380, and 2.084 in control, Nf1+/−, and Nf1−/−embryos, respectively. Pericytes were 23% (control), 49% (Nf1+/−), and 69% (Nf1−/−) BrdU-positive. Endothelial cells from the same embryos were 29% (control), 47% (Nf1+/−), and 62% (Nf1−/−) BrdU-positive. Angiogenesis is accelerated in NF1 due to hyperproliferation of pericytes and endothelial cells. Mitotically activated NG2-positive pericytes, and endothelial cells may serve as potential therapeutic targets in NF1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BrdU:
-
bromodeoxyuridine
- CD31:
-
PECAM-1
- CD105:
-
endoglin
- flk 1:
-
VEGF receptor-2
- MPNST:
-
malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
- NG2:
-
nerve/glial antigen 2
- NF1:
-
neurofibromatosis type 1
- Nf1 :
-
neurofibromatosis type1 gene
- PAS:
-
periodic acid-Schiff method
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PDGF β-receptor:
-
platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor
References
L Angelov B Salhia L. Roncari et al. (1999) ArticleTitleInhibition of angiogenesis by blocking activation of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 leads to decreased growth of neurogenic sarcomas Cancer Res 59 IssueID21 5536–5541 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXnt1Gisr8%3D Occurrence Handle10554031
MM Feldkamp DH Gutmann A. Guha (1998) ArticleTitleNeurofibromatosis type 1: Piecing the puzzle together Can J Neurol Sci 25 IssueID3 181–191 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cznt1SitA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9706718
KK Hirschi SA Rohovsky PA. D’Amore (1997) ArticleTitleCell-cell interactions in vessel assembly: A model for the fundamentals of vascular remodelling Transpl Immunol 5 IssueID3 177–178 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0966-3274(97)80034-2 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2Fms1ejsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9402682
DM McDonald PL. Choyke (2003) ArticleTitleImaging of angiogenesis: From microscope to clinic Nat Med 9 IssueID6 713–25 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nm0603-713 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXktFOnurs%3D Occurrence Handle12778170
U Ozerdem WB. Stallcup (2003) ArticleTitleEarly contribution of pericytes to angiogenic sprouting and tube formation Angiogenesis 6 IssueID3 241–249 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:AGEN.0000021401.58039.a9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXisVKrtrg%3D Occurrence Handle15041800
U Ozerdem E Monosov WB. Stallcup (2002) ArticleTitleNG2 proteoglycan expression by pericytes in pathological microvasculature Microvasc Res 63 IssueID1 129–134 Occurrence Handle10.1006/mvre.2001.2376 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXptFOktrc%3D Occurrence Handle11749079
U Ozerdem KA Grako K. Dahlin-Huppe et al. (2001) ArticleTitleNG2 proteoglycan is expressed exclusively by mural cells during vascular morphogenesis Dev Dyn 222 IssueID2 218–227 Occurrence Handle10.1002/dvdy.1200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXot1Klt7s%3D Occurrence Handle11668599
KK Norton J Xu DH. Gutmann (1995) ArticleTitleExpression of the neurofibromatosis I gene product, neurofibromin, in blood vessel endothelial cells and smooth muscle Neurobiol Dis 2 IssueID1 13–21 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXotFGgsrs%3D Occurrence Handle8980005
SJ Hamilton JM. Friedman (2000) ArticleTitleInsights into the pathogenesis of neurofibromatosis 1 vasculopathy Clin Genet 58 IssueID5 341–344 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1399-0004.2000.580501.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7itlygtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11140831
AD Gitler Y Zhu FA. Ismat et al. (2003) ArticleTitleNf1 has an essential role in endothelial cells Nat Genet 33 IssueID1 75–79 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XpvVeqs78%3D Occurrence Handle12469121
V Muthukkaruppan R. Auerbach (1979) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis in the mouse cornea Science 205 IssueID4413 1416–1418 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSaB2cfotVA%3D Occurrence Handle472760
BM Kenyon EE Voest CC. Chen et al. (1996) ArticleTitleA model of angiogenesis in the mouse cornea Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 37 IssueID8 1625–1632 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymB1MrjvVQ%3D Occurrence Handle8675406
U Ozerdem WB. Stallcup (2004) ArticleTitlePathological angiogenesis is reduced by targeting pericytes via the NG2 proteoglycan Angiogenesis 7 IssueID3 269–276 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10456-004-4182-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXht1Kjtrs%3D Occurrence Handle15609081
BM Kenyon F Browne RJ. D’Amato (1997) ArticleTitleEffects of thalidomide and related metabolites in a mouse corneal model of neovascularization Exp Eye Res 64 IssueID6 971–978 Occurrence Handle10.1006/exer.1997.0292 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXks1aqurY%3D Occurrence Handle9301478
CI Brannan AS Perkins KS. Vogel et al. (1994) ArticleTitleTargeted disruption of the neurofibromatosis type-1 gene leads to developmental abnormalities in heart and various neural crest-derived tissues Genes Dev 8 IssueID9 1019–1029 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXktVGrt7c%3D Occurrence Handle7926784
LE Smith E Wesolowski A. McLellan et al. (1994) ArticleTitleOxygen-induced retinopathy in the mouse Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 35 IssueID1 101–111 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuC3s7ntlA%3D Occurrence Handle7507904
B Dawson RG. Trapp (2001) Basic and Clinical Biostatistics EditionNumber3 McGraw-Hill New York
CJ Drake PA. Fleming (2000) ArticleTitleVasculogenesis in the day 6.5 to 9.5 mouse embryo Blood 95 IssueID5 1671–1679 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhsVGgtLc%3D Occurrence Handle10688823
YS Chang E Tomaso Particledi DM McDonald et al. (2000) ArticleTitleMosaic blood vessels in tumors: Frequency of cancer cells in contact with flowing blood Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97 IssueID26 14608–14613 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.97.26.14608 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXitVGitw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11121063
H Gerhardt C. Betsholtz (2003) ArticleTitleEndothelial-pericyte interactions in angiogenesis Cell Tissue Res 314 IssueID1 15–23 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00441-003-0745-x Occurrence Handle12883993
I Rajantie M Ilmonen A. Alminaite et al. (2004) ArticleTitleAdult bone marrow-derived cells recruited during angiogenesis comprise precursors for periendothelial vascular mural cells Blood 104 IssueID7 2084–2086 Occurrence Handle10.1182/blood-2004-01-0336 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXotVOqur0%3D Occurrence Handle15191949
F Dolbeare H Gratzner MG Pallavicini JW. Gray (1983) ArticleTitleFlow cytometric measurement of total DNA content and incorporated bromodeoxyuridine Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80 IssueID18 5573–5577 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXlsFCkurg%3D Occurrence Handle6577444
PN Dean F Dolbeare H. Gratzner et al. (1984) ArticleTitleCell-cycle analysis using a monoclonal antibody to BrdUrd Cell Tissue Kinet 17 IssueID4 427–436 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXlt1KjurY%3D Occurrence Handle6733753
RS Nowakowski SB Lewin MW. Miller (1989) ArticleTitleBromodeoxyuridine immunohistochemical determination of the lengths of the cell cycle and the DNA-synthetic phase for an anatomically defined population. J Neurocytol 18 IssueID3 311–318 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01190834 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXltlSjtrw%3D Occurrence Handle2746304
T Ezaki P Baluk G. Thurston et al. (2001) ArticleTitleTime course of endothelial cell proliferation and microvascular remodeling in chronic inflammation Am J Pathol 158 IssueID6 2043–2055 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MzislGktg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11395382
P Lindahl BR Johansson P Leveen C. Betsholtz (1997) ArticleTitlePericyte loss and microaneurysm formation in PDGF-B-deficient mice Science 277 IssueID5323 242–245 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.277.5323.242 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXksFCksb0%3D Occurrence Handle9211853
JA Ahlgren-Beckendorf WW Maggio F Chen TA. Kent (1993) ArticleTitleNeurofibromatosis 1 mRNA expression in blood vessels Biochem Biophys Res Commun 197 IssueID2 1019–24 Occurrence Handle10.1006/bbrc.1993.2580 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuD1M3htVQ%3D Occurrence Handle7505566
KK Norton J Xu DH. Gutmann (1995) ArticleTitleExpression of the neurofibromatosis I gene product, neurofibromin, in blood vessel endothelial cells and smooth muscle Neurobiol Dis 2 IssueID1 13–21 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXotFGgsrs%3D Occurrence Handle8980005
DH Gutmann YL Wu NM. Hedrick et al. (2001) ArticleTitleHeterozygosity for the neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) tumor suppressor results in abnormalities in cell attachment, spreading and motility in astrocytes Hum Mol Genet 10 IssueID26 3009–3016 Occurrence Handle10.1093/hmg/10.26.3009 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnsVGhtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11751683
ML Bajenaru MR Hernandez A Perry et al. (2003) ArticleTitleOptic nerve glioma in mice requires astrocyte Nf1 gene inactivation and Nf1 brain heterozygosity Cancer Res 63 IssueID24 8573–8577 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhtVSqtLrL Occurrence Handle14695164
DA Ingram L Zhang J. McCarthy et al. (2002) ArticleTitleLymphoproliferative defects in mice lacking the expression of neurofibromin: Functional and biochemical consequences of Nf1 deficiency in T-cell development and function Blood 100 IssueID10 3656–3662 Occurrence Handle10.1182/blood-2002-03-0734 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XoslKmu74%3D Occurrence Handle12393709
MR Bennett TA Rizvi S. Karyala et al. (2003) ArticleTitleAberrant growth and differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitors in neurofibromatosis type 1 mutants J Neurosci 23 IssueID18 7207–7217 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXmtlyhtrg%3D Occurrence Handle12904481
HC Etchevers C Vincent NM Le Douarin GF. Couly (2001) ArticleTitleThe cephalic neural crest provides pericytes and smooth muscle cells to all blood vessels of the face and forebrain Development 128 IssueID7 1059–1068 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjtFOlt78%3D Occurrence Handle11245571
J Korn B Christ H. Kurz (2002) ArticleTitleNeuroectodermal origin of brain pericytes and vascular smooth muscle cells J Comp Neurol 442 IssueID1 78–88 Occurrence Handle10.1002/cne.1423 Occurrence Handle11754368
G Bergers S Song N Meyer-Morse et al. (2003) ArticleTitleBenefits of targeting both pericytes and endothelial cells in the tumor vasculature with kinase inhibitors J Clin Invest 111 IssueID9 1287–1295 Occurrence Handle10.1172/JCI200317929 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjsFCrsr4%3D Occurrence Handle12727920
P Saharinen K. Alitalo (2003) ArticleTitleDouble target for tumor mass destruction J Clin Invest 111 IssueID9 1277–80 Occurrence Handle10.1172/JCI200318539 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjsFOhtbo%3D Occurrence Handle12727916
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozerdem, U. Targeting neovascular pericytes in neurofibromatosis type 1. Angiogenesis 7, 307–311 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-004-6643-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-004-6643-3