Abstract
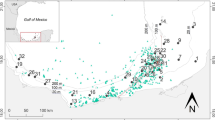
Structural habitat enhancement has been long established as a popular tool to counter habitat loss due to land-use and development. One enhancement approach is the introduction of Coarse Woody Habitat (CWH) to improve the establishment of macrophyte, macroinvertebrate, and fish communities. Here we test for the effects of CWH in Northern boreal lakes in the context of mitigation projects. We constructed Coarse Woody Habitat structures in a structure-less littoral zone of Lake Steepbank within the Oil Sands Region of Alberta, Canada. Enhancement structures featured increased macrophyte and invertebrate richness and biomass compared to reference sites and pre-treatment assessments over three years. Enhanced sites also retained improved richness (macrophytes), diversity (macroinvertebrates), and biomass (both), despite STIN loss and degradation of enhancement structures over time. Using beta diversity components, constituting richness agreement, community differentiation, and site relationships, and testing their relative importance revealed that replacement was more dominant for invertebrates and increasing similarity more important for macrophyte communities post-enhancement. Our study shows the value of CWH addition for macroinvertebrate and macrophyte communities in what is otherwise a structure-less environment. Community changes over time showcase how beta diversity should be more strongly incorporated in restoration and enhancement studies to quantify community shifts that otherwise would not be captured in alternative diversity measures.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data is available through figshare: 10.6084/m9.figshare.16371525.
References
Alahuhta J, Kosten S, Akasaka M, Auderset D, Azzella MM, Bolpagni R, Bove CP, Chambers PA, Chappuis E, Clayton J, De Winton M, Ecke F, Gacia E, Gecheva G, Grillas P, Hauxwell J, Hellsten S, Hjort J, Hoyer MV, Heino J (2017) Global variation in the beta diversity of lake macrophytes is driven by environmental heterogeneity rather than latitude. J Biogeogr 44(8):1758–1769. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12978
ALMS (2016) Aquatic plants of Alberta (1st ed.). Jag Printing. https://d3n8a8pro7vhmx.cloudfront.net/lswc/pages/21/attachments/original/1487109804/ALMS-Aquatic-Plant-Book-1st-Edition-Nov-2016.pdf?1487109804
Anderson MJ (2001) Permutation tests for univariate or multivariate analysis of variance and regression. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 58(3):626–639. https://doi.org/10.1139/f01-004
Anderson MJ, Ellingsen KE, McArdle BH (2006) Multivariate dispersion as a measure of beta diversity. Ecol Lett 9(6):683–693. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00926.x
Andringa JI, Zuo J, Berg MP, Klein R, Van’t Veer J, De Geus R, De Beaumont M, Goudzwaard L, Van Hal J, Broekman R, Van Logtestijn RS, Li Y, Fujii S, Lammers M, Hefting MM, Sass-Klaassen U, Cornelissen JH (2019) Combining tree species and decay stages to increase invertebrate diversity in dead wood. For Ecol Manag 441:80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2019.03.029
Arbizue PM (2020) Pmartinezarbizu/pairwiseAdonis. GitHub. https://github.com/pmartinezarbizu/pairwiseAdonis
Astorga A, Death R, Death F, Paavola R, Chakraborty M, Muotka T (2014) Habitat heterogeneity drives the geographical distribution of beta diversity: the case of New Zealand stream invertebrates. Ecol Evol 4(13):2693–2702. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.1124
Barbosa FS, Barbosa CS (1994) The bioecology of snail vectors for schitosomiasis in Brazil. Cad Saude Publica 10(2):200–209. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0102-311x1994000200007
Baselga A (2009) Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 19(1):134–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2009.00490.x
Benke AC (1976) Dragonfly production and prey turnover. Ecology 57(5):915–927. https://doi.org/10.2307/1941057
Bennett JR, Gilbert B (2015) Contrasting beta diversity among regions: How do classical and multivariate approaches compare? Glob Ecol Biogeogr 25(3):368–377. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12413
Bull JW, Suttle KB, Gordon A, Singh NJ, Milner-Gulland EJ (2013) Biodiversity offsets in theory and practice. Oryx 47(3):369–380. https://doi.org/10.1017/s003060531200172x
Carreras Gamarra MJ, Lassoie JP, Milder J (2018) Accounting for no net loss: a critical assessment of biodiversity offsetting metrics and methods. J Environ Manag 220:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.05.008
Chisholm C, Lindo Z, Gonzalez A (2011) Metacommunity diversity depends on connectivity and patch arrangement in heterogeneous habitat networks. Ecography 34(3):415–424. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0587.2010.06588.x
Clifford HF (1991) Aquatic invertebrates of Alberta. University of Alberta
Cornell HV, Lawton JH (1992) Species interactions, local and regional processes, and limits to the richness of ecological communities: a theoretical perspective. J Anim Ecol 61(1):1. https://doi.org/10.2307/5503
Cowx IG, Portocarrero Aya M (2011) Paradigm shifts in fish conservation: moving to the ecosystem services concept. J Fish Biol 79(6):1663–1680. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2011.03144.x
Cramer MJ, Willig MR (2005) Habitat heterogeneity, species diversity and null models. Oikos 108(2):209–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2005.12944.x
Czarnecka M (2015) Coarse Woody debris in temperate littoral zones: implications for biodiversity, food webs and lake management. Hydrobiologia 767(1):13–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2502-z
Daly HE (1991) Elements of environmental macroeconomics. In: Costanza PR (Ed.), Ecological economics: the science and management of sustainability. Columbia University Press
Doig LE, Schiffer ST, Liber K (2015) Reconstructing the ecological impacts of eight decades of mining, metallurgical, and municipal activities on a small boreal lake in Northern Canada. Integr Environ Assess Manag 11(3):490–501. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.1616
Duarte CM, Kalff J, Peters RH (1986) Patterns in biomass and cover of aquatic macrophytes in lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 43(10):1900–1908. https://doi.org/10.1139/f86-235
Dudgeon D, Arthington AH, Gessner MO, Kawabata ZI, Knowler DJ, Lévêque C, Naiman RJ, Prieur-Richard AH, Soto D, Stiassny ML, Sullivan CA (2006) Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol Rev 81(2):163–182. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1464793105006950
Francis TB, Schindler DE, Holtgrieve GW, Larson ER, Scheuerell MD, Semmens BX, Ward EJ (2011) Habitat structure determines resource use by zooplankton in temperate lakes. Ecol Lett 14(4):364–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01597.x
Gammons CH, Harris LN, Castro JM, Cott PA, Hanna BM (2009) Creating lakes from open pit mines: processes and considerations, emphasis on northern environments. Can Tech Rep Fish Aquat Sci 2826:ix + 106
Gauch HG, Whittaker RH (1972) Coenocline simulation. Ecology 53(3):446–451. https://doi.org/10.2307/1934231
Gennaretti F, Arseneault D, Bégin Y (2013) Millennial stocks and fluxes of large Woody debris in lakes of the North American Taiga. J Ecol 102(2):367–380. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12198
Gilinsky E (1984) The role of fish predation and spatial heterogeneity in determining benthic community structure. Ecology 65(2):455–468. https://doi.org/10.2307/1941408
Gunnill FC (1982) Effects of plant size and distribution on the numbers of invertebrate species and individuals inhabiting the Brown alga Pelvetia fastigiata. Mar Biol 69(3):263–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00397492
Haase P, Hering D, Jähnig SC, Lorenz AW, Sundermann A (2012) The impact of hydromorphological restoration on river ecological status: a comparison of fish, benthic invertebrates, and macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 704(1):475–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1255-1
Håkanson L (1977) The influence of wind, fetch, and water depth on the distribution of sediments in lake Vänern, Swedan. Canad J Earth Sc 14(3):397–412. https://doi.org/10.1139/e77-040
Helmus MR, Sass GG (2008) The rapid effects of a whole-lake reduction of coarse Woody debris on fish and benthic macroinvertebrates. Freshw Biol 53(7):1423–1433. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2008.01974.x
Hood GA, Larson DG (2013) Beaver-created habitat heterogeneity influences aquatic invertebrate assemblages in boreal Canada. Wetlands 34(1):19–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-013-0476-z
Horvath TG (2004) Retention of particulate matter by macrophytes in a first-order stream. Aquat Bot 78(1):27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2003.09.003
Hui C, McGeoch MA (2014) Zeta diversity as a concept and metric that unifies incidence-based biodiversity patterns. Am Nat 184(5):684–694. https://doi.org/10.1086/678125
Hurlbert SH (1971) The nonconcept of species diversity: a critique and alternative parameters. Ecology 52(4):577–586. https://doi.org/10.2307/1934145
Jeppesen E, Peder Jensen J, Søndergaard M, Lauridsen T, Junge Pedersen L, Jensen L (1997) Top-down control in freshwater lakes: the role of nutrient state, submerged macrophytes and water depth. Shallow Lakes 95:151–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-5648-6_17
Legendre P, De Cáceres M (2013) Beta diversity as the variance of community data: dissimilarity coefficients and partitioning. Ecol Lett 16(8):951–963. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12141
Leibold MA, Holyoak M, Mouquet N, Amarasekare P, Chase JM, Hoopes MF, Holt RD, Shurin JB, Law R, Tilman D, Loreau M, Gonzalez A (2004) The metacommunity concept: a framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecol Lett 7(7):601–613. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00608.x
Levi HW (1966) The care of alcoholic collections of small invertebrates. Syst Zool 15(3):183. https://doi.org/10.2307/2411389
Lourenço-de-Moraes R, Malagoli LR, Guerra V, Ferreira RB, Affonso ID, Haddad CF, Sawaya RJ, Bastos RP (2018) Nesting patterns among neotropical species assemblages: Can reserves in urban areas be failing to protect anurans? Urban Ecosyst 21(5):933–942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11252-018-0767-5
Lusardi RA, Jeffres CA, Moyle PB (2018) Stream macrophytes increase invertebrate production and fish habitat utilization in a California stream. River Res Appl 34(8):1003–1012. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.3331
McCullough CD, Van Etten EJ (2011) Ecological restoration of novel lake districts: new approaches for new landscapes. Mine Water Environ 30(4):312–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-011-0161-5
Moore JJ, O’Sullivan A (1970) A comparison between the results of the braun-blanquet method and those of “Cluster analysis.” Gesellschaftsmorphologie. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-3353-4_3
Moser KA, Smol JP, Lean DR, MacDonald GM (1998) Physical and chemical limnology of northern boreal lakes, Wood Buffalo National Park, northern Alberta and the Northwest Territories, Canada. Hydrobiologia 377:25–43. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003225527053
Nelson KA, Collins SF, Sass GG, Wahl DH (2017) A response-surface examination of competition and facilitation between native and invasive juvenile fishes. Funct Ecol 31(11):2157–2166. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12922
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PR, O'Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Henry M, Stevens H, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2020) Package 'vegan'. The comprehensive R archive network. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/vegan.pdf
Olsen DA, Matthaei CD, Townsend CR (2007) Patch history, invertebrate patch dynamics and heterogeneous community composition: perspectives from a manipulative stream experiment. Mar Freshw Res 58(4):307. https://doi.org/10.1071/mf06202
Palmer MA, Menninger HL, Bernhardt E (2010) River restoration, habitat heterogeneity and biodiversity: a failure of theory or practice? Freshw Biol 55:205–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02372.x
Pearce DW, Atkinson GD (2017) Capital theory and the measurement of sustainable development: an indicator of “weak” sustainability. In: Pezzey JC, Toman MA (Eds.), The economics of sustainability (3rd ed., pp 227–233). Routledge
Peet RK (1975) Relative diversity indices. Ecology 56(2):496–498. https://doi.org/10.2307/1934984
Pienitz R, Smol JP, Lean DR (1997) Physical and chemical limnology of 24 lakes located between Yellowknife and Contwoyto lake, Northwest Territories (Canada). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 54(2):347–358. https://doi.org/10.1139/f96-275
Pik AJ, Dangerfield JM, Bramble RA, Angus C, Nipperess DA (2002) The use of invertebrates to detect small-scale habitat heterogeneity and its application to restoration practices. Environ Monit Assess 75:179–199. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014444032375
Podani J, Ricotta C, Schmera D (2013) A general framework for analyzing beta diversity, nestedness and related community-level phenomena based on abundance data. Ecol Complex 15:52–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecocom.2013.03.002
Purvis A, Hector A (2000) Getting the measure of biodiversity. Nature 405(6783):212–219. https://doi.org/10.1038/35012221
Quigley JT, Harper DJ (2006) Effectiveness of fish habitat compensation in Canada in achieving no net loss. Environ Manage 37(3):351–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-004-0263-y
R Core Team (2016) Adonis: permutational multivariate analysis of variance using in vegan: community ecology package. R package documentation. https://rdrr.io/rforge/vegan/man/adonis.html
R Core Team (2020a) R: the R project for statistical computing. https://www.r-project.org/index.html
R Core Team (2020b) R: the R stats package. https://stat.ethz.ch/R-manual/R-devel/library/stats/html/00Index.html
Reid AJ, Carlson AK, Creed IF, Eliason EJ, Gell PA, Johnson PT, Kidd KA, MacCormack TJ, Olden JD, Ormerod J, Smol JP, Taylor WW, Tockner K, Vermaine JC, Dudgeon D, Cooke SJ (2018) Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol Rev 94(3):849–873. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12480
Rosine WN (1955) The distribution of invertebrates on submerged aquatic plant surfaces in Muskee lake, Colorado. Ecology 36(2):308–314. https://doi.org/10.2307/1933237
Ruppert JL, Hogg J, Poesch MS (2018) Community assembly and the sustainability of habitat offsetting targets in the first compensation lake in the oil sands region in Alberta, Canada. Biol Cons 219:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2018.01.014
Sánchez-Hernández J, Finstad AG, Arnekleiv JV, Kjærstad G, Amundsen P (2020) Beyond ecological opportunity: Prey diversity rather than abundance shapes predator niche variation. Freshw Biol 66(1):44–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.13606
Sass GG, Shaw SL, Rooney TP, Rypel AL, Raabe JK, Smith QC, Hrabik TR, Toshner ST (2019) Coarse Woody habitat and glacial lake fisheries in the midwestern United States: knowns, unknowns, and an experiment to advance our knowledge. Lake Reserv Manag 35(4):382–395. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402381.2019.1630530
Schindler DE, Scheuerell MD (2002) Habitat coupling in lake ecosystems. Oikos 98(2):177–189. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0706.2002.980201.x
Schmera D, Podani J, Legendre P (2020) What do beta diversity components reveal from presence-absence community data? Let us connect every indicator to an indicandum! Ecol Ind 117:106540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106540
Schoukens H, Cliquet A (2016) Biodiversity offsetting and restoration under the European Union habitats directive: Balancing between no net loss and deathbed conservation? Ecol Soc. https://doi.org/10.5751/es-08456-210410
Shupryt MP, Stelzer RS (2009) Macrophyte beds contribute disproportionately to benthic invertebrate abundance and biomass in a sand plains stream. Hydrobiologia 632(1):329–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9856-z
Smokorowski KE, Pratt TC, Cole WG, McEachern LJ, Mallory EC (2006) Effects on periphyton and macroinvertebrates from removal of submerged wood in three Ontario lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 63(9):2038–2049. https://doi.org/10.1139/f06-104
Socolar JB, Gilroy JJ, Kunin WE, Edwards DP (2016) How should beta-diversity inform biodiversity conservation? Trends Ecol Evol 31(1):67–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2015.11.005
Theis S, Ruppert JL, Roberts KN, Minns CK, Koops M, Poesch MS (2019) Compliance with and ecosystem function of biodiversity offsets in North American and European freshwaters. Conserv Biol 34(1):41–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/cobi.13343
Tomarken AJ, Serlin RC (1986) Comparison of ANOVA alternatives under variance heterogeneity and specific noncentrality structures. Psychol Bull 99(1):90–99. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.99.1.90
Ulrich W, Gotelli J, N. (2007) Disentangling community patterns of nestedness and species Co-occurrence. Oikos 116(12):2053–2061. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2007.0030-1299.16173.x
Vadeboncoeur Y, Lodge DM (2000) Periphyton production on wood and sediment: Substratum-specific response to laboratory and whole-lake nutrient manipulations. J N Am Benthol Soc 19(1):68–81. https://doi.org/10.2307/1468282
Vaissière A, Levrel H, Scemama P (2017) Biodiversity offsetting: clearing up misunderstandings between conservation and economics to take further action. Biol Cons 206:258–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2016.11.036
Vaughn CC (1986) The role of periphyton abundance and quality in the microdistribution of a stream grazer, Helicopsyche borealis (Trichoptera: Helicopsychidae). Freshw Biol 16(4):485–493. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.1986.tb00991.x
Viana DS, Figuerola J, Schwenk K, Manca M, Hobaek A, Mjelde M, Preston CD, Gornall RJ, Croft JM, King RA, Green AJ, Santamaría L (2015) Assembly mechanisms determining high species turnover in aquatic communities over regional and continental scales. Ecography 39(3):281–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecog.01231
Watson AM, Ormerod S (2005) The distribution and conservation of threatened Sphaeriidae on British grazing marshland. Biodivers Conserv 14(9):2207–2220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-004-4670-4
Whittaker RH (1972) Evolution and measurement of species diversity. Taxon 21(2/3):213–259. https://doi.org/10.2307/1218190
Wiggins GB (2005) Caddisflies: the underwater architects. University of Toronto Press
Wikum DA, Shanholtzer GF (1978) Application of the braun-blanquet cover-abundance scale for vegetation analysis in land development studies. Environ Manag 2(4):323–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01866672
Wilkinson K (2010) Trees and shrubs of Alberta. Lone Pine Publishing
Wilson MV, Shmida A (1984) Measuring beta diversity with presence-absence data. J Ecol 72(3):1055. https://doi.org/10.2307/2259551
Wohl E, Kramer N, Ruiz-Villanueva V, Scott DN, Comiti F, Gurnell AM, Piegay H, Lininger KB, Jaeger KL, Walters DM, Fausch KD (2019) The natural wood regime in rivers. Bioscience 69(4):259–273. https://doi.org/10.1093/biosci/biz013
Ziegler JP, Gregory-Eaves I, Solomon CT (2017) Refuge increases food chain length: modeled impacts of littoral structure in lake food webs. Oikos 126(9):1347–1356. https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.03517
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The Author(s) declare(s) that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Handling Editor: Télesphore Sime-Ngando.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix
Appendix
See Fig. 7
Structural Integrity (STIN) assessment for coarse wood bundles and whole tree structures a as part of the Coarse Woody Habitat (CWH) study in Lakeland County, Northern Alberta, 1-week, 1-month, 1-year and 2-years post construction related to mean biomass, richness and diversity changes in aquatic macroinvertebrates and invertebrates b. Significant differences in STIN values are indicated by Holm corrected p-values (accepted alpha < 0.05). Whole tree structures STIN over time: n = 10; df = 3; chi-square = 33.936; p < 0.001. Coarse wood bundles STIN over time: n = 10; df = 3; chi-square = 27.176; p < 0.001
.
.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Theis, S., Ruppert, J.L.W., Shirton, J.R. et al. Measuring beta diversity components and beneficial effects of coarse woody habitat introduction on invertebrate and macrophyte communities in a shallow northern boreal lake; implications for offsetting. Aquat Ecol 56, 793–814 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-022-09949-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-022-09949-7