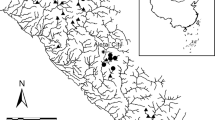
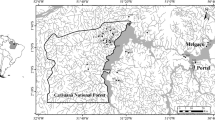
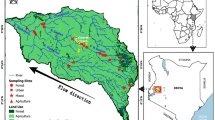
Abstract
Woody debris (CWD) is an important habitat component in northern Gulf of Mexico coastal plain streams, where low gradients and low flows allow accumulation of CWD and promote low dissolved oxygen (DO) concentrations. We tested the influences of CWD and DO on stream macroinvertebrates experimentally by placing two surface area CWD treatments each in three concentrations of ambient DO in two streams in Louisiana, USA, with macroinvertebrates collected from ambient woody debris used as a control. We also sampled macroinvertebrates in benthic and woody debris habitats in three streams twice yearly over 2 years to examine the applicability of the experimental results. Total abundance, richness (generic), and Shannon–Wiener diversity were all higher in lower DO conditions during the experiment, and total abundance was higher in the larger CWD treatment. Stream sampling corroborated the relationship between higher diversity and low DO in both benthic and woody debris habitats, but the relationship between richness and low DO only was supported in benthic habitats. Few taxa correlated with DO or CWD in the experiment (5 of 21 taxa) or stream survey (2 of 54 taxa). Whereas most taxa were uncorrelated with experimentally manipulated and in-stream measured variables, we suggest these taxa respond as generalists to stream habitat and physicochemistry. Based on this experiment and stream sampling, we believe the majority of macroinvertebrates in these streams are tolerant of seasonally low DO conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CWD:
-
woody debris
- DO:
-
dissolved oxygen
- BOD:
-
biochemical oxygen demand
- DOC:
-
dissolved organic carbon
References
Adams SB, Warren ML Jr, Haag WR (2004) Spatial and temporal patterns in fish assemblages of upper coastal plain streams, Mississippi, USA. Hydrobiologia 528:45–61
Agresti A (1996) An introduction to categorical data analysis. Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York
American Public Health Association (1998) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association. Washington, District of Columbia
Anderson MJ, Willis TJ (2003) Canonical analysis of principal coordinates: a useful method of constrained ordination for ecology. Ecology 84:511–525
Anderson NH, Sedell JR, Roberts LM, Trisha FJ (1978) The role of aquatic invertebrates in processing of wood debris in coniferous forest streams. Am Midl Nat 100:64–82
Barbour MT, Gerritsen J, Snyder BD, Stribling JB (1999) Rapid Bioassessment Protocols for Use in Streams and Wadeable Rivers: Periphyton, Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Fish, Second Edition. EPA 841-B-99-002. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; Office of Water; Washington, District of Columbia
Barr CB, Chapin JB (1981) The aquatic Dryopoidea of Louisiana (Coleoptera: Psephenidae, Dryopidae, Elmidae). Tulane Stud Zool Bot 26:91–164
Benke AC, Van Ardsall TC, Gillespie DM, Parrish FK (1984) Invertebrate productivity in a subtropical blackwater river: the importance of habitat and life history. Ecol Monogr 54:25–63
Benke AC, Wallace JB (1990) Wood dynamics in coastal blackwater streams. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 47:92–99
Benke AC, Wallace JB (2003) Influence of wood on invertebrate communities in streams and rivers. In: Gregory S, Boyer K, Gurnell A (eds) The ecology and management of wood in world rivers. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, Maryland, pp 149–177 American Fisheries Society Symposium 37
Berner L, Pescador ML (1988) The Mayflies of Florida. University of Florida Press, Gainesville, Florida
Bink GH (1957) The Odonata of Louisiana. Tulane Stud Zool 5:71–135
Brown AV, Matthews MJ (1995) Stream ecosystems of the central United States. In: Cushing CE, Cummins KW, Minshall GW (eds) River and stream ecosystems. Ecosystems of the World 22. Elsevier, The Netherlands, pp 89–116
Bryan CF, Kelso WE, Rutherford DA, Walker-Bryan B, Monzyk FR, Kelly DG, Noguera JH (1995) Effects of forest management practices on water quality, drifting and benthic macroinvertebrates and fishes in streams in Louisiana. Final Report to Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality, Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Burcher CL, Smock LA (2002) Habitat distribution, dietary composition and life history characteristics of odonate nymphs in a blackwater coastal plain stream. Am Midl Nat 148:75–89
Chen LY, Heath AG, Neves RJ (2001) Comparisons of oxygen consumption in freshwater mussels (Unionidae) from different habitats during declining dissolved oxygen concentrations. Hydrobiologia 450:209–214
Conner JV, Suttkus RD (1986) Zoogeography of freshwater fishes of the western Gulf Slope of North America. In: Hocutt CH, Wiley EO (eds) The zoogeography of North American freshwater fishes. John Wiley and Sons, New York, New York, pp 413–456
Connolly NM, Crossland MR, Pearson RG (2004) Effect of low dissolved oxygen on survival, emergence, and drift of tropical stream macroinvertebrates. J N Am Benthol Soc 23:251–270
Cushing CE, Allan JD (2001) Streams: their ecology and life. Academic Press, Hong Kong, China
Dangles O (2002) Functional plasticity of benthic macroinvertebrates: implications for trophic dynamics in acid streams. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 59:1562–1573
Davis S, Golladay SW, Vellidis G, Pringle CM (2003) Macroinvertebrate biomonitoring in intermittent coastal plain streams impacted by animal agriculture. J Environ Qual 32:1036–1043
Death RG, Winterbourn MJ (1995) Diversity patterns in stream benthic invertebrate communities: the influence of habitat stability. Ecology 76:1446–1460
Didonato GT, Summers JK, Roush TH (2003) Assessing the ecological condition of a coastal plain watershed using a probabilistic survey design. Environ Monit Assess 85:1–21
Dowdy S, Wearden S, Chilko D (2004) Statistics for research, 3rd edn. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, New York
Drury DM, Kelso WE (2000) Invertebrate colonization of woody debris in coastal plain streams. Hydrobiologia 434:63–72
Dudley T, Anderson NH (1982) A survey of invertebrates associated with wood debris in aquatic habitats. Melandria 39:5–21
Ellis MM (1931) Some factors affecting the replacement of the commercial fresh-water mussels. US Bur Fish Bull 22:365–347
Epler JH (2001) Identification Manual for the Larval Chironomidae (Diptera) of North and South Carolina. A Guide to the Taxonomy of the Midges of the Southeastern United States, including Florida. North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources and St. Johns River Water Management District. Raleigh, North Carolina
Fuller SLH (1974) Clams and mussels (Mollusca: Bivalvia). In: Hart CW, Fuller SLH (eds) Pollution ecology of freshwater invertebrates. Academic Press, Inc., New York, New York, pp 215–274
Glitzenstein JS, Platt WJ, Streng DR (1995) Effects of fire regime and habitat on tree dynamics in north Florida longleaf pine savannas. Ecol Monog 65:441–476
Gittens R (1985) Canonical analysis: a review with applications in ecology. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Germany
Harman WN (1974) Snails (Mollusca: Gastropoda). In: Hart CW, Fuller SLH (eds) Pollution ecology of freshwater invertebrates. Academic Press, Inc., New York, New York, pp 275–313
Hartman KH, Faller MD, Howell JW (2005) How much do valley fills influence streams. Hydrobiologia 523:91–102
Hobbs HH, Hall ET (1974) Crayfishes (Decapoda: Astacidae). In: Hart CW, Fuller SLH (eds) Pollution ecology of freshwater invertebrates. Academic Press, Inc., New York, New York, pp 195–214
Holland WC, Hough LW, Murray GE (1952) Geology of Beauregard and Allen Parishes. Geological Bulletin No. 27. Louisiana Geological Survey, Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Ice G, Sugden B (2003) Summer dissolved oxygen concentrations in forested streams of northern Louisiana. S J Appl Forestry 27:92–99
Jacob U, Walther H (1981) Aquatic insect larvae as indicators of limiting minimal contents of dissolved oxygen. Aquat Insect 3:219–224
Jacob U, Walther H, Klenke R (1984) Aquatic insect larvae as indicators of limiting minimal contents of dissolved oxygen—Part II. Aquat Insect 6:185–190
Johnson LB, Breneman DH, Richards C (2003) Macroinvertebrate community structure and function associated with large wood in low gradient streams. River Res Appl 19:199–218
Johnson PD, McMahon RF (1998) Effects of temperature and chronic hypoxia on survivorship of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) and Asian clam (Corbicula fulminea). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 55:1564–1572
Johnson RA, Wichern DW (2002) Applied multivariate statistical analysis, 5th edn. Prentice Hall, New York, New York
Johnson ZB, Kennedy JH (2003) Macroinvertebrate assemblages of submerged woody debris in the Elm Fork of the Trinity River, Texas. J Freshwater Ecol 18:187–197
Kaller MD (2005) Macroinvertebrate community ecology of lowland, subtropical streams in Louisiana. Ph.D. Dissertation, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, Louisiana.
Kaller MD, Hartman KJ (2004) Evidence of a threshold level of fine sediment accumulation for altering benthic macroinvertebrate communities. Hydrobiologia 518:95–104
Kaller MD, Kelso WE (2006) Swine activity alters invertebrate and microbial communities in a coastal watershed. Am Midl Nat 156:165–179
Kaller MD, Kelso WE (2003) Effects of feral swine on water quality in a coastal bottomland stream. P Annu Conf Southeastern Assoc Fish Wildl Agencies 57:291–298
Lepš J, šmilauer P (2003) Multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom
Leurgans SE, Moyeed RA, Silverman BW (1993) Canonical correlation analysis when the data are curves. J␣Roy Stat Soc B 55:725–740
Lydeard C, Mayden RL (1995) A diverse and endangered aquatic ecosystem of the southeast United States. Consery Biol 9:800–805
Mathooko JM, Otieno CO (2002) Does surface textural complexity of woody debris in lotic ecosystems influence their colonization by aquatic invertebrates. Hydrobiologia 489:11–20
Mayden RL (1985) Biogeography of Ouachita Highland fishes. Southwest Nat 30:195–211
Mayden RL (1988) Vicariance biogeography, parsimony, and evolution in North American freshwater fishes. Syst Zool 37:329–355
Nebecker AV (1972) Effect of low oxygen concentration on survival and emergence of aquatic insects. Trans Am Fish Soc 4:675–679
Nebecker AV, Onjukka ST, Stevens DG, Chapman GA, Dominguez SE (1992) Effects of low dissolved oxygen on survival, growth, and reproduction of Daphnia, Hyalella, and Gammarus. Environ Toxicol Chem 11:373–379
Noonan GR (1988) Biogeography of North American and Mexican insects, and a Critique of vicariance biogeography. Syst Zool 37:366–384
O’Connor NA (1991) The effects of habitat complexity on the macroinvertebrates colonizing wood substrates in a lowland stream. Oecologia 85:504–512
Peckarsky BL, Hughes JM, Mather PB, Hillyer M, Encalda AC (2005) Are populations of mayflies living in adjacent fish and fishless streams genetically differentiated? Freshwater Biol 50:42–51
Phillips EC (2003) Habitat preference of aquatic macroinvertebrates in an east Texas sandy stream. J Freshwater Ecol 18:1–11
Phillips L, Perry B (2002) Assessment of potential environmental health risks of residue of high-explosive munitions on military test ranges—comparison in a humid and arid climate. Federal Facilities Environ J 13:7–25
Rebertus AJ, Williamson GB, Platt WJ (1993) Impact of temporal variation in fire regime on savanna oaks and pines. P Tall Timbers Fire Ecol Conf 18:215–225
Rempel LL, Richardson JS, Healey MC (2000) Macroinvertebrate community structure along gradients of hydraulic and sedimentary conditions in a large gravel-bed river. Freshwater Biol 45:57–73
Rinella DJ (2002) Influence of coarse woody debris on macroinvertebrate assemblages in Alabama coastal plains streams. M.S. Thesis, Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama
Rinella DJ, Feminella JW (2005) Comparison of benthic macroinvertebrates colonizing sand, wood, and artificial substrates in a low-gradient stream. J Freshwater Ecol 20:209–220
Roback SS (1974) Insects (Arthropoda: Insecta). In: Hart CW Jr, Fuller SLH (eds) Pollution ecology of freshwater invertebrates. Academic Press, Inc., New York, New York, pp 314–376
Roeding CE, Smock LA (1989) Ecology of macroinvertebrate shredders in a low-gradient sandy-bottomed stream. J N Am Benthol Soc 8:149–161
Ruse LP (1996) Multivariate techniques relating macroinvertebrate and environmental data from a river catchment. Water Res 30:3017–3024
Saloom ME, Duncan RS (2005) Low dissolved oxygen levels reduce anti-predation behaviours of the freshwater clam Corbicula fulminea. Freshwater Biol 50:1233–1238
Sawyer RT (1974) Leeches (Annelida: Hirudinea). In: Hart CW Jr, Fuller SLH (eds) Pollution ecology of freshwater invertebrates. Academic Press, Inc., New York, New York, pp 82–142
Sinclair RM (1964) Water quality requirements of the family Elmidae (Coleoptera) (with keys to the larvae and adults of the eastern genera). Tennessee Stream Pollution Control Board, Tennessee Department of Public Health, Nashville, Tennessee
Smith DG (2001) Pennak’s freshwater invertebrates of the United States: Porifera to Crustacea. Wiley and Sons Inc., New York, New York
Stewart KW, Stark BP, Higgins TG (1976) The Stoneflies (Plecoptera) of Louisiana. Great Basin Nat 36:366–384
Stevens JP (2002) Applied multivariate statistics for the social sciences, 4th edn. Lawrence Erlbaum Publishers, New Jersey
ter Braak CJF (1995) Ordination. In: Jongman RHG, ter Braak CJF, Van Tongeren OFR (eds) Data analysis in community and landscape ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, pp 91–173
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1986) Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Dissolved Oxygen. EPA. 440/5-86-003. Criteria and Standards Division. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, District of Columbia
Waters TF (1995) Sediment in streams: Sources, biological effects, and controls. American Fisheries Society Monograph 7, American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, Maryland
Welch RN (1942) Geology of Vernon Parish, Geological Bulletin No. 22. Louisiana Geological Survey, Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Wiggins GB (1998) Larvae of the North American Caddisfly Genera (Trichoptera), 2nd edn. University of Toronto Press, Toronto, Canada
Williams LR, Bonner TH, Hudson JD, III, Williams MG, Leavy TR, Williams CS (2005) Interactive effects of environmental variability and military training on stream biota of three headwater drainages in western Louisiana. Trans Am Fish Soc 134:192–206
Wood DL, Sites RW (2002) Submerged rootmats: a mesohabitat harboring a distinct insect community in Ozark streams. J Freshwater Ecol 17:431–440
Acknowledgements
We thank our cooperators: Boise Cascade Holdings, LLC; Roy O. Martin Lumber Company; Louisiana Department of Wildlife and Fisheries; United States Forest Service; and United States Army Ft. Polk. Specifically, we thank James D. Hudson III and Dick Myers for assistance and insights. We thank D. Allen Rutherford, James P. Geaghan, John W. Fleeger, Sammy L. King, Frank C. Rohwer, and John W. Day for constructive advice. We thank Rebecca Sweany, Rachel Walley, Melinda Ragsdale, Deb Kelly, Adam Piehler, Jaimie (Thompson) David, Jonathan Fisher, Matt Engel, Tory Mason, Nicole Salvi, Seema Ahmed, Tahn Nguyen, Aaron Podey, Chad Thomas, Jón Einar Jónsson, Checo Colon-Gaud, Mike Krumrine, Aimee (Bourgeouis) Fortier, and B. Thorpe Halloran for assistance. This manuscript was approved for publication by the Director of the Louisiana Agricultural Experiment Station as manuscript 04-400-0702.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaller, M.D., Kelso, W.E. Association of macroinvertebrate assemblages with dissolved oxygen concentration and wood surface area in selected subtropical streams of the southeastern USA. Aquat Ecol 41, 95–110 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-006-9046-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-006-9046-2