Abstract
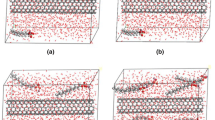
The insolubility of graphene nanosheets in aqueous media has been a limitation for the practical applications of this unique material. The non-covalent functionalization of graphene with mixed surfactants is an effective procedure for preparation of stable graphene dispersions. Physical adsorption of surfactants onto graphene surfaces is a significant stage in the dispersion of graphene nanosheets in the aqueous environment. Studies have shown that the presence of electrolyte greatly affects the adsorption process of pure surfactants on solid surfaces. Examination of mixed surfactants adsorption on graphene in the presence of electrolyte will help to better understand the mechanism of molecular interactions between the graphene nanosheets and mixed surfactants. Therefore, in this study, we used molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the adsorption of mixed surfactants on graphene in the presence of electrolyte and to study the morphology of assemblies formed from mixed surfactants on graphene. We investigate the effects of electrolyte concentration and surface coverage of surfactants' mixture on the adsorption process and structural changes in the assemblies formed on graphene nanosheets. We have found that increasing the ionic strength of electrolyte reinforces stretching of surfactants adsorbed on graphene toward the aqueous phase, and this leads to a clear volume expansion in the structure of graphene-surfactant mixture hemi-spherical micelles. In fact, screening effect of electrolyte ions on electrostatic repulsion between charged head-groups made molecules approach each other, leading to a more compact assembly of surfactants on graphene surface. As hemi-spherical micelles of mixed surfactants-graphene expanded, the steric repulsion between these micelles also increased, which in turn, inhibited the re-aggregation of graphene sheets covered with surfactants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M.J., Tung, V.C., Kaner, R.B.: Honeycomb carbon: a review of graphene. Chem. Rev. 110, 132–145 (2010)
Atkin, R., Craig, V.S.J., Biggs, S.: Adsorption kinetics and structural arrangements of cationic surfactants on silica surfaces. Langmuir 16, 9374–9380 (2000)
Auffinger, P., Cheatham, T.E., Vaiana, A.C.: Spontaneous formation of \uppercase KCl aggregates in biomolecular simulations: a force field issue? J. Chem. Theory Comput. 3, 1851–1859 (2007)
Berendsen, H.J.C., Grigera, J.R., Straatsma, T.P.: The missing term in effective pair potentials. J. Phys. Chem. 91, 6269–6271 (1987)
Cai, M., Thorpe, D., Adamson, D.H., Schniepp, H.C.: Methods of graphite exfoliation. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 24992–25002 (2012)
Chialvo, A.A., Simonson, J.M.: The structure of CaCl2 aqueous solutions over a wide range of concentration. Interpretation of diffraction experiments via molecular simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 119, 8052–8061 (2003)
Choi, W., Lahiri, I., Seelaboyina, R., Kang, Y.S.: Synthesis of graphene and its applications: a review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 35, 52–71 (2010)
Ciesielski, A., Samorì, P.: Graphene via sonication assisted liquid-phase exfoliation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 381–398 (2014)
Coleman, J.N.: Liquid-phase exfoliation of nanotubes and graphene. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 3680–3695 (2009)
Dai, L.: Functionalization of graphene for efficient energy conversion and storage. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 31–42 (2013)
Darden, T., York, D., Pedersen, L.: Particle mesh Ewald: an N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 98, 10089 (1993)
Duque, J.G., Densmore, C.G., Doorn, S.K.: Saturation of surfactant structure at the single-walled carbon nanotube surface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 16165–16175 (2010)
Geim, A.K., Novoselov, K.S.: The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 6, 183–191 (2007)
Green, A.A., Hersam, M.C.: Solution phase production of graphene with controlled thickness via density differentiation. Nano Lett. 9, 4031–4036 (2009)
Grossiord, N., van der Schoot, P., Meuldijk, J., Koning, C.E.: Determination of the surface coverage of exfoliated carbon nanotubes by surfactant molecules in aqueous solution. Langmuir 23, 3646–3653 (2007)
Hess, B., Kutzner, C., Van Der Spoel, D., Lindahl, E.: GROMACS 4: algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 4, 435–447 (2008)
Humphrey, W., Dalke, A., Schulten, K.: VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 14, 33–38 (1996)
Imanishi, A., Suzuki, M., Nakato, Y.: In situ AFM studies on self-assembled monolayers of adsorbed surfactant molecules on well-defined H-Terminated Si (111) surfaces in aqueous solutions. Langmuir 23, 12966–12972 (2007)
Islam, M.F., Rojas, E., Bergey, D.M., Johnson, A.T., Yodh, A.G.: Solubilization of single-wall carbon nanotubes in water. Nano Lett. 3, 269–273 (2003)
Lamont, R.E., Ducker, W.A.: Surface-induced transformations for surfactant aggregates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 7602–7607 (1998)
Lin, S., Shih, C.J., Strano, M.S., Blankschtein, D.: Molecular insights into the surface morphology, layering structure, and aggregation kinetics of surfactant-stabilized graphene dispersions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 12810–12823 (2011)
Liu, S., Wu, B., Yang, X.: Electrolyte-induced reorganization of SDS self-assembly on graphene: a molecular simulation study. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6, 5789–5797 (2014)
Liu, S., Wu, D., Yang, X.: Coarse-grained molecular simulation of self-assembly nanostructures of CTAB on nanoscale graphene. Mol. Simul. 42, 31–38 (2016)
Lokar, W.J., Ducker, W.A.: Proximal adsorption of dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide to the silica—electrolyte solution interface. Langmuir 18, 3167–3175 (2002)
Lotya, M., Hernandez, Y., King, P.J., Smith, R.J., Nicolosi, V., Karlsson, L.S., Blighe, F.M., De, S., Zhiming, W., McGovern, I.T., Duesberg, G.S., Coleman, J.N.: Liquid phase production of graphene by exfoliation of graphite in surfactant/water solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 3611–3620 (2009)
Lotya, M., King, P.J., Khan, U., De, S., Coleman, J.N.: High-concentration, surfactant-stabilized graphene dispersions. ACS Nano 4, 3155–3162 (2010)
Martínez, L., Andrade, R., Birgin, E.G., Martínez, J.M.: PACKMOL: a package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 30, 2157–2164 (2009)
Miyamoto, S., Kollman, P.A.: SETTLE: an analytical version of the SHAKE and RATTLE algorithms for rigid water models. J. Comp. Chem. 13, 952–962 (1992)
Mohr, A., Nylander, T., Piculell, L., Lindman, B., Boyko, V., Bartels, F.W., Liu, Y., Kurkal-Siebert, V.: Mixtures of cationic copolymers and oppositely charged surfactants: effect of polymer charge density and ionic strength on the adsorption behavior at the silica-aqueous interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 4, 1500–1511 (2012)
Niyogi, S., Boukhalfa, S., Chikkannanavar, S.B., Mcdonald, T.J., Heben, M.J., Doorn, S.K.: Selective aggregation of single-walled carbon nanotubes via salt addition. JACS Commun. 10–11 (2007).
Niyogi, S., Densmore, C.G., Doorn, S.K., Soc, J.A.C., Asap, A.: Electrolyte tuning of surfactant interfacial behavior for enhanced density-based separations of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Society 131, 1144–1153 (2009)
Nosé, S.: A molecular dynamics method for simulations in the canonical ensemble. Mol. Phys. 52, 255–268 (1984)
Novoselov, K.S., Geim, A.K., Morozov, S.V., Jiang, D., Zhang, Y., Dubonos, S.V., Grigorieva, I.V., Firsov, A.A.: Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306, 666–669 (2004)
Parrinello, M., Rahman, A.: Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: a new molecular dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 52, 7182–7190 (1981)
Patra, M., Karttunen, M.: Systematic comparison of force fields for microscopic simulations of NaCl in aqueous solutions: diffusion, free energy of hydration, and structural properties. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 678–689 (2004)
Poorgholami-Bejarpasi, N., Sohrabi, B.: Self-assembly of cationic surfactants on the carbon nanotube surface: insights from molecular dynamics simulations. J. Mol. Model. 19, 4319–4335 (2013)
Poorsargol, M., Sohrabi, B., Dehestani, M.: Study of the Gemini surfactants’ self-assembly on graphene nanosheets: insights from molecular dynamic simulation. J. Phys. Chem. A. 122, 3873–3885 (2018)
Poorsargol, M., Alimohammadian, M., Sohrabi, B., Dehestani, M.: Dispersion of graphene using surfactant mixtures: experimental and molecular dynamics simulation studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 464, 440–450 (2019)
Poorsargol, M., Razmara, Z., Amiri, M.M.: The role of hydroxyl and carboxyl functional groups in adsorption of copper by carbon nanotube and hybrid graphene–carbon nanotube: insights from molecular dynamic simulation. Adsorption. 26, 397–405 (2020)
Qu, L., Liu, Y., Baek, J.B., Dai, L.: Nitrogen-doped graphene as efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction in fuel cells. ACS Nano 4, 1321–1326 (2010)
Rafiee, M.A.: Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 442, 282–286 (2011)
Sandwich, S., Wang, Z., Wang, W., Coombs, N., Soheilnia, N., Ozin, G.: Graphene oxide—periodic mesoporous vertically oriented channels. ACS Nano 4, 7437–7450 (2010)
Silvera-Batista, C.A., Scott, D.C., McLeod, S.M., Ziegler, K.J.: A mechanistic study of the selective retention of SDS-suspended single-wall carbon nanotubes on agarose gels. J. Phys. Chem. C. 115, 9361–9369 (2011)
Stiernstedt, J., Fröberg, J.C., Tiberg, F., Rutland, M.W.: Forces between silica surfaces with adsorbed cationic surfactants: influence of salt and added nonionic surfactants. Langmuir 21, 1875–1883 (2005)
Tummala, N.R., Striolo, A.: Role of counterion condensation in the self-assembly of SDS surfactants at the water-graphite interface. J. Phys. Chem. B. 112, 1987–2000 (2008)
Verlet, L.: Computer “experiments” on classical fluids. I. Thermodynamical properties of Lennard-Jones molecules. Phys. Rev. 159, 98 (1967)
Wang, D., Choi, D., Li, J., Yang, Z., Nie, Z., Kou, R., Hu, D., Wang, C., Saraf, L.V., Zhang, J., Aksay, I.A., Liu, J.: Self-assembled TiO2-graphene hybrid nanostructures for enhanced Li-ion insertion. ACS Nano 3, 907–914 (2009)
Wang, D., Kou, R., Choi, D., Yang, Z., Nie, Z., Li, J., Saraf, L.V.: Ternary self-assembly of ordered metal oxide/graphene nanocomposites for electrochemical energy storage. ACS Nano 4, 1587–1595 (2010)
Wanless, E.J., Ducker, W.: Organization of sodium dodecyl sulfate at the graphite-solution interface. J. Phys. Chem. 100, 3207–3214 (1996)
Wu, B., Yang, X.: Molecular simulation of electrolyte-induced interfacial interaction between SDS/graphene assemblies. J. Phys. Chem. C. 117, 23216–23223 (2013)
Xu, Z., Yang, X., Yang, Z.: A molecular simulation probing of structure and interaction for supramolecular sodium dodecyl sulfate/single-wall carbon nanotube assemblies. Nano Lett. 10, 985–991 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The Iran University of Science and Technology, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman support us indeed in this work very much. Therefore, we want to thanks them absolute for all their helps.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poorsargol, M., Sohrabi, B. & Dehestani, M. Self-assembly of the surfactant mixtures on graphene in the presence of electrolyte: a molecular simulation study. Adsorption 27, 69–79 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-020-00264-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-020-00264-x