Abstract
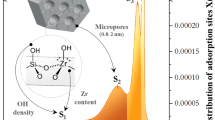
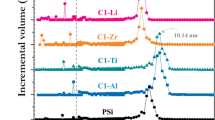
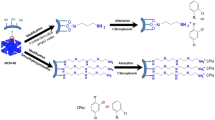
–SO3H modified mesoporous silica adsorbent with water sorption capacity and fast desorption kinetics for water sorption was synthesized and studied via a combined experimental and numerical approach. Mesoporous silica was synthesized using sol–gel method in H2SO4 medium. The water adsorption isotherms and kinetics over the silica were evaluated by a dynamic water vapor sorption analyzer. Mesoporous silica was modeled using annealing simulation with CVFF forcefield. –SO3H modified mesoporous silica was modeled by the attachment of –SO3H to the surface hydroxyl groups and validated. Simulation results show water sorption capacity at low relative humidity (RH) increases with –SO3H loading on mesoporous silica. Energy distribution of intermolecular interaction and micro-view of water sorption over –SO3H modified mesoporous silica reveal that although strong interaction (intermolecular interaction of −40 to −20 kcal/mol) between hydrophilic groups (–SO3H) with water can increase water sorption capacity at low RH, weak H2O–H2O interaction (intermolecular interaction of −20 to −10 kcal/mol) dominated water sorption capacity at both low and high RH.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourg, I.C., Steefel, C.I.: Molecular dynamics simulations of water structure and diffusion in silica nanopores. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(21), 11556–11564 (2012)
Brennan, J.K., Bandosz, T.J., Thomson, K.T., Gubbins, K.E.: Water in porous carbons. Colloids Surf. A 187, 539–568 (2001)
Builes, S., Lopez-Aranguren, P., Fraile, J., Vega, L.F., Domingo, C.: Alkylsilane-functionalized microporous and mesoporous materials: molecular simulation and experimental analysis of gas adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(18), 10150–10161 (2012)
Coasne, B., Galarneau, A., Di Renzo, F., Pellenq, R.J.M.: Gas adsorption in mesoporous micelle templated silicas: Mcm-41, mcm-48, and sba-15. Langmuir 22(26), 11097–11105 (2006)
De Boer, J.H., Everett, D.H., Stone, F.S.: The Structure and Properties of Porous Materials, vol. 10, p. 68. Butterworths, London (1958)
Demiralp, E., Çağin, T., Goddard III, W.A.: Morse stretch potential charge equilibrium force field for ceramics: application to the quartz-stishovite phase transition and to silica glass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82(8), 1708 (1999)
Düren, T., Millange, F., Férey, G., Walton, K.S., Snurr, R.Q.: Calculating geometric surface areas as a characterization tool for metal-organic frameworks. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(42), 15350–15356 (2007)
Ho, L.N., Perez Pellitero, J., Porcheron, F., Pellenq, R.J.M.: Enhanced co2 solubility in hybrid mcm-41: molecular simulations and experiments. Langmuir 27(13), 8187–8197 (2011)
Huff, N.T., Demiralp, E., Cagin, T., Goddard III, W.A.: Factors affecting molecular dynamics simulated vitreous silica structures. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 253(1), 133–142 (1999)
Jorgensen, W.L., Chandrasekhar, J., Madura, D.J., Impey, R.W., Klein, M.L.: Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 79(2), 926–935 (1983)
Kocherbitov, V., Alfredsson, V.: Hydration of mcm-41 studied by sorption calorimetry. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(35), 12906–12913 (2007)
Landmesser, H., Kosslick, H., Storek, W., Fricke, R.: Interior surface hydroxyl groups in ordered mesoporous silicates. Solid State Ion. 101, 271–277 (1997)
Li, X., Li, Z., Xia, Q., Xi, H.: Effects of pore sizes of porous silica gels on desorption activation energy of water vapour. Appl. Therm. Eng. 27(5), 869–876 (2007)
Maddox, M.W., Gubbins, K.E.: Molecular simulation of fluid adsorption in buckytubes. Langmuir 11(10), 3988–3996 (1995)
Mancinelli, R., Imberti, S., Soper, A.K., Liu, K.H., Mou, C.Y., Bruni, F., Ricci, M.A.: Multiscale approach to the structural study of water confined in mcm41. J. Phys. Chem. B 113(50), 16169–16177 (2009)
Roque-Malherbe, M.M.A.: Adsorption and Diffusion in Nanoporous Materials. CRC Press, Florida (2007)
Schumacher, C., Gonzalez, J., Perez-Mendoza, M., Wright, P.A., Seaton, N.A.: Design of hybrid organic/inorganic adsorbents based on periodic mesoporous silica. Industrial Eng. Chem. Res. 45(16), 5586–5597 (2006)
Tominaga, Y., Hong, I.-C., Asai, S., Sumita, M.: Proton conduction in nafion composite membranes filled with mesoporous silica. J. Power Sour. 171(2), 530–534 (2007)
Wang, W.L., Wang, X.X., Song, C.S., Wei, X., Ding, J., Xiao, J.: Sulfuric acid-modified bentonite as the support of tetraethylenepentamine for CO2 capture. Energy Fuels 27(3), 1538–1546 (2013)
Wang, W.L., Xiao, J., Ding, J., Wang, X.X., Song, C.S.: Development of a new clay supported polyethylenimine composite for CO2 capture. Appl. Energy 113, 334–341 (2014)
Acknowledgments
We are pleased to acknowledge the funding support by NSFC-Guangdong Joint Fund Project (U1034005), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51106185), Nature Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (S2012040007694), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (121gpy23) and National Basic Research Program of China (2012CB720404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Wang, W., Wei, X. et al. Experimental and numerical study on water sorption over modified mesoporous silica. Adsorption 21, 67–75 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-015-9650-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-015-9650-3