Abstract
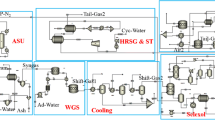
A novel hydrogen pressure swing adsorption system has been studied that is applied to an advanced integrated gasification combined cycle plant for cogenerating power and ultrapure hydrogen (99.99+ mol%) with CO2 capture. In designing the H2 PSA, it is essential to increase the recovery of ultrapure hydrogen product to its maximum since the power consumption for compressing the H2 PSA tail gas up to the gas turbine operating pressure should be minimised to save the total auxiliary power consumption of the advanced IGCC plant. In this study, it is sought to increase the H2 recovery by increasing the complexity of the PSA step configuration that enables a PSA cycle to have a lower feed flow to one column for adsorption and more pressure equalisation steps. As a result the H2 recovery reaches a maximum around 93 % with a Polybed H2 PSA system having twelve columns and the step configuration contains simultaneous adsorption at three columns and four-stage pressure equalisation.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ac :
-
Internal column surface area, m2
- Ap :
-
Pellet surface area, m2
- b ji :
-
Adsorption equilibrium constant of site j for comp. i, bar−1
- b ji,0 :
-
Pre-exponential adsorption equilibrium constant coefficient of site j for comp. i, bar−1
- ci :
-
Gas concentration of component i, mol m−3
- c mi :
-
Gas concentration of component i in the macropore, mol m−3
- cT :
-
Total gas concentration, mol m−3
- \(c_{P,s}\) :
-
Specific heat capacity at constant pressure of the adsorbent, J kg−1 K−1
- DL :
-
Axial mass dispersion coefficient, m2s−1
- Dc :
-
Column diameter, m
- Dm :
-
Molecular diffusivity, m2 s−1
- Dp,i :
-
Macropore diffusivity of component i, m2 s−1
- dp :
-
Pellet averaged diameter, m
- hw :
-
Heat transfer coefficient at the column wall, W m−2 K−1
- Hf :
-
Enthalpy in the fluid phase per unit volume, J m−3
- \(\widetilde{H}_{i}\) :
-
Partial molar enthalpy in the fluid phase of component i, J mol−1
- \(\varDelta \widetilde{H}_{i}^{j}\) :
-
Heat of adsorption of site j for component i, J mol−1
- Ji :
-
Diffusive flux of component i, mol m−2 s−1
- JT :
-
Thermal diffusive flux, W m−2
- kg :
-
Gas conductivity, W m−1 K−1
- k pi ·Ap/Vp :
-
LDF mass transfer coefficient of component i in the pellet, s−1
- k cri ·3/rc :
-
LDF mass transfer coefficient of component i in the crystal, s−1
- Lc :
-
Column length, m
- Mads :
-
Adsorbent mass, kg
- P:
-
Pressure, bar
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number, [-]
- \(\bar{q}_{i}\) :
-
Average adsorbed concentration of component i in the crystal, mol kg−1
- q *i :
-
Adsorbed concentration of component i at equilibrium, mol kg−1
- q ji,s :
-
Saturation capacity of site j for comp. i, mol kg−1
- \(\bar{Q}_{i}\) :
-
Average adsorbed concentration of component i in the pellet, mol m−3
- Qfeed :
-
Feed flow rate, mol s−1
- R:
-
Ideal gas constant J mol−1 K−1
- Re:
-
Reynolds number, [-]
- rc :
-
Crystal radius, m
- rp :
-
Pellet radius, m
- Sc:
-
Schimdt number, [-]
- t:
-
Time, s
- tcycle :
-
Cycle time, s
- T:
-
Temperature, K
- Tf :
-
Fluid temperature, K
- Tw :
-
Column wall temperature, K
- u:
-
Velocity, m s−1
- Uf :
-
Internal energy in the fluid phase per unit volume, J m−3
- UP :
-
Internal energy in the pellet per unit volume, J m−3
- UP,f :
-
Internal energy in the macropore per unit volume, J m−3
- UP,s :
-
Internal energy in the solid phase per unit volume, J m−3
- v:
-
Interstitial flow velocity, m s−1
- Vc :
-
Column volume, m3
- Vp :
-
Pellet volume, m3
- xi, yi :
-
Molar fraction of component i, [-]
- z:
-
Spatial dimension, m
- ε:
-
External bed void fraction, [-]
- εp :
-
Pellet void fraction, [-]
- λL :
-
Axial thermal dispersion coefficient, W m−1 K−1
- μ:
-
Viscosity, bar s
- ρf :
-
Fluid density, kg m−3
- ρp :
-
Pellet density, kg m−3
References
Ahn, H., Yang, J., Lee, C.-H.: Effects of feed composition of coke oven gas on a layered bed H2 PSA process. Adsorption 7, 339–356 (2001)
Ahn, S., You, Y.-W., Lee, D.-G., Kim, K.-H., Oh, M., Lee, C.-H.: Layered two- and four-bed PSA processes for H2 recovery from coal gas. Chem. Eng. Sci. 68, 413–423 (2012)
Cassidy, R.T.: Polybed pressure-swing adsorption hydrogen processing. ACS Symposium Series, vol. 135, Chapter 13, pp. 247–259 (1980)
Committee on climate change, reducing emissions from buildings and industry through the 2020s, Chapter 5 (2011)
DECC, Final emissions estimates by fuel type and end-user sector (2009)
DOE NETL, Cost and performance baseline for fossil energy plants (2007)
Ergun, S.: Fluid flow through packed columns. Chem. Eng. Prog. 48, 89–94 (1952)
Friedrich, D., Ferrari, M.-C., Brandani, S.: Efficient simulation and acceleration of convergence for a dual piston pressure swing adsorption system. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 8897–8905 (2013)
Fuderer, A., Rudelstorfer, E.: US Patent 3986849 to Union Carbide Corporation (1976)
Kapetaki, Z., Ahn, H., Brandani, S.: Detailed process simulation of pre-combustion IGCC plants using coal-slurry and dry coal gasifiers. Energy Procedia 37, 2196–2203 (2013)
Lopes, F.V.S., Grande, C.A., Ribeiro, A.M., Loureiro, J.M., Evaggelos, O., Nikolakis, V., Rodrigues, A.E.: Adsorption of H2, CO2, CH4, CO, N2 and H2O in activated carbon and zeolite for hydrogen production. Sep. Sci. Technol. 44, 1045–1073 (2009)
Lopes, F.V.S., Grande, C.A., Rodrigues, A.E.: Activated carbon for hydrogen purification by pressure swing adsorption: multicomponent breackthrough curves and PSA performance. Chem. Eng. Sci. 66, 303–317 (2011)
Malek, A., Farooq, S.: Study of a six-bed pressure swing adsorption process. AIChE J. 43, 2509–2523 (1997)
OriginLab: Data analysis and graphing software. Origin 8, 5 (2010)
Park, J.-H., Kim, J.-D., Yang, R.T.: Adsorber dynamics and optimal design of layered beds for multicomponent gas adsorption. Chem. Eng. Sci. 53, 3951–3963 (1998)
Ribeiro, A.M., Grande, C.A., Lopes, F.V.S., Loureiro, J.M., Rodrigues, A.E.: A parametric study of layered bed PSA for hydrogen purification. Chem. Eng. Sci. 63, 5258–5273 (2008)
Ribeiro, A.M., Grande, C.A., Lopes, F.V.S., Loureiro, J.M., Rodrigues, A.E.: Four beds pressure swing adsorption for hydrogen purification: case of humid feed and activated carbon beds. AIChE J. 55, 2292–2302 (2009)
SEPA’s National Air Quality Report (2008)
Wakao, N., Funazkri, T.: Effect of fluid dispersion coefficients on particle-to-fluid mass transfer coefficients in packed beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 33, 1375–1384 (1978)
Xu, J., Weist, E.L.: US Patent 6454838 B1 to Air Products and Chemicals Inc (2002)
Xu, J., Rarig, D.L., Cook, T.A., Hsu, K.K., Schoonover, M., Agrawal, R.: US Patent 6565628 B2 to Air Products and Chemicals Inc (2003)
Yang, R.T.: Gas separation by adsorption processes. Butterworth Publishers (1987)
Yang, J., Lee, C.-H.: Adsorption dynamics of a layered bed PSA for H2 recovery from coke oven gas. AIChE J. 44, 1325–1334 (1998)
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude for the financial support from KETEP (Grant No.: 2011-8510020030) and EPSRC (Grant Nos.: EP/F034520/1, EP/G062129/1, and EP/J018198/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luberti, M., Friedrich, D., Brandani, S. et al. Design of a H2 PSA for cogeneration of ultrapure hydrogen and power at an advanced integrated gasification combined cycle with pre-combustion capture. Adsorption 20, 511–524 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-013-9598-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-013-9598-0