Abstract
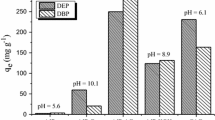
The adsorption and desorption characteristics of some phenoxy herbicides (CPA 2,4-D, and MCPA) from an aqueous solution on the active carbon materials (GAC, F-400) were studied. Adsorption equilibrium capacities of the phenoxy herbicides increased with a decrease in pH of the solution. Adsorption equilibrium isotherms were represented by the Sips equation. Kinetic parameters were measured in a batch adsorber to analyze the adsorption rates of the phenoxy herbicides. The internal diffusion coefficients were determined by comparing the experimental concentration curves with those predicted from the surface diffusion model and the pore diffusion model. The adsorption model based on the linear driving force approximation (LDFA) was used to simulate the adsorption behavior of the phenoxy herbicides in a fixed bed adsorber. Over 95 percent desorption of the phenoxy herbicides was obtained using distilled water.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A s :
-
surface area of the adsorbent particles, m2
- b :
-
isotherm parameter, m3/mol
- c :
-
equilibrium concentration of the solution, mol/m3
- c o :
-
initial liquid phase concentration, mol/m3
- c i :
-
initial concentration of bulk fluid, mol/m3
- c s :
-
concentration on the surface of adsorbent, mol/m3
- D e,p :
-
effective diffusion coefficient, m2/sec
- D L :
-
axial dispersion coefficient, m2/sec
- D m :
-
molecular diffusion coefficient, m2/sec
- d p :
-
particle diameter, m
- D p :
-
effective pore diffusion coefficient, m2/sec
- D s :
-
effective surface diffusion coefficient, m2/sec
- k :
-
isotherm parameter, [mol/kg][mol/m3]−1/n
- k f :
-
film mass transfer coefficient, m/sec
- M :
-
total mass of sorbent particle, kg
- n :
-
isotherm parameter, –
- N A :
-
rate of mass transfer of adsobates to the external surface of the adsorbent, mol/s
- q m :
-
maximum adsorption capacity of adsorbent, mol/kg
- q o :
-
initial adsorbed phase adsorbate concentration, mol/kg
- r :
-
radial distance, m
- R p :
-
particle radius, m
- t :
-
time, sec, hr
- V :
-
volume of solution, m3
- v :
-
interstitial velocity, m/s
- W :
-
weight of adsorbent, kg
- ρ p :
-
particle density, kg/m3
- ε b :
-
bed porosity
- ε p :
-
particle porosity
- τ p :
-
tortuosity factor
- Bi:
-
Biot number
- GAC:
-
granular activated carbon
- PDM:
-
pore diffusion model
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- Sc:
-
Schmidt number
- SDM:
-
surface diffusion model
References
Aksu, Z., Kabasakal, E.: Batch adsorption of 2,4-dichlorophenoxy-acetic acid (2,4-D) from aqueous solution by granular activated carbon. Sep. Pur. Technol. 35, 223–240 (2004)
Areerachakul, N., Vigneswaran, S., Ngo, H.H.: Kandasamy Granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorption-photocatalysis hybrid system in the removal of herbicide from water. Sep. Pur. Technol. 55, 206–211 (2007)
Cohen, D.B.: Groundwater contamination by toxic substances—a California assessment. In: Garner, W.Y., Honeycutt, R.C., Nigg, H.N. (eds.) Evaluation of Pesticides in Groundwater. ACS Symposium Series, vol. 315, pp. 499–529. American Chemical Society, Washington (1986)
Fielding, M., Barcelo, D., Helweg, A., Galassi, S., Torstensson, L., Zoonen, P., Wolte, R., Angeletti, G.: Pesticides in ground and drinking water. Water Pollution Research Report 27, Commission of the European Communities, Brussels (1992)
Freundlich, H.: Uber die adsorption in loesungen. J. Phys. Chem. 57, 385–470 (1907)
Hodgson, E.P., Levi, E.: Pesticides: an important but underused model for the environmental health science. Environ. Health Perspect. 104, 97–105 (1996)
Kah, M., Brown, C.D.: Changes in pesticide adsorption with time at high soil to solution ratios. Chemosphere 68, 1335–1343 (2007)
Langmuir, I.: Adsorption of gases on plain surfaces of glass mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40, 1361–1403 (1918)
Ma, Y.H., Lee, T.Y.: Transient diffusion in solids with a bipore distribution. AICHE. J. 22, 147–152 (1976)
Mangat, S.S., Elefsiniotis, P.: Biodegradation of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) in sequencing batch reactors. Water Res. 33, 861–867 (1999)
Masamune, S., Smith, J.M.: Adsorption rate studies-significance of pore diffusion. AICHE. J. 10, 246–252 (1964)
Misic, D.M., Sudo, Y., Suzuki, M., Kawazeo, K.: Liqiid to particle mass transfer in a stirred batch adsorptiom tank with nonlinear isotherm. J. Chem, Eng. Jpn. 15, 490 (1982)
Ravenzwaay, B.V., Pigott, G., Leibold, E.: Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid (MCPA) in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 42, 115–125 (2004)
Reid, R.C., Prausnitz, J.M., Pokung, B.E.: The Properties of Gases and Liquidss. MaGraw-Hill Co., New York (1994)
Roberto, L.R., Geankoplis, C.J.: Diffusion in liquid filled pores of activated carbon. I: Pore volume diffusion. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 72, 262–271 (1994)
Roberto, L.R., Rangel, J.R., Bernal, L.A., Berber, M.S.: Intraparticle diffusion of cadmium and zinc ions during adsorption from aqueous solution on activated carbon. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 80(8), 924–933 (2005)
Ruthven, D.M.: Principles of Adsorption and Adsorption Processes. Wiley, New York (1984)
Sips, R.: On the structure of a catalyst surface. J. Chem. Phys. 16(5), 490–495 (1948)
Traegner, U.K., Suidan, M.T.: Evaluation of surface and film diffusion coefficients for carbon adsorption. Water Res. 23, 267–273 (1989)
Thorstensen, C.W., Lode, O., Christiansen, A.L.: Development of a solid-phase extraction method for phenoxy acids and bentazone in water and comparison to a liquid-liquid extraction method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48, 5829–5833 (2000)
Wakao, N., Funazkri: Effect of fluid dispersion coefficient on particle to fluid mass transfer coefficients in packed bed. Chem. Eng. Sci. 33, 1375–1384 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, TY., Park, SS., Kim, SJ. et al. Separation characteristics of some phenoxy herbicides from aqueous solution. Adsorption 14, 611–619 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-008-9129-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-008-9129-6