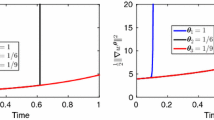
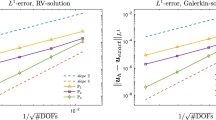
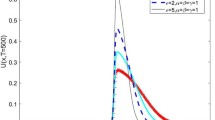
Abstract
For the incompressible MHD equations, we present a fully discrete second-order-in-time scheme based on a blended BDF and extrapolation treatments for nonlinear terms. The proposed scheme is more accurate than the two-step BDF with additional nominal computational time and is still A-stable. Then, unconditional stability, long-time stability, and optimal convergence rate of the scheme are presented. At last, the numerical findings are verified by comparison with the two-step BDF scheme in several 2D and 3D numerical experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Adams, R.A., Fournier, J.F.: Sobolev spaces, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York (2003)
Arnold, D.N., Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: A stable finite element for the Stokes equations. Calcolo 21, 337–344 (1984)
Baker, G.A., Dougalis, V.A., Karakashian, O.A.: On a higher order accurate fully discrete Galerkin approximation to the Navier-Stokes equations. Math. Comp. 39(160), 339–375 (1982)
Cao, C., Wu, J.: Two regularity criteria for the 3D MHD equations. J. Differ. Equ. 248(9), 2263–2274 (2010)
Çıbık, A., Fatma, F. G., Songul. K.: Long time stability of a linearly extrapolated blended BDF scheme for multiphysics flows. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mod., 2020, 17(1): 24-41
Costabel, M., Dauge, M.: Maxwell and Lamé eigenvalues on polyhedra. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 22(3), 243–258 (1999)
Dahlquist, G.: A special stability problem for linear multistep methods. BIT Numer. Math. 3(1), 27–43 (1963)
Dahlquist, G.: G-stability is equivalent to A-stability. BIT Numer. Math. 18, 384–401 (1978)
Davidson, P.: An introduction to magnetohydrodynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
DeCaria, V., Layton, W., Zhao, H.: A time-accurate, adaptive discretization for fluid flow problems. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mod. 17(2), 254–280 (2020)
Ding, Q., Mao, S.P., Sun, J.: Error estimates of H(div)-conforming method for nonstationary magnetohydrodynamic system. Adv. Comput. Math. 48, 55 (2022)
Gao, H., Qiu, W.: A semi-implicit energy conserving finite element method for the dynamical incompressible magnetohydrodynamics equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 346, 982–1001 (2019)
Galdi, G.P.: An introduction to the mathematical theory of the Navier-Stokes equations. Steady-State Problems. Springer, New York (2011)
Gerbeau, J.F.: A stabilized finite element method for the incompressible magnetohydrodynamic equations. Numer. Math. 87(1), 83–111 (2000)
Gerbeau, J.F., Le, Bris, C., Lelièvre, T.: Mathematical methods for the magnetohydrodynamics of liquid metals. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2006)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite element method for Navier-Stokes equations: theory and algorithms. Springer, New York (1986)
Greif, C., Li, D., Schötzau, D., et al.: A mixed finite element method with exactly divergence-free velocities for incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 199(45–48), 2840–2855 (2010)
Gunzburger, M.D., Meir, A.J., Peterson, J.S.: On the existence and uniqueness and finite element approximation of solutions of the equations of stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Math. Comp. 56, 523–563 (1991)
Hairer, E., Wanner, G.: Solving ordinary differential equations. Stiff and Differential Algebraic Problems. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2002)
Hasler, U., Schneebeli, A., Schötzau, D.: Mixed finite element approximation of incompressible MHD problems based on weighted regularization. Appl. Numer. Math. 51(1), 19–45 (2004)
He, Y.: Unconditional convergence of the Euler semi-implicit scheme for the three-dimensional incompressible MHD equations. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 35(2), 767–801 (2015)
He, C., Wang, Y.: On the regularity criteria for weak solutions to the magnetohydrodynamic equations. J. Differ. Equ. 238(1), 1–17 (2007)
Hiptmair, R., Li, L., Mao, S., et al.: A fully divergence-free finite element method for magnetohydrodynamic equations. Math. Mod. Meth. Appl. Sci. 28(4), 659–695 (2018)
Houston, P., Schötzau, D., Wei, X.: A mixed DG method for linearized incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. J. Sci. Comput., 2209, 40: 281-314
Huang, P.Z.: A finite element algorithm for the nonstationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamic system based on a correction method. Mediterr. J. Math. 19, 113 (2022)
Jiang, N.: A second-order ensemble method based on a blended backward differentiation formula timestepping scheme for time-dependent Navier-Stokes equations. Numer. Meth. Part. Diff. Equs. 33(1), 34–61 (2017)
Keram, A., Huang, P.Z.: The Arrow-Hurwicz iterative finite element method for the stationary thermally coupled incompressible magnetohydrodynamics flow. J. Sci. Comput. 92, 11 (2022)
Lin, F., Xu, L., Zhang, P.: Global small solutions of 2D incompressible MHD system. J. Differ. Equ. 259(10), 5440–5485 (2015)
Lin, F., Zhang, P.: Global small solutions to an MHD-type system: the three-dimensional case. Comm. Pure Appl. Math. 67(4), 531–580 (2014)
Liu, S., Huang, P., He, Y.: An optimal error estimate of the BDF-Galerkin FEM for the incompressible MHD system. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 515(2), 126460 (2022)
Lu, X., Huang, P.Z.: A modular grad-div stabilization for the 2D/3D nonstationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamic equations. J. Sci. Comput. 82(1), 1–24 (2020)
Lu, X., Huang, P. Z., He, Y. N.: Fully discrete finite element approximation of the 2D/3D unsteady incompressible magnetohydrodynamic-Voigt regularization flows. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst.-Ser. B, 2021, 26: 815-845
Ma, H.M., Huang, P.Z.: A vector penalty-projection approach for the time-dependent incompressible magnetohydrodynamics flows. Comput. Math. Appl. 120, 28–44 (2022)
Moreau, R.: Magneto-hydrodynamics. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1990)
Nielsen, E.J., Jones, W.T.: Integrated design of an active flow control system using a time-dependent adjoint method. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 6(3), 141–165 (2011)
Nyukhtikov, M., Smelova, N., Mitchell, B.E., Holme, D.G.: Optimized dual-time stepping technique for time-accurate Navier-Stokes calculations. In: Hall, K.C., Kielb, R.E., Thomas, J.P. (eds.) Unsteady Aerodynamics. Aeroacoustics and Aeroelasticity of Turbomachines. Springer, Dordrecht (2006)
Priest, E.R., Hood, A.W.: Advances in solar system magnetohydrodynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1991)
Prohl, A.: Convergent finite element discretizations of the nonstationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics system. M2AN Math. Model. Numer. Anal., 2008, 42(6): 1065-1087
Ravindran, S.S.: An analysis of the blended three-step backward differentiation formula time-stepping scheme for the Navier-Stokes-type system related to Soret convection. Numer. Funct. Anal. Optim. 36, 658–686 (2015)
Rong, Y., Hou, Y., Zhang, Y.: Numerical analysis of a second order algorithm for simplified magnetohydrodynamic flows. Adv. Comput. Math. 43(4), 823–848 (2017)
Schötzau, D.: Mixed finite element methods for stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Numer. Math. 96(4), 771–800 (2004)
Sermange, M., Temam, R.: Some mathematical questions related to the MHD equations. Comm. Pure. Appl. Math. 36(5), 635–664 (1983)
Shen, J.: Long time stability and convergence for fully discrete nonlinear Galerkin methods. Appl. Anal. 38(4), 201–229 (1990)
Vatsa, V. N., Carpenter, M. H., Lockard, D. P.: Re-evaluation of an optimized second order backward difference (BDF2OPT) scheme for unsteady flow applications. 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, 2010, 122
Wacker, B., Arndt, D., Lube, G.: Nodal-based finite element methods with local projection stabilization for linearized incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 302, 170–192 (2016)
Wang, L., Li, J., Huang, P.Z.: An efficient two-level algorithm for the 2D/3D stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics based on the finite element method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 98, 183–190 (2018)
Wiedmer, M.: Finite element approximation for equations of magnetohydrodynamics. Math. Comp. 69(229), 83–101 (2000)
Yang, J.J., Mao, S.P.: Second order fully decoupled and unconditionally energy-stable finite element algorithm for the incompressible MHD equations. Appl. Math. Lett. 121, 107467 (2021)
Zhang, G.D., He, Y.N.: Decoupled schemes for unsteady MHD equations II: finite element discretization and numerical implementation. Comput. Math. Appl. 69, 1390–1406 (2015)
Zhang, G.D., He, Y.N., Zhang, Y.: Streamline diffusion finite element method for stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Numer. Meth. Part. Differ. Equs. 30(6), 1877–1901 (2014)
Zhang, Y., Hou, Y., Shan, L.: Numerical analysis of the Crank-Nicolson extrapolation time discrete scheme for magnetohydrodynamics flows. Numer. Meth. part. Diff. Equs. 31(6), 2169–2208 (2015)
Zhang, G.D., Yang, J., Bi, C.: Second order unconditionally convergent and energy stable linearized scheme for MHD equations. Adv. Comput. Math. 44(2), 505–540 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions which lead to a considerably improved presentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Gianluigi Rozza
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (grant numbers 2023D14014, 2021D01E11) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 12361077, 12271465).
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Huang, P. & He, Y. A second-order scheme based on blended BDF for the incompressible MHD system. Adv Comput Math 49, 74 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-023-10073-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-023-10073-9