Abstract
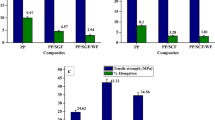
This study fabricated Kevlar-Hemp and Kevlar-Pineapple leaf fiber-based hybrid composites with different weaving architectures using the compression molding method. The quasi-static indentation behavior of hybrid composites was examined. The indentation behavior of hybrid composites was measured using peak load and energy absorption, load-displacement performance, and specimen damage size. The results show that the twill weave type Kevlar-Pineapple leaf fiber and Kevlar-Hemp fiber-based hybrid composites showed better energy absorption and peak load than all types of composites. Moreover, the hybrid composites exhibited beneficial results for peak force and absorbed energy than pure composites. After the indentation behavior, the front and back damaged surfaces of the composites were examined. The specimen damage size was assessed utilizing ultrasonic C-scan images. According to the findings, the hybrid composites’ surface damage was influenced by the different weaving architecture.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Das, S.C., et al.: Effect of stacking sequence on the performance of hybrid natural/synthetic fiber reinforced polymer composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 276, 114525 (2021)
Sangilimuthukumar, J., Thiagamani, S.M.K., Kumar, C.M., Krishnasamy, S., Arpitha, G.R., Mayakannan, S.: Erosion characteristics of epoxy-based Jute, Kenaf and Banana fibre reinforced hybrid composites. Mater. Today Proc. (2022)
Thiagamani, S.M.K., et al.: Investigation into mechanical, absorption and swelling behaviour of hemp/sisal fibre reinforced bioepoxy hybrid composites: Effects of stacking sequences. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 140, 637–646 (2019)
Chandrasekar, M., et al.: Flax and sugar palm reinforced epoxy composites: Effect of hybridization on physical, mechanical, morphological and dynamic mechanical properties. Mater. Res. Express. 6(10), 105331 (2019)
Krishnasamy, S., et al.: Effects of stacking sequences on static, dynamic mechanical and thermal properties of completely biodegradable green epoxy hybrid composites. Mater. Res. Express. 6(10), 105351 (2019)
Senthilkumar, K., et al.: Performance of sisal/hemp bio-based epoxy composites under accelerated weathering. J. Polym. Environ. 29(2), 624–636 (2021)
Krishnasamy, S., et al.: Effect of fibre loading and ca (OH) 2 treatment on thermal, mechanical, and physical properties of pineapple leaf fibre/polyester reinforced composites. Mater. Res. Express. 6(8), 85545 (2019)
Atiqah, A., Chandrasekar, M., Kumar, T.S.M., Senthilkumar, K., Ansari, M.N.M.: Characterization and interface of natural and synthetic hybrid composites. (2019)
Chandrasekar, M., Siva, I., Kumar, T.S.M., Senthilkumar, K., Siengchin, S., Rajini, N.: Influence of Fibre Inter-ply Orientation on the Mechanical and Free Vibration Properties of Banana Fibre Reinforced Polyester Composite Laminates. J. Polym. Environ. 28(11), 2789–2800 (2020)
Jeyaguru, S., et al.: Mechanical, acoustic and vibration performance of intra-ply Kevlar/PALF epoxy hybrid composites: Effects of different weaving patterns. Polym. Compos. 43(6), 3902–3914 (2022)
Senthilkumar, K., et al.: Dual cantilever creep and recovery behavior of sisal/hemp fibre reinforced hybrid biocomposites: Effects of layering sequence, accelerated weathering and temperature. J. Ind. Text. 51(2_suppl), 2372S-2390S (2022)
Nasimudeen, N.A., et al.: Mechanical, absorption and Swelling Properties of Vinyl Ester Based Natural Fibre Hybrid Composites. Appl. Sci. Eng. Prog. 14(4), 680–688 (2021)
Shahroze, R.M., et al.: Mechanical, interfacial and thermal properties of silica aerogel-infused flax/epoxy composites. Int. Polym. Process. 36(1), 53–59 (2021)
Jeyaguru, S., et al.: Effects of different weaving patterns on thermomechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of Kevlar/pineapple leaf fiber hybrid composites. Polym. Compos. 43(8), 4979–4997 (2022)
Senthil Muthu Kumar, T., Chandrasekar, M., Senthilkumar, K., Ayrilmis, N., Siengchin, S., Rajini, N.: Utilization of bamboo fibres and their influence on the mechanical and thermal properties of polymer composites. In: Bamboo Fiber Composites, pp. 81–96. Springer (2021)
Verma, S.K., Gupta, A., Singh, T., Gangil, B., Jánosi, E., Fekete, G.: Influence of dolomite on mechanical, physical and erosive wear properties of natural-synthetic fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Res. Express. 6(12), 125704 (2019)
Jeyaguru, S., Thiagamani, S.M.K., Rajkumar, A.G., Rangappa, S.M., Siengchin, S.: Solid particle erosion, water absorption and thickness swelling behavior of intra ply Kevlar/PALF fiber epoxy hybrid composites. Polym. Compos. (2022)
Muthusamy, A.R., et al.: Erosion performance of natural fiber reinforced vinyl ester hybrid composites: Effect of layering sequences. Mater. Today Proc. (2022)
Sutherland, L.S., Soares, C.G.: The use of quasi-static testing to obtain the low-velocity impact damage resistance of marine GRP laminates. Compos. Part. B Eng. 43(3), 1459–1467 (2012)
Imielińska, K., Castaings, M., Wojtyra, R., Haras, J., Le Clezio, E., Hosten, B.: Air-coupled ultrasonic C-scan technique in impact response testing of carbon fibre and hybrid: Glass, carbon and Kevlar/epoxy composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 157, 513–522 (2004)
Pach, J., Frączek, N., Kaczmar, J.: The effects of hybridisation of composites consisting of aramid, carbon, and hemp fibres in a quasi-static penetration test. Mater. (Basel). 13(20), 4686 (2020)
Nettles, A.T., Douglas, M.J.: A comparison of quasi-static indentation testing to low velocity impact testing. ASTM Spec. Tech. Publ. 1416, 116–130 (2002)
Sarasini, F., et al.: Quasi-static and low-velocity impact behavior of intraply hybrid flax/basalt composites. Fibers. 7(3), 26 (2019)
Yahaya, R., Sapuan, S.M., Jawaid, M., Leman, Z., Zainudin, E.S.: Quasi-static penetration and ballistic properties of kenaf–aramid hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 63, 775–782 (2014)
Feng, N.L., Malingam, S.D., Subramaniam, K., Selamat, M.Z., Ali, M.B., Bapokutty, O.: The influence of fibre stacking configurations on the indentation behaviour of pineapple leaf/glass fibre reinforced hybrid composites. Def. S T Tech. Bull. 12, 113–123 (2019)
Ng, L.F., Malingam, S.D., Subramaniam, K., Selamat, M., Juan, W.: The investigation of the tensile and quasi-static indentation properties of pineapple leaf/kevlar fibre reinforced hybrid composites. Def. ST Tech. Bull 13, 117–129 (2020)
Salman, S.D., Leman, Z., Ishak, M.R., Sultan, M.T.H., Cardona, F.: Quasi-static penetration behavior of plain woven kenaf/aramid reinforced polyvinyl butyral hybrid laminates. J. Ind. Text. 47(7), 1427–1446 (2018)
Bulut, M., Erkliğ, A.: The investigation of quasi-static indentation effect on laminated hybrid composite plates. Mech. Mater. 117, 225–234 (2018)
Hassan, S.A., et al.: Effect of fiber stacking sequence and orientation on quasi-static indentation properties of sustainable hybrid carbon/ramie fiber epoxy composites. Curr. Res. Green. Sustain. Chem. 5, 100284 (2022)
Patil, P.P., Lila, M.K.: The tension and quasi-static indentation properties of coir/glass fibre reinforced hybrid composites. Webology 18(5), 2856–2861 (2021)
Malingam, S.D., Ng, L.F., Chan, K.H., Subramaniam, K., Selamat, M.Z., Zakaria, K.A.: The static and dynamic mechanical properties of kenaf/glass fibre reinforced hybrid composites. Mater. Res. Express. 5(9), 95304 (2018)
Habibi, M., Abbassi, F., Laperrière, L.: Quasi-static indentation and acoustic emission to analyze failure and damage of bio-composites subjected to low-velocity impact. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 158, 106976 (2022)
Karimzadeh, A., Yahya, M.Y., Abdullah, M.N., Wong, K.J.: Effect of stacking sequence on mechanical properties and moisture absorption characteristic of hybrid PALF/glass fiber composites. Fibers Polym. 21(7), 1583–1593 (2020)
Suresha, K.V., Shivanand, H.K., Amith, A., Vidyasagar, H.N.: Evaluation of mechanical properties of hybrid fiber (hemp, jute, kevlar) reinforced composites. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1943, no. 1, p. 20109. (2018)
Colomer-Romero, V., Rogiest, D., García-Manrique, J.A., Crespo, J.E.: Comparison of mechanical properties of hemp-fibre biocomposites fabricated with biobased and regular epoxy resins. Mater. (Basel). 13(24), 5720 (2020)
Jeyaguru, S., Thiagamani, S.M.K., Rangappa, S.M., Siengchin, S.: Experimental studies on the absorption, swelling and erosion performance of hybrid woven Kevlar/hemp reinforced epoxy composites. Express Polym. Lett. 17(4), 353–372 (2023)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education, Srivilliputhur, Tamil Nadu, India and Hindustan Institute of Technology and Science, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India for providing fabrication and testing facilities.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors have read and agreed to publish the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sangilimuthukumar, J., Thiagamani, S.M.K., Siengchin, S. et al. Quasi-static Indentation Behavior of Kevlar-Hemp and Kevlar-PALF Composites: Influence of Weaving Architecture and Intra-ply Hybridization. Appl Compos Mater 30, 937–953 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-023-10124-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-023-10124-w