Abstract
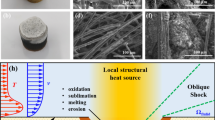
Based on the inherent ablation issues under the hostile thermochemical environment in solid rocket motors (SRM), a dual-scale ablation model of C/C composite nozzle is established. It investigates the ablation rate from both macroscopic and microscopic perspectives. The mechanical erosion of particles and the chemical reaction of gas are comprehensively considered. At macroscale, the turbulence model is proposed to obtain the temperature distribution and the flow field of the nozzle; the particle tracking model is applied to analyze the degree of mechanical erosion and it demonstrates 0.94% ~ 1.88% of the particles will eventually be deposited on the wall. At microscale, the regression and morphology of the surface of C/C composites are simulated by level set method, and the thermochemical ablation law of fibers and matrix is revealed. In addition, the influence of changes in microscopic morphology on surface reaction is input to the macroscale model, and a more convincing chemical ablation rate is evaluated. In the typical ablation conditions, the chemical ablation rate and mechanical erosion rate of the nozzle are respectively estimated as 0.03 mm/s and 0.0063 mm/s, which accords well with the reported data. Thus, our model identifies two extreme situations, i.e., when there are lots of Al2O3 particles, nozzle erosion is dominated by mechanical erosion, but when Al2O3 particles are very few, chemical ablation plays a major role. The limit ratio of mechanical erosion and chemical ablation are calculated. The results of the present study provide a deeper understanding of the ablation mechanism of C/C composite nozzle, which is useful for the thermal performance research and design of C/C nozzle.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Liggett, N., Menon, S.: in 45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. (2007)
Lu, J., et al.: Ablation resistance of SiC–HfC–ZrC multiphase modified carbon/carbon composites. Corros. Sci. 103, 1–9 (2016)
Qin, F., Peng, L.-N., Li, J., He, G.-Q.: Numerical Simulations of Multiscale Ablation of Carbon/Carbon Throat with Morphology Effects. AIAA J. 55, 3476–3485 (2017)
Huang, J.F., Zeng, X.R., Li, H.J., Xiong, X.B., Huang, M.: Mullite-Al2O3-SiC oxidation protective coating for carbon/carbon composites. Carbon 41, 2825–2829 (2003)
Yoon, J.-Y., Kim, C.-G., Lim, J.: Numerical Study on Density Gradient Carbon-Carbon Composite for Vertical Launching System. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space 19, 72–79 (2018)
Lee, S., Park, G., Kim, J.G., Paik, J.G.: Evaluation System for Ablative Material in a High-Temperature Torch. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space 20, 620–635 (2019)
Zhang, X.: Coupled simulation of heat transfer and temperature of the composite rocket nozzle wall. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 15, 402–408 (2011)
Vignoles, G.L., Aspa, Y., Quintard, M.: Modelling of carbon-carbon composite ablation in rocket nozzles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70, 1303–1311 (2010)
Li, Q., Li, J., He, G.-Q., Liu, P.-J.: Erosion of carbon/carbon composites using a low-velocity, high-particle-concentration two-phase jet in a solid rocket motor. Carbon 67, 140–145 (2014)
Yang, B. C., Cheung, F. B., Koo, J. H.: Modeling of One-Dimensional Thermomechanical Erosion of High-Temperature Ablatives. J. Appl. Mech. 60, (1993)
Kumar, S., et al.: Fabrication and ablation testing of 4D C/C composite at 10 MW/m(2) heat flux under a plasma arc heater. Mat. Sci. Eng. a-Struct. 566, 102–111 (2013)
Hui, W-H., Bao, F-T., Wei, X-G., Liu, Y.: Ablation performance of a 4D-braided C/C composite in a parameter-variable channel of a Laval nozzle in a solid rocket motor. Carbon 124, (2017)
Zhang, B., Li, X.D.: Numerical Simulation of Thermal Response and Ablation Behavior of a Hybrid Carbon/Carbon Composite. Appl. Compos. Mater. 25, 675–688 (2018)
Li, W., Huang, H., Wang, Q., Zhang, Z.: Protection of pyrolysis gases combustion against charring materials’ surface ablation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 102, 10–17 (2016)
Li, W., Huang, H., Xu, X.: A coupled thermal/fluid/chemical/ablation method on surface ablation of charring composites. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 109, 725–736 (2017)
Li, K.-Z., et al.: Ablation of the carbon/carbon composite nozzle-throats in a small solid rocket motor. Carbon 49, 1208–1215 (2011)
Chen, B., Zhang, L.-T., Cheng, L.-F., Luan, X.-G.: Ablation of pierced C/C composite nozzles in an oxygen/ethanol combustion gas generator. Carbon 47, 545–550 (2009)
Sutton, G. P. : Rocket propulsion elements: An introduction to the engineering of rockets. J. Wiley (1956)
Chen, B., Zhang, L.T., Chen, L. F.: Ablation Characteristic of the Pierced C/C Composite Nozzle in a Combustion Gas Generator. J. Inorg. Mater. (2008)
Wang, L., Tian, W., Chen, L., Guo, Y.: Investigation of Carbon-Carbon Nozzle Throat Erosion in a Solid Rocket Motor Under Acceleration Conditions. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space 22, 42–51 (2020)
Liu, Y., Pei, J.-Q., Li, J., He, G.-Q.: Ablation characteristics of a 4D carbon/carbon composite under a high flux of combustion products with a high content of particulate alumina in a solid rocket motor. New Carbon Mater. 32, 143–150 (2017)
Zhao, S., Tian, H., Wang, P., Yu, N., Cai, G.: Steady-state coupled analysis of flowfields and thermochemical erosion of C/C nozzles in hybrid rocket motors. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 58, 574–586 (2015)
Zhang, X., Xiang, H.: Coupled simulation of wall temperature and ablation with heat transfer in solid rocket nozzle. Guti Huojian Jishu/J. Solid Rocket Technol. 41, 414–423 (2018)
Thakre, P., Yang, V.: Chemical Erosion of Carbon-Carbon/Graphite Nozzles in Solid-Propellant Rocket Motors. J. Propul. Power 24, 822–833 (2008)
Thakre, P., Rawat, R., Clayton, R., Yang, V.: Mechanical Erosion of Graphite Nozzle in Solid-Propellant Rocket Motor. J. Propul. Power 29, 593–601 (2013)
Borie, V., Brulard, J., Lengelle, G.: Aerothermochemical analysis of carbon-carbon nozzle regression in solid-propellant rocket motors. J. Propul. Power 5, 665–673 (1989)
Zhang, B., Li, X.: Numerical Simulation of Thermal Response and Ablation Behavior of a Hybrid Carbon/Carbon Composite. Appl. Compos. Mater. 25, 675–688 (2017)
Peng, L.-N., He, G.-Q., Li, J., Wang, L., Qin, F.: Effect of combustion gas mass flow rate on carbon/carbon composite nozzle ablation in a solid rocket motor. Carbon 50, 1554–1562 (2012)
Ferguson, J.C., et al.: Modeling the oxidation of low-density carbon fiber material based on micro-tomography. Carbon 96, 57–65 (2016)
Song, Y., Qi, L., Zhang, S., Zhang, J., Li, H.: Simulation on mass loss of C/C composites ablation with fiber scale. Guti Huojian Jishu/J. Solid Rocket Technol. 41, 363–368 (2018)
Song, Y., et al.: Simulation on Morphology Evolution of Micro Ablation for C/C Composites. Mech. Sci. Technol. Aeros. Eng. (2018)
Lachaud, J., Vignoles, G. L., Goyhénèche, J., Epherre, J. F.: Ablation in Carbon/Carbon Composites: Microscopic Observations and 3D Numerical Simulation of Surface Roughness Evolution. (Interfaces in Heterogeneous Ceramic Systems: Ceramic Transactions Series, 2006), pp. 191
Vignoles, G.L., Lachaud, J., Aspa, Y., Goyhénèche, J.-M.: Ablation of carbon-based materials: Multiscale roughness modelling. Compos. Sci. Technol. 69, 1470–1477 (2009)
Vignoles, G. L., Lachaud, J., Yvan, A., Michel, Q.: Effective surface recession laws for the physico-chemical ablation of C/C composite materials. Ceramic Eng. Ence. Proc. 31, (2010)
Acknowledgements
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants Nos. 51972268, 51702100), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2018M643075) and Project of National Engineering Research Center of Ceramic Matrix Composite Manufacture Technology, (Grant No. ZZRF2101). The authors also acknowledge the Northwestern Polytechnical University High Performance Computing Center for the allocation of computing time on their machines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Guan, K., Peng, C. et al. A Dual-scale Model for Estimating the Ablation Rate of C/C Composite Nozzle. Appl Compos Mater 29, 1653–1673 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-022-10035-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-022-10035-2