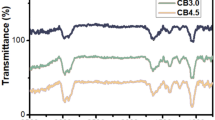
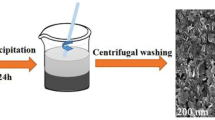
Abstract
Honeycomb structural composites were fabricated by impregnating aramid paper frame with modified whisker carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and polyurethane resin (PU). CNTs were oxidized by using mixed acid and strong oxidant. Vector network analysis was used to measure the reflection loss (RL) of the honeycomb composites and the compressive test of honeycomb composites was carried out with a universal testing machine. For the double-layers honeycomb composites, the method of concentration gradient design can bring double absorption peak resonance benefit, which expand the microwave absorption bandwidth. Therefore, RL achieves the absorption bandwidth (< -10 dB) of 14 GHz covering 4–18 GHz for double-layer honeycomb composites. In addition, an effective model is proposed through the logarithmic law and equivalent circuit theory. The absorption property of the composites is attributed to the quarter-wavelength cancellation interference and multiple scattering, harmonic peaks move to a low-frequency stage with the increase of the CNTs average content. Compared to pristine double-layers honeycomb core, the compression strength and the elastic modulus are enhanced by 64% and 123%, respectively. The composites benefiting from the excellent mechanical and absorption performance have significant potential in stealth technology fields.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
Tang, M., Zhang, J.Y., Bi, S., Hou, Z.L., Cao, M.S., et al.: Ultrathin topological insulator absorber: unique dielectric behavior of Bi2Te3 Nanosheets based on conducting surface states. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(36), 33285–33291 (2019)
Li, Z.J., Hou, Z.L., Song, W.L., Liu, X.D., Cao, W.Q., Cao, M.S., et al.: Unusual continuous dual absorption peaks in Ca-doped BiFeO3 nanostructures for broadened microwave absorption. Nanoscale 8(19), 10415–10424 (2016)
Xue, W., Yang, G., Bi, S., Zhang, J.Y., Hou, Z.L.: Construction of caterpillar-like hierarchically structured Co/MnO/CNTs derived from MnO2/ZIF-8@ ZIF-67 for electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 173, 521–527 (2021)
Khan, Z.I., Mohamad, Z., Rahmat, A.R., et al.: Synthesis and Characterization of Composite Materials with Enhanced Thermo-Mechanical Properties for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (Uavs) and Aerospace Technologies. Pertanika J. Sci. Technology 29(3), (2021)
Gupta, T.K., Singh, B.P., Mathur, R.B., et al.: Multi-walled carbon nanotube–graphene–polyaniline multiphase nanocomposite with superior electromagnetic shielding effectiveness. Nanoscale 6(2), 842–851 (2014)
Hu, Q., Zhang, Y., Mao, Y., et al.: A comparative study on interlaminar properties of l-shaped two-dimensional (2d) and three-dimensional (3d) woven composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 26(3), 723–744 (2019)
Li, W., Xu, L., Zhang, X., et al.: Investigating the effect of honeycomb structure composite on microwave absorption properties. Composites Communications 19, 182–188 (2020)
Kwak, B.S., Jeong, G.W., Choi, W.H., et al.: Microwave-absorbing honeycomb core structure with nickel-coated glass fabric prepared by electroless plating. Compos. Struct. 256, 113148 (2021)
Yang, Y.N., Xia, L., Zhang, T., Shi, B., et al.: Fe3O4@ LAS/RGO composites with a multiple transmission-absorption mechanism and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 352, 510–518 (2018)
Qiu, J., Qiu, T.T.: Fabrication and microwave absorption properties of magnetite nanoparticle–carbon nanotube–hollow carbon fiber composites. Carbon 81, 20–28 (2015)
Geeri, S., Kolakoti, A.: Electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of MWCNTs based polymer nanocomposites. World J. Eng. (2021)
Wang, L., Bai, X., Wen, B., et al.: Honeycomb-like Co/C composites derived from hierarchically nanoporous ZIF-67 as a lightweight and highly efficient microwave absorber. Compos. B Eng. 166, 464–471 (2019)
Liu, P.B., Gao, S., Wang, Y., Huang, Y., et al.: Carbon nanocages with N-doped carbon inner shell and Co/N-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 381, 122653 (2020)
Das, S., Sharma, S., Yokozeki, T., et al.: Conductive layer-based multifunctional structural composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Struct. 261, 113293 (2021)
Guo, R.Q., Zhang, L.X., Lu, Y., et al.: Research progress of nanocellulose for electrochemical energy storage: A review. J. Energy Chem. 51, 342–361 (2020)
Liu, P., Gao, S., Wang, Y., et al.: Core–shell CoNi@ graphitic carbon decorated on B, N-codoped hollow carbon polyhedrons toward lightweight and high-efficiency microwave attenuation[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(28), 25624–25635 (2019)
Luo, H., Chen, F., Wang, F., et al.: Preparation and microwave absorption properties of honeycomb core structures coated with composite absorber. AIP Adv. 8(5), 056635 (2018)
Khurram, A.A., Ali, N., Rakha, S.A., et al.: Optimization of the carbon coating of honeycomb cores for broadband microwave absorption. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 56(5), 1061–1066 (2014)
Shi, K., Li, J., Wu, Y., et al.: Lightweight composite microwave absorption materials based on graphene aerogels with honeycomb structure. physica status solidi (RRL)–Rapid Res. Lett. 13(8), 1900179.
Tang, J., Bi, S., Su, Z.A., et al.: Surface modification and microwave absorption properties of lightweight CNT absorbent[J]. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(24), 21048–21058 (2019)
Zhang, K.L., Hou, Z.L., Bi, S., Fang, H.M., et al.: Modeling for multi-resonant behavior of broadband metamaterial absorber with geometrical substrate. Chin. Phys. B 26(12), 585–590 (2017)
Liu, Y., Su, X.L., He, X.H., et al.: Influence of carbothermic reduction temperature on electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of double loss Ti3SiC2/Co3Fe7 powders. J. Alloy. Compd. 779, 286–292 (2019)
Wang, Y., Gao, X., Fu, Y.Q., et al.: Enhanced microwave absorption performances of polyaniline/graphene aerogel by covalent bonding. Compos. B Eng. 169, 221–228 (2019)
Lu, S.R., Xia, L., Xu, J.M., et al.: Permittivity-regulating strategy enabling superior electromagnetic wave absorption of lithium aluminum silicate/rGO nanocomposites[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(20), 18626–18636 (2019)
Zhao, B., Li, Y., Zeng, Q.W., Che, R.C., et al.: Galvanic Replacement Reaction Involving Core-Shell Magnetic Chains and Orientation-Tunable Microwave Absorption Properties. Small 16(40), 2003502 (2020)
Zhang, K.L., Zhang, J.Y., Hou, Z.L., et al.: Multifunctional broadband microwave absorption of flexible graphene composites. Carbon 141, 608–617 (2019)
Cao, M.S., Han, C., Wang, X.X., et al.: Graphene nanohybrids: excellent electromagnetic properties for the absorbing and shielding of electromagnetic waves. J. Mater. Chem. C 6(17), 4586–4602 (2018)
Luo, C.J., Jiao, T., Gu, J.W., et al.: Graphene shield by SiBCN ceramic: a promising high-temperature electromagnetic wave-absorbing material with oxidation resistance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10(45), 39307–39318 (2018)
Liu, J., Cao, M.S., Luo, Q., et al.: Electromagnetic property and tunable microwave absorption of 3D nets from nickel chains at elevated temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(34), 22615–22622 (2016)
Cao, M.S., Cai, Y.Z., He, P., et al.: 2D MXenes: electromagnetic property for microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 359, 1265–1302 (2019)
Liu, Z.W., Che, R.C., Wei, Y., et al.: Broadening microwave absorption via a multi-domain structure. APL Mater. 5(4), 046104 (2017)
Liu, P.B., Gao, S., Zhang, G.Z., et al.: Hollow Engineering to Co@ N‐Doped Carbon Nanocages via Synergistic Protecting‐Etching Strategy for Ultrahigh Microwave Absorption. Adv. Functional Mater. 2102812 (2021)
Wu, Z.C., Pei, K., Xing, L.S., Che, R.C., et al.: Enhanced microwave absorption performance from magnetic coupling of magnetic nanoparticles suspended within hierarchically tubular composite. Adv. Func. Mater. 29(28), 1901448 (2019)
Gato, L.B.L., Ribeiro Filho. S.L.M., Panzera, T.H., et al.: Sandwich Structures Made of Discarded Bottle Caps Core and Hybrid Glass Fibre Composite Skins. Appl. Compos. Maters. 1–23 (2021)
Li, D., Li, X., Dai, J., et al.: A comparison of curing process-induced residual stresses and cure shrinkage in micro-scale composite structures with different constitutive laws[J]. Appl. Compos. Mater. 25(1), 67–84 (2018)
Gu, W.H., Sheng, J.Q., Huang, Q.Q., Ji, G.B., et al.: Environmentally friendly and multifunctional shaddock peel-based carbon aerogel for thermal-insulation and microwave absorption[J]. Nano-Micro Letters 13(1), 1–14 (2021)
Quan, B., Gu, W.H., Sheng, J.Q., Ji, G.B., et al.: From intrinsic dielectric loss to geometry patterns: dual-principles strategy for ultrabroad band microwave absorption[J]. Nano Res. 14(5), 1495–1501 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62005010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, S., Zhao, Y., Hou, G. et al. Microwave Absorption and Mechanical Properties of CNTs/ PU Composites with Honeycomb Structure. Appl Compos Mater 29, 1393–1407 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-022-10021-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-022-10021-8