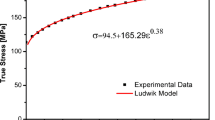
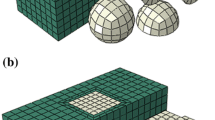
Abstract
Mechanical behavior of aluminum matrix composites reinforced with SiC particles are predicted using an axisymmetric micromechanical finite element model. The model aims to study initiation and propagation of interphase damage subjected to combination of thermal and uniaxial loading. Effects of manufacturing process thermal residual stresses and interphase de-bonding are considered. The model includes a square Representative Volume Element (RVE) from a cylindrical unit cell representing a quarter of SiC particle surrounded by Al-3.5wt.%Cu matrix. Suitable boundary conditions are defined to include effects of combined thermal and uniaxial tension loading on the RVE. An appropriate damage criterion with a linear relationship between radial and shear stresses for interphase damage is introduced to predict initiation and propagation of interphase de-bonding during loading. A damage user subroutine is developed and coupled to the finite element software to model interphase damage. Overall Stress-strain behavior of particulate metal-matrix composite by considering residual stresses is compared with experimental data to estimate interphase strength. Effects of thermal residual stresses in elastic, de-bonding and plastic zones of composite system are discussed in details. Furthermore, parametric study results show high influence of interphase strength on the overall mechanical behavior of composite material.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwarts, M.M.: Properties, nondestructive testing and repair. Composite materials. New Jersey, USA (1997)
Ceschini, L., Bosi, C., Casagrande, A., Garagnani, G.L.: Effect of thermal treatment and recycling on the tribological behaviour of an AlSiMg-SiCp composite. Wear 25, 1377–1385 (2001)
Lloyd, D.J.: Particle reinforced aluminium and magnesium matrix composites. Int. Mater. Rev. 39(1), 1–23 (1994)
Llorca, J., Needleman, A., Suresh, S.: An analysis of the effects of matrix viod growth on deformation and ductility in metal-matrix composites. Acta. Metall. Mater. 39(10), 2317–2335 (1991)
Majumdar, B.S., Newaz, G.M.: Inelastic deformation of metal-matrix composites: plasticity and damage mechanisms. Philos. Mag. A 66(2), 187–212 (1992)
Eshelby, J.D.: The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion, and related problems. Proc. Roy. Soc. London 241, 376–396 (1957)
Qu, J.: Eshelby tensor for an elastic inclusion with slightly weakened interfaces. J. Appl. Mech. 60(4), 1048–1050 (1993)
Aboudi, J.: Damage in composites modelling of imperfect bonding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 28, 103–128 (1987)
Mura, T., Furuhashi, R.: The elastic inclusion with a sliding interface. ASME. J. Appl. Mech. 51, 308–310 (1984)
Hashin, Z.: The spherical inclusion with imperfect interface. ASME. J. Appl. Mech. 62, 860–866 (1990)
Wang, W.H., Sadeghpour, K., Baran, G.: Finite element analysis of the effect of an interphase on toughening of a particle reinforced polymer composite. Compos. Part A 39, 956–964 (2008)
Voyiadjis, G.Z., Allen, D.H.: Damage and interfacial debonding in composites. Studies in Applied Mechanics. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1996)
Shao, J.C., Xiao, B.L., Wang, Q.Z., Yang, K.: An enhanced FEM model for particle size dependent flow strengthening and interface damage in particle reinforced metal matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 71(1), 39–45 (2011)
Yang, H., Chen, P., Jiang, J., Tohgo, K.: Incremental damage theory of particulate-reinforced composites with a ductile interphase. Compos. Struct. 93, 2655–2662 (2011)
Lauke, B.: Determination of adhesion strength between a coated particle and polymer matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 66, 3153–3160 (2006)
Shabana, M.: A micromechanical model for composites containing multi-layered interphases. Compos. Struct. 101, 265–273 (2013)
Lee, H.K., Pyo, S.H.: An elasto plastic multi-level damage model for ductile matrix composites considering evolutionary weakend interface. Int. J. Solids Struct. 45, 1614–1631 (2008)
Benabou, L., Benseddiq, N., Naїt-Abdelaziz, M.: Comparative analysis of damage at interfaces of composites. Compos. Part B 33, 215–224 (2002)
Qing, H.: Automatic generation of 2D micromechanical finite element model silicon-carbide/aluminium metal matrix composites: effects of the boundary conditions. Mater. Des. 44, 446–453 (2013)
Wisnom, M.R.: Micromechanical Modelling of the Transverse Tensile Ductility of Unidirectional Silicon Carbide/6061 Aluminum. Compos. Technol. Res. 14(2), 61–69 (1992)
Aghdam, M.M., Falahatgar, S.R., Gorji, M.: Micromechanical consideration of interface damage in fiber reinforced Ti-alloy under various combined loading conditions. Compos. Sci. Technol. 8, 3406–3411 (2008)
Shokrieh, M.M., Ghanei Mohammadi, A.R.: Finite element modeling of residual thermal stresses in fiber-reinforced composites using different representative volume elements. Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, London 2010, ISBN: 978-988-18210-7-2
Durodola, J.F., Derby, B.: An analysis of thermal residual stresses in Ti-6Al-4V alloy reinforced with SiC and Al2O3 fibers. Acta. Metall. Mater. 42(5), 1525–1534 (1994)
Liu, H.T., Sun, L.Z.: Effects of thermal residual stresses on effective elastoplastic behaviour of metal matrix composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41(8), 2189–2203 (2004)
Bouafia, F., Serier, B., Bouiadjra, B.A.: Finite element analysis of the thermal residual stresses of Sic particle reinforced aluminium composite. Comput. Mater. Sci. 54, 195–203 (2012)
Yanese, K., Ju, J.W.: Size-dependent probabilistic micromechanical damage mechanics for particle-reinforced metal matrix composites. Int. J. Damage Mech. 20(7), 1021–1048 (2011)
Hibbitt, K. & Sorenson, Inc., ABAQUS/Standard user subroutines reference manual, “USDFLD”, Section 1.1.45, Version 6.9.1., USA (2009)
Llorca, J., Martin, A., Ruiz, J., Elices, M.: Particulate Fracture during Deformation of a Spray Formed Metal- Matrix Composite. Metall. Trans. A 24, 1575 (1993)
Segurado, J., Gonzalez, C., LLorca, J.: A numerical investigation of the effect of particle clustering on the mechanical properties of composites. Acta Mater. 51, 2355–2369 (2003)
Tvergaard, V.: On localization in ductile materials containing spherical voids. Int. J. Fract. 18, 237–252 (1982)
Marur, P.R.: Estimation of effective elastic properties and interface stress concentration in particulate composites by unit cell methods. Acta Mater. 52, 1263–1270 (2004)
Zong, Li, J., Wang, B.Y., Zhuang, Y.M.: Experiment and modeling of mechanical properties on iron matrix composites reinforced by different types of ceramic particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527, 7545–7551 (2010)
Su, X.F., Chen, H.R., Kennedy, D., Williams, F.W.: Effects of interphase strength on the damage modes and mechanical behaviour of metal-matrix composites. Compos. Part A 30, 257–266 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aghdam, M.M., Shahbaz, M. Effects of Interphase Damage and Residual Stresses on Mechanical Behavior of Particle Reinforced Metal-Matrix Composites. Appl Compos Mater 21, 429–440 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-013-9348-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-013-9348-1