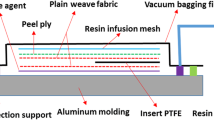
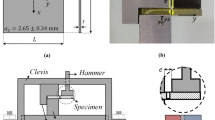
Abstract
A test method, with specimen design similar to that proposed by O’Brien et al. (see [23–26]) but under 3-point bending, is proposed to measure the critical strain energy release rate (G c) for delamination in fibre-reinforced polymers (FRP) under out-of-plane (transverse) loading. Unlike end-notch-flexure (ENF) test or double-cantilever-beam (DCB) test that are currently used, the new method does not require an insert film or a pre-crack to initiate delamination. Instead, the delamination was initiated from a FRP layer of the same composition but with different fibre orientation. Difference of the fibre orientation used in this study was 90○, i.e. one 90○ layer in the mid-thickness and the rest 0○ layers. Under 3-point bending, matrix shear cracking was firstly initiated in the 90○ layer, mimicking the mechanism for delamination initiation in the FRP when subjected to transverse loading. The matrix shear cracking led to delamination in the adjacent interlaminar regions, of which area can be measured after the test. Calculation of G c was based on “area method”, that is, dividing the total energy loss by the delamination area. The G c was compared with that from plate specimens of the same composition and fibre lay-up but subjected to transverse point loading. The comparison suggests that very similar G c values were produced from the two types of testing, even though unstable crack growth occurred under 3-point bending and stable crack growth under transverse point loading. Therefore, the proposed method has the potential of quantifying delamination resistance of FRP under the transverse loading conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hashemi, S., Kinloch, A. J. and Williams, J. G., ‘The Analysis of Interlaminar Fracture in Uniaxial Fibre-Polymer Composites’, Proceedings of the Royal Society. London. Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences 427, 1990, 173–199.
Davies, P., Blackman, B. R. K. and Brunner, A. J., ‘Standard Test Methods for Delamination Resistance of Composite Materials: Current Status’, Applied Composite Materials 5, 1998, 345–364.
JIS K 7086, ‘Testing Method for Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Plastics’, Tokyo, 1993.
ASTM D5528–01, ‘Standard Test Method for Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites’.
Protocols for Interlaminar Fracture Testing of Composites, European Structural Integrity Society (ESIS), Delft, The Netherlands, 1993.
ISO 15024: 2001. ‘Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Composites – Determination of Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness, G Ic, for Unidirectionally Reinforced Materials’.
O’Brien, T. K., ‘Interlaminar Fracture Toughness: The Long and Winding Road to Standardization’, Composites: Part B 29, 1998, 57–62.
Davies, P., Sims, G. D., Blackman, B. R. K., Brunner, A. J., Kageyama, K., Hojo, M., Tanaka, K., Murri, G., Rousseau, C., Gieseke, B. and Martin, R. H., ‘Comparison of Test Configurations for Determination of Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness Results from International Collaborative Test Programme’, Plastics, Rubber and Composites 28, 1999, 432–437.
Carlsson, L. A., Gillespie, J. W., Jr. and Pipes, R. B., ‘On the Analysis and Design of the End Notched Flexure (ENF) Specimen for Mode II Testing’, Journal of Composite Materials 20, 1986, 594–604.
Tanaka, K., Kageyama, K. and Hojo, M., ‘Prestandardization Study on Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness Test for CFRP in Japan’, Composites 26, 1995, 257–267.
Martin, R. H. and Davidson, B. S., ‘Mode II Fracture Using a 4 Point Bend End-Notched Flexure Test’, in: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Deformation and Fracture of Composites, Manchester, UK, March 1997.
Ozdil, F., Carlsson, L. A. and Davies, P., ‘Beam Analysis of Angle-Ply Laminate End-Notched Flexure Specimens’, Composites Science and Technology 58, 1998, 1929–1938.
de Morais, A.B., ‘Analysis of Mode II Interlaminar Fracture of Multidirectional Laminates’, Composites: Part A 35, 2004, 51–57.
Pereira, A. B., de Morais, A. B., Marques, A. T. and de Castro, P. T., ‘Mode II Interlaminar Fracture of Carbon/Epoxy Multidirectional laminates’, Composites Science and Technology 64, 2004, 1653–1659.
Chai, H., ‘Interlaminar Shear Fracture of Laminated Composites’, International Journal of Fracture 43, 1990, 117–131.
Choi, N. S., Kinloch, A. J. and Williams, J. G., ‘Delamination Fracture of Multidirectional Carbon-Fiber/Epoxy Composites under Mode I, Mode II and Mixed-Mode I/II Loading’, Journal of Composite Materials 33, 1999, 73–101.
Tao, J. and Sun, C. T., ‘Influence of Ply Orientation on Delamination in Composite Laminates’, Journal of Composite Materials 32, 1998, 1933–1947.
Polaha, J. J., Davidson, B. D., Hudson, R. C. and Pieracci, A., ‘Effects of Mode Ratio, Ply Orientation and Precracking on the Delamination Toughness of a Laminated Composite’, Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites 15, 1996, 141–173.
Chou, I., Kimpara, I., Kageyama, K. and Ohsawa, I., ‘Mode I and Mode II fracture toughness measured between differently oriented plies in graphite/epoxy composites’, in Composite Materials: Fatigue and Fracture, Vol. 5, ASTM STP 1230, R. H. Martin (ed.), American Society for Testing and Materials, 1995, pp. 132–151.
Compston, P., ‘Matrix-to-Composite Toughness Transfer in Mode I and Mode II Interlaminar Fracture of Glass-Fibre/Vinyl Ester Composites’, Ph.D. Thesis, The Australian National University, Australia, 1999.
Kuboki, T., Jar, P.-Y. B. and Cheng, J. J. R., ‘Interlaminar Fracture Toughness and the Associated Fracture Behavior for Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers (GFRP)’, Journal of Materials Science 39, 2004, 1419–1423.
Kuboki, T., Jar, P. Y. B. and Cheng, J. J. R., ‘Damage development in Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers (GFRP) under transverse loading’, in Proceedings of Annual Technical Conference 2003 of Society of Plastics Engineers, 2003, pp. 2168–2172.
O’Brien, T. K., ‘Characterization of delamination onset and growth in a composite laminate’, in Damage in Composite Materials, ASTM STP 775, K. L. Reifsnider (ed.), American Society for Testing and Materials, 1982, pp. 140–167.
O’Brien, T. K., Johnston, N. J., Morris, D. H. and Simonds, R. A., ‘A Simple Test for the Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Composites’, SAMPE Journal July/August, 1982, 8–15.
O’Brien, T. K., ‘Mixed-mode strain-energy-release rate effects on edge delamination of composites’, in Effects of Defects in Composite Materials, ASTM STP 836, American Society for Testing and Materials, 1984, pp. 125–142.
O’Brien, T. K., Raju, I. S. and Garber, D. P., ‘Residual Thermal and Moisture Influences on the Strain Energy Release Rate Analysis of Edge Delamination’, Journal of Composites Technology and Research 8(2), Summer 1986, 37–47.
Kuboki, T., Hilvo, T. and Jar, P.-Y. B., ‘Detection of Interlaminar Cracks in Fibre-Reinforced Polymers (FRP)’, Journal of Materials Science Letters 21, 2002, 1789–1791.
ASTM D3763-02, ‘Standard Test Method for High Speed Puncture Properties of Plastics Using Load and Displacement Sensors’.
Joshi, S. P. and Sun, C. T., ‘Impact Induced Fracture in a Laminated Composite’, Journal of Composite Materials 19, 1985, 51–66.
Doxsee, L. E., Rubbrecht, P., Li, L. and Verpoest, I., ‘Delamination Growth in Composite Plates Subjected to Transverse Loads’, Journal of Composite Materials 27, 1993, 764–781.
Kuboki, T., Gallagher, E., Jar, P.-Y. B. and Cheng, J. J. R., ‘Evaluation of Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Fibre Reinforced Polymers (FRP) under Transverse Loading using Plate Specimens’, CSME-2004, London, Ontario, 2004, 10 pages.
Nairn, J. A., ‘Fracture Mechanics of Composites with Residual Thermal Stresses’, Journal of Applied Mechanics 64, 1997, 804–810.
Nairn, J. A., ‘Energy Release Rate Analysis for Adhesive and Laminate Double Cantilever Beam Specimens Emphasizing the Effect of Residual Stresses’, International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives 20, 2000, 59–70.
de Morais, A. B., ‘Double Cantilever Beam Testing of Multidirectional Laminates’, Composites: Part A 34, 2003, 1135–1142.
Pereira, A. B. and de Morais, A. B., ‘Mode I Interlaminar Fracture of Carbon/Epoxy Multidirectional Laminates’, Composites Science and Technology 64, 2004, 2261–2270.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T. Kuboki: Corresponding author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuboki, T., Gallagher, E., Jar, P.Y.B. et al. A New Method to Quantify Delamination Resistance of Fibre Reinforced Polymers (FRP) under Transverse Loading. Appl Compos Mater 12, 93–108 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-004-6205-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-004-6205-2