Abstract
In virtue of a curved insertion path inside tissues, needle steering techniques have revealed the potential with the assistance of medical robots and images. The superiority of this technique has been preliminarily verified with several maneuvers: target realignment, obstacle circumvention, and multi-target access. However, the momentum of needle steering approaches in the past decade leads to an open question—“How to choose an applicable needle steering approach for a specific clinical application?” This survey discusses this question in terms of design choices and clinical considerations, respectively. In view of design choices, this survey proposes a hierarchical taxonomy of current needle steering approaches. Needle steering approaches of different manipulations and designs are classified to systematically review the design choices and their influences on clinical treatments. In view of clinical consideration, this survey discusses the steerability and acceptability of the current needle steering approaches. On this basis, the pros and cons of the current needle steering approaches are weighed and their suitable applications are summarized. At last, this survey concluded with an outlook of the needle steering techniques, including the potential clinical applications and future developments in mechanical design.






Similar content being viewed by others
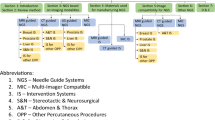
Abbreviations
- BT:
-
Brachytherapy
- CED:
-
Convection-enhanced delivery
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CTN:
-
Concentric tube needle
- DBS:
-
Deep brain stimulation
- DOF:
-
Degree of freedom
- G:
-
Gauge
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- TBNA:
-
Transbronchial needle aspiration
- ICH:
-
Intracranial hemorrhage
- MIS:
-
Minimally invasive surgery
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MWA:
-
Microwave ablation
- PAI:
-
Pubic arch interference
- PBN:
-
Programmable bevel-tip needle
- PCNL:
-
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy
- RFA:
-
Radiofrequency ablation
- ROC:
-
Radius of curvature
- SMA:
-
Shape memory alloy
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- 3D:
-
Three dimensional
References
Ayvali, E., and J. P. Desai. Optical flow-based tracking of needles and needle-tip localization using circular hough transform in ultrasound images. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43(8):1828–1840, 2015.
Pratt, R. L., and A. J. Petruska. Empirically comparing magnetic needle steering models using expectation-maximization. Robotics. 11(2):49, 2022.
Berg, N. J., J. Dankelman, and J. J. Dobbelsteen. Design of an actively controlled steerable needle with tendon actuation and fbg-based shape sensing. Med. Eng. Phys. 37(6):617–622, 2015.
Matheson, E., and F. R. Y. Baena. Biologically inspired surgical needle steering: technology and application of the programmable bevel-tip needle. Biomimetics. 5(4):68, 2020.
Glozman, D., and M. Shoham. Flexible needle steering and optimal trajectory planning for percutaneous therapies. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. New York: Springer, pp. 137–144.
Farooq, M. U., B. Xu, and S. Y. Ko. A concentric tube-based 4-dof puncturing needle with a novel miniaturized actuation system for vitrectomy. Biomed. Eng. Online. 18(1):1–16, 2019.
Berg, N. J., F. C. Meeuwsen, M. Doukas, G. Kronreif, A. Moelker, and J. J. Dobbelsteen. Steerable needles for radio-frequency ablation in cirrhotic livers. Sci. Rep. 11(1):309, 2021.
Rox, M., M. Emerson, T. E. Ertop, I. Fried, M. Fu, J. Hoelscher, A. Kuntz, J. Granna, J. E. Mitchell, M. Lester, F. Maldonado, E. A. Gillaspie, J. A. Akulian, R. Alterovitz, and I. J. RobertWebster. Decoupling steerability from diameter: helical dovetail laser patterning for steerable needles. IEEE Access. 8:181411–181419, 2020.
Schlich, T., and C. L. Tang. Patient choice and the history of minimally invasive surgery. The Lancet. 388(10052):1369–1370, 2016.
Topal, H., R. Aerts, A. Laenen, A. Collignon, J. Jaekers, J. Geers, and B. Topal. Survival after minimally invasive vs open surgery for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. JAMA Netw. Open. 5(12):2248147–2248147, 2022.
Tsumura, R., and H. Iwata. Trajectory planning for abdominal fine needle insertion based on insertion angles. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2(2):1226–1231, 2017.
Kim, Y.-J., S. B. Park, C.-H. Yoon, Y. Kim, H.-S. Kang, and Y.-H. Jo. Robust deflected path planning method for superelastic nitinol coaxial biopsy needle: application to an automated magnetic resonance image-guided breast biopsy robot. IEEE Trans. Robot. 38(4):2220–2237, 2022.
Berg, N. J., D. J. Gerwen, J. Dankelman, and J. J. Dobbelsteen. Design choices in needle steering—a review. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 20(5):2172–2183, 2015.
Rossa, C., and M. Tavakoli. Issues in closed-loop needle steering. Control Eng. Pract. 62:55–69, 2017.
Scali, M., T. P. Pusch, P. Breedveld, and D. Dodou. Needle-like instruments for steering through solid organs: a review of the scientific and patent literature. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 231(3):250–265, 2017.
Li, P., Z. Yang, and S. Jiang. Needle-tissue interactive mechanism and steering control in image-guided robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery: a review. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 56(6):931–949, 2018.
Audette, M. A., S. P. A. Bordas, and J. E. Blatt. Robotically steered needles: a survey of neurosurgical applications and technical innovations. Robot. Surg. 7:1–23, 2020.
Babaiasl, M., F. Yang, and J. P. Swensen. Robotic needle steering: state-of-the-art and research challenges. Intell. Serv. Robot. 15(5):679–711, 2022.
Wu, K., B. Li, Y. Zhang, and X. Dai. Review of research on path planning and control methods of flexible steerable needle puncture robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 27(1):91–112, 2022.
Lu, M., Y. Zhang, C. M. Lim, and H. Ren. Flexible needle steering with tethered and untethered actuation: current states, targeting errors, challenges and opportunities. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 51(5):905–924, 2023.
Su, H., K. W. Kwok, K. Cleary, I. Iordachita, M. C. Cavusoglu, J. P. Desai, and G. S. Fischer. State of the art and future opportunities in mri-guided robotassisted surgery and interventions. Proc. IEEE. 110(7):968–992, 2022.
Omisore, O. M., S. Han, J. Xiong, H. Li, Z. Li, and L. Wang. A review on flexible robotic systems for minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 52(1):631–644, 2022.
Yaniv, Z., P. Cheng, E. Wilson, T. Popa, D. Lindisch, E. Campos-Nanez, H. Abeledo, V. Watson, K. Cleary, and F. Banovac. Needle-based interventions with the image-guided surgery toolkit (igstk): from phantoms to clinical trials. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57(4):922–933, 2010.
Yu, X., H. Wang, X. Ning, R. Sun, H. Albadawi, M. Salomao, A. C. Silva, Y. Yu, L. Tian, A. Koh, C. M. Lee, A. Chempakasseril, P. Tian, M. Pharr, J. Yuan, Y. Huang, R. Oklu, and J. A. Rogers. Needle-shaped ultrathin piezoelectric microsystem for guided tissue targeting via mechanical sensing. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2(3):165–172, 2018.
Li, A. D. R., Y. Liu, J. Plott, L. Chen, J. S. Montgomery, and A. Shih. Multi-bevel needle design enabling accurate insertion in biopsy for cancer diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 68(5):1477–1486, 2021.
McDermott, S., and D. A. Gervais. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 30(1):49–55, 2013.
Ramakonar, H., B. C. Quirk, R. W. Kirk, J. Li, A. Jacques, C. R. Lind, and R. A. McLaughlin. Intraoperative detection of blood vessels with an imaging needle during neurosurgery in humans. Sci. Adv. 4(12):4992, 2018.
Gilbert, H. B., J. Neimat, I. Robert, and J. Webster. Concentric tube robots as steerable needles: achieving follow-the-leader deployment. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31(2):246–258, 2015.
Ahn, W., J. Bahk, Y. Lim, and Y. Kim. The effect of introducer gauge, design and bevel direction on the deflection of spinal needles. Anaesthesia. 57(10):1007–1011, 2002.
Bernardes, M. C., B. V. Adorno, P. Poignet, N. Zemiti, and G. A. Borges. Adaptive path planning for steerable needles using duty-cycling. In: 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 2545–2550.
Girerd, C., A. V. Kudryavtsev, P. Rougeot, P. Renaud, K. Rabenorosoa, and B. Tamadazte. Automatic tip-steering of concentric tube robots in the trachea based on visual slam. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics. 2(4):582–585, 2020.
Fu, M., A. Kuntz, I. Webster, J. Robert, and R. Alterovitz. Safe motion planning for steerable needles using cost maps automatically extracted from pulmonary images. In: 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 4942–4949, 2018.
Webster, R. J., J. S. Kim, N. J. Cowan, G. S. Chirikjian, and A. M. Okamura. Nonholonomic modeling of needle steering. Int. J. Robot. Res. 25(5–6):509–525, 2006.
Hoelscher, J., I. Fried, M. Fu, M. Patwardhan, M. Christman, J. Akulian, I. Webster, J. Robert, and R. Alterovitz. A metric for finding robust start positions for medical steerable needle automation. In: 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 9526–9533, 2022.
Cowan, N. J., K. Goldberg, G. S. Chirikjian, G. Fichtinger, R. Alterovitz, K. B. Reed, V. Kallem, W. Park, S. Misra, and A. M. Okamura. Chapter 23. Robotic needle steering: Design, modeling, planning, and image guidance, pp. 557–582, 2011.
Northcutt, B. G., A. A. Shah, Y. R. Sheu, and L. Carmi. Wires, catheters, and more: a primer for residents and fellows entering interventional radiology. RadioGraphics. 35(5):1621–1622, 2015.
Jeong, S., Y. Chitalia, and J. P. Desai. Design, modeling, and control of a coaxially aligned steerable (coast) guidewire robot. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 5(3):4947–4954, 2020.
Ali, A., D. H. Plettenburg, and P. Breedveld. Steerable catheters in cardiology: classifying steerability and assessing future challenges. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63(4):679–693, 2016.
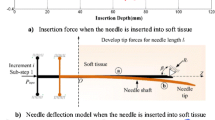
Abolhassani, N., R. Patel, and M. Moallem. Needle insertion into soft tissue: a survey. Med. Eng. Phys. 29(4):413–431, 2007.
Lehmann, T., R. Sloboda, N. Usmani, and M. Tavakoli. Model-based needle steering in soft tissue via lateral needle actuation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3(4):3930–3936, 2018.
Gerboni, G., J. D. Greer, P. F. Laeseke, G. L. Hwang, and A. M. Okamura. Highly articulated robotic needle achieves distributed ablation of liver tissue. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2(3):1367–1374, 2017.
Zhao, Y.-J., Z.-H. Liu, Y.-D. Zhang, and Z.-Q. Liu. Kinematic model and its parameter identification for cannula flexible needle insertion into soft tissue. Adv. Mech. Eng. 11(6):1687814019852185, 2019.
Yamada, A., N. Nitta, S. Naka, D. Khiem Tran, S. Morikawa, and T. Tani. Design and implementation of loop shaped steering mechanisms for flexible needles. In: 7th International Conference on the Development of Biomedical Engineering in Vietnam (BME7) Translational Health Science and Technology for Developing Countries 7, vol. 69, pp. 15–19.
Okamura, A. M., C. Simone, and M. D. O’Leary. Force modeling for needle insertion into soft tissue. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51(10):1707–1716, 2004.
Zhao, B., L. Lei, L. Xu, S. Li, Y. Hu, J. Zhang, X. Yang, and Y. Zhang. Needle deflection modeling and preoperative trajectory planning during insertion into multilayered tissues. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 26(2):943–954, 2021.
Khadem, M., C. Rossa, R. S. Sloboda, N. Usmani, and M. Tavakoli. Mechanics of tissue cutting during needle insertion in biological tissue. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 1(2):800–807, 2016.
Webster, R. J., and B. A. Jones. Design and kinematic modeling of constant curvature continuum robots: a review. Int. J. Robot. Res. 29(13):1661–1683, 2010.
Wedlick, T. R., and A. M. Okamura. Characterization of pre-curved needles for steering in tissue. In: 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 1200–1203.
Majewicz, A., T. R. Wedlick, K. B. Reed, and A. M. Okamura. Evaluation of robotic needle steering in ex vivo tissue. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2068–2073.
Majewicz, A., S. P. Marra, M. G. V. Vledder, M. Lin, M. A. Choti, D. Y. Song, and A. M. Okamura. Behavior of tip-steerable needles in ex vivo and in vivo tissue. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59(10):2705–2715, 2012.
Karimi, S., and B. Konh. Kinematics modelling and dynamics analysis of an smaactuated active flexible needle for feedback-controlled manipulation in phantom. Med. Eng. Phys.107:103846, 2022.
Burgner, J., P. J. Swaney, T. L. Bruns, M. S. Clark, D. C. Rucker, E. C. Burdette, and R. J. Webster. An autoclavable steerable cannula manual deployment device: design and accuracy analysis. J. Med. Devices.6(4):041007, 2012.
Konh, B., B. Padasdao, Z. Batsaikhan, and J. Lederer. Steering a tendon-driven needle in high-dose-rate prostate brachytherapy for patients with pubic arch interference. In: 2021 International Symposium on Medical Robotics (ISMR), pp. 1–7.
Yamada, A., S. Naka, N. Nitta, S. Morikawa, and T. Tani. A loop-shaped flexible mechanism for robotic needle steering. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3(2):648–655, 2018.
Lindenroth, L., S. Bano, A. Stilli, J. G. Manjaly, and D. Stoyanov. A fluidic soft robot for needle guidance and motion compensation in intratympanic steroid injections. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6(2):871–878, 2021.
Gilbert, H. B., and R. J. Webster. Can concentric tube robots follow the leader? In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4881–4887.
Swaney, P. J., J. Burgner, H. B. Gilbert, and R. R. J. Webster. A flexure-based steerable needle: high curvature with reduced tissue damage. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60(4):906–909, 2013.
Lehmann, T., C. Rossa, N. Usmani, R. Sloboda, and M. Tavakoli. Deflection modeling for a needle actuated by lateral force and axial rotation during insertion in soft phantom tissue. Mechatronics. 48:42–53, 2017.
A. Krupa. A new duty-cycling approach for 3d needle steering allowing the use of the classical visual servoing framework for targeting tasks. In: 2014 5th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference for Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), pp. 301–307.
Moreira, P., and S. Misra. Biomechanics-based curvature estimation for ultrasoundguided flexible needle steering in biological tissues. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43(8):1716–1726, 2015.
Khadem, M., C. Rossa, N. Usmani, R. S. Sloboda, and M. Tavakoli. A two-body rigid/flexible model of needle steering dynamics in soft tissue. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 21(5):2352–2364, 2016.
Khadem, M., C. Rossa, N. Usmani, R. S. Sloboda, and M. Tavakoli. Geometric control of 3d needle steering in soft-tissue. Automatica. 101:36–43, 2019.
Reed, K. B., A. M. Okamura, and N. J. Cowan. Controlling a robotically steered needle in the presence of torsional friction. In: 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3476–3481.
Khadem, M., C. Rossa, N. Usmani, R. S. Sloboda, and M. Tavakoli. Feedbacklinearization-based 3d needle steering in a frenet-serret frame using a reduced order bicycle model. In: 2017 American Control Conference (ACC), pp. 1438–1443.
Reed, K. B., A. M. Okamura, and N. J. Cowan. Modeling and control of needles with torsional friction. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 56(12):2905–2916, 2009.
K. B. Reed. Compensating for torsion windup in steerable needles. In: 2008 2nd IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), pp. 936–941.
Swensen, J. P., M. Lin, A. M. Okamura, and N. J. Cowan. Torsional dynamics of steerable needles: modeling and fluoroscopic guidance. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61(11):2707–2717, 2014.
Berg, N. J., T. L. Jong, D. J. Gerwen, J. Dankelman, and J. J. Dobbelsteen. The influence of tip shape on bending force during needle insertion. Sci. Rep. 7:40477, 2017.
Engh, J. A., G. Podnar, D. Kondziolka, and C. N. Riviere. Toward effective needle steering in brain tissue. In: 2006 International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 559–562.
Qi, Z., Q. Luo, and H. Zhang. A tube-based robust mpc for duty-cycled rotation needle steering systems with bounded disturbances. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 44(4):960–970, 2021.
Engh, J. A., D. S. Minhas, D. Kondziolka, and C. N. Riviere. Percutaneous intracerebral navigation by duty-cycled spinning of flexible bevel-tipped needles. Neurosurgery. 67(4):1117–1122, 2010.
Lin, C. L., and Y. A. Huang. Simultaneously reducing cutting force and tissue damage in needle insertion with rotation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 67(11):3195–3202, 2020.
Tsumura, R., Y. Takishita, Y. Fukushima, and H. Iwata. Histological evaluation of tissue damage caused by rotational needle insertion. In: 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 5120–5123.
Majewicz, A., J. J. Siegel, A. A. Stanley, and A. M. Okamura. Design and evaluation of duty-cycling steering algorithms for robotically-driven steerable needles. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 5883–5888.
Konh, B., D. Sasaki, T. K. Podder, and H. Ashrafiuon. 3d manipulation of an active steerable needle via actuation of multiple sma wires. Robotica. 38(3):410–426, 2020.
Adebar, T. K., J. D. Greer, P. F. Laeseke, G. L. Hwang, and A. M. Okamura. Methods for improving the curvature of steerable needles in biological tissue. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63(6):1167–1177, 2016.
Berg, N. J., J. Dankelman, and J. J. Dobbelsteen. Endpoint accuracy in manual control of a steerable needle. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 28(2):276–283, 2017.
Scali, M., P. A. H. Veldhoven, P. W. J. Henselmans, D. Dodou, and P. Breedveld. Design of an ultra-thin steerable probe for percutaneous interventions and preliminary evaluation in a gelatine phantom. PLoS ONE. 14(9):0221165, 2019.
De Falco, I., C. Culmone, A. Menciassi, J. Dankelman, and J. J. Dobbelsteen. A variable stiffness mechanism for steerable percutaneous instruments: integration in a needle. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 56(12):2185–2199, 2018.
Henken, K. R., P. R. Seevinck, J. Dankelman, and J. J. Dobbelsteen. Manually controlled steerable needle for MRI-guided percutaneous interventions. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 55(2):235–244, 2017.
Varnamkhasti, Z. K., and B. Konh. Design and performance study of a novel minimally invasive active surgical needle. J. Med. Devices.13(4):041006, 2019.
Datla, N. V., and P. Hutapea. Flexure-based active needle for enhanced steering within soft tissue. J. Med. Devices.9(4):041005, 2015.
Ayvali, E., C. P. Liang, M. Ho, Y. Chen, and J. P. Desai. Towards a discretely actuated steerable cannula for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Int. J. Robot. Res. 31(5):588–603, 2012.
Pratt, R. L., and A. J. Petruska. Magnetic needle steering model identification using expectation-maximization. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 5432–5437.
Petruska, A. J., F. Ruetz, A. Hong, L. Regli, O. Sürücü, A. Zemmar, and B. J. Nelson. Magnetic needle guidance for neurosurgery: initial design and proof of concept. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4392–4397.
Hong, A., A. J. Petruska, A. Zemmar, and B. J. Nelson. Magnetic control of a flexible needle in neurosurgery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 68(2):616–627, 2021.
Hong, A., Q. Boehler, R. Moser, A. Zemmar, L. Stieglitz, and B. J. Nelson. 3d path planning for flexible needle steering in neurosurgery. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 15(4):1998, 2019.
Babaiasl, M., F. Yang, S. Boccelli, and J. P. Swensen. Fracture-directed waterjet needle steering: Design, modeling, and path planning. In: 2020 8th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference for Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), pp. 1166–1173.
Babaiasl, M., F. Yang, and J. P. Swensen. Duty cycling of waterjet can improve steerability and radius-of-curvature (roc) for waterjet steerable needles. In: 2020 International Symposium on Medical Robotics (ISMR), pp. 50–56, 2020.
Frasson, L., S. Y. Ko, A. Turner, T. Parittotokkaporn, J. F. Vincent, and F. Baena. Sting: a soft-tissue intervention and neurosurgical guide to access deep brain lesions through curved trajectories. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H. 224(6):775–788, 2010.
Ko, S. Y., B. L. Davies, and F. R. Y. Baena. Two-dimensional needle steering with a “programmable bevel” inspired by nature: Modeling preliminaries. In: 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 2319–2324.
Watts, T., R. Secoli, and F. R. Y. Baena. A mechanics-based model for 3-d steering of programmable bevel-tip needles. IEEE Trans. Robot. 35(2):371–386, 2019.
Favaro, A., R. Secoli, F. Baena, and E. De Momi. Model-based robust pose estimation for a multi-segment, programmable bevel-tip steerable needle. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 5(4):6780–6787, 2020.
Donder, A., and F. R. Y. Baena. Kalman-filter-based, dynamic 3-d shape reconstruction for steerable needles with fiber bragg gratings in multicore fibers. IEEE Trans. Robot. 38(4):2262–2275, 2022.
Lee, J., J. Wang, and W. Park. Efficient mechanism design and systematic operation planning for tube-wire flexible needles. J. Mech. Robot.10(6):065001, 2018.
Okazawa, S., R. Ebrahimi, J. Chuang, S. E. Salcudean, and R. Rohling. Handheld steerable needle device. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 10(3):285–296, 2005.
Bui, V. K., S. Park, J.-O. Park, and S. Y. Ko. A novel curvature-controllable steerable needle for percutaneous intervention. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 230(8):727–738, 2016.
Torabi, M., K. Hauser, R. Alterovitz, V. Duindam, and K. Goldberg. Guiding medical needles using single-point tissue manipulation. In: 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2705–2710.
Mallapragada, V. G., N. Sarkar, and T. K. Podder. Robot-assisted real-time tumor manipulation for breast biopsy. IEEE Trans. Robot. 25(2):316–324, 2009.
DiMaio, S. P., and S. E. Salcudean. Needle steering and model-based trajectory planning. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. New York: Springer, 2003, pp. 33–40.
DiMaio, S. P., and S. E. Salcudean. Needle steering and motion planning in soft tissues. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 52(6):965–974, 2005.
Glozman, D., and M. Shoham. Image-guided robotic flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans. Robot. 23(3):459–467, 2007.
Neubach, Z., and M. Shoham. Ultrasound-guided robot for flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57(4):799–805, 2010.
Chevrie, J., N. Shahriari, M. Babel, A. Krupa, and S. Misra. Flexible needle steering in moving biological tissue with motion compensation using ultrasound and force feedback. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3(3):2338–2345, 2018.
Chevrie, J., A. Krupa, and M. Babel. Needle steering fusing direct base manipulation and tip-based control. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4450–4455. IEEE.
Shahriari, N., J. R. Georgiadis, M. Oudkerk, and S. Misra. Hybrid control algorithm for flexible needle steering: demonstration in phantom and human cadaver. PLoS ONE. 13(12):0210052, 2018.
Duan, Y., Y. Zhang, Y. Shen, J. Ling, and Y. Zhu, A three-rhombus configured remote center of motion mechanism for robot-assisted surgery. In: 2022 37th Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation (YAC), pp. 930–934.
Varnamkhasti, Z. K., and B. Konh. Design, fabrication, and testing of a flexible three-dimensional printed percutaneous needle with embedded actuators. J. Med. Devices.15(2):021007, 2021.
Varnamkhasti, Z. K., and B. Konh. Cable-driven 3d steerable surgical needle for needle-based procedures. In: Proceedings of the 2020 Design of Medical Devices Conference (DMD2020), vol. 83549, pp. 001–06008.
Padasdao, B., and B. Konh. Shape memory alloy actuators in an active needlemodeling, precise assembly, and performance evaluation. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng.143(2):021003, 2021.
Konh, B., M. Honarvar, and P. Hutapea. Simulation and experimental studies of the sma-activated needle behavior inside the tissue. In: Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems 2015, vol. 9431, pp. 693–697.
Ayvali, E., and J. P. Desai. Towards a discretely actuated steerable cannula. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1614–1619.
Ryu, S. C., Z. F. Quek, J.-S. Koh, P. Renaud, R. J. Black, B. Moslehi, B. L. Daniel, K.-J. Cho, and M. R. Cutkosky. Design of an optically controlled mr-compatible active needle. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31(1):1–11, 2015.
Ryu, S .C., P. Renaud, R. J. Black, B. L. Daniel, and M. R. Cutkosky. Feasibility study of an optically actuated mr-compatible active needle. In: 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 2564–2569.
Ryu, S. C., Z. F. Quek, P. Renaud, R. J. Black, B. L. Daniel, and M. R. Cutkosky. An optical actuation system and curvature sensor for a mr-compatible active needle. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1589–1594.
Black, R. J., S. Ryu, B. Moslehi, and J. M. Costa. Characterization of optically actuated mri-compatible active needles for medical interventions. In: Behavior and Mechanics of Multifunctional Materials and Composites 2014, vol. 9058, pp. 160–167.
Mitros, Z., S. M. H. Sadati, R. Henry, L. Da Cruz, and C. Bergeles. From theoretical work to clinical translation: progress in concentric tube robots. Annu. Rev. Control Robot. Autonom. Syst. 5:335–359, 2022.
Webster, R. J., A. M. Okamura, and N. J. Cowan. Toward active cannulas: Miniature snake-like surgical robots. In: 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 2857–2863.
Garriga-Casanovas, A., and F. Baena. Complete follow-the-leader kinematics using concentric tube robots. Int. J. Robot. Res. 37(1):197–222, 2017.
Bergeles, C., A. H. Gosline, N. V. Vasilyev, P. J. Codd, P. J. Del Nido, and P. E. Dupont. Concentric tube robot design and optimization based on task and anatomical constraints. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 31(1):67–84, 2015.
Qi, B., Z. Yu, Z. K. Varnamkhasti, Y. Zhou, and J. Sheng. Toward a telescopic steerable robotic needle for minimally invasive tissue biopsy. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6(2):1989–1996, 2021.
Swaney, P. J., A. W. Mahoney, A. A. Remirez, E. Lamers, B. I. Hariley, R. H. Feins, R. Alterovitz, I. Webster, and J. Robert. Tendons, concentric tubes, and a bevel tip: three steerable robots in one transoral lung access system. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 5378–5383.
Khadem, M., J. O’Neill, Z. Mitros, L. Cruz, and C. Bergeles. Autonomous steering of concentric tube robots for enhanced force/velocity manipulability. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 2197–2204.
Khadem, M., J. O’Neill, Z. Mitros, L. Cruz, and C. Bergeles. Autonomous steering of concentric tube robots via nonlinear model predictive control. IEEE Trans. Robot. 36(5):1595–1602, 2020.
Roesthuis, R. J., N. J. V. D. Berg, J. J. V. D. Dobbelsteen, and S. Misra. Modeling and steering of a novel actuated-tip needle through a soft-tissue simulant using fiber bragg grating sensors. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2283–2289.
Shahriari, N., R. J. Roesthuis, N. J. Berg, J. J. Dobbelsteen, and S. Misra. Steering an actuated-tip needle in biological tissue: Fusing fbg-sensor data and ultrasound images. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4443–4449.
Burdette, E. C., D. C. Rucker, P. Prakash, C. J. Diederich, J. M. Croom, C. Clarke, P. Stolka, T. Juang, E. M. Boctor, I. Webster, and J. Robert. The acusitt ultrasonic ablator: The first steerable needle with an integrated interventional tool. In: Medical Imaging 2010: Ultrasonic Imaging, Tomography, and Therapy, vol. 7629, pp. 283–292.
Vries, M., J. Sikorski, S. Misra, and J. Dobbelsteen. Axially rigid steerable needle with compliant active tip control. PLoS ONE. 170:0261089, 2022.
Watts, T., R. Secoli, F. R. Y. Baena. Needle steerability measures: definition and application for optimized steering of the programmable bevel-tip needle. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), pp. 59–64.
Arif, M., A. Moelker, and T. Walsum. Needle tip visibility in 3d ultrasound images. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 41:145–152, 2018.
Berg, N. J., J. A. Sanchez-Margallo, T. Lango, and J. J. Dobbelsteen. Compliant joint echogenicity in ultrasound images: towards highly visible steerable needles. In: Medical Imaging 2018: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, vol. 10576, 2018, pp. 219–224.
Li, M., B. Gonenc, K. Kim, W. Shang, and I. Iordachita. Development of an MRI-compatible needle driver for in-bore prostate biopsy. In: 2015 International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), pp. 130–136, 2015.
Su, H., M. Zervas, G. A. Cole, C. Furlong, and G. S. Fischer. Real-time mri-guided needle placement robot with integrated fiber optic force sensing. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1583–1588.
Reisch, R., A. Stadie, R. A. Kockro, and N. Hopf. The keyhole concept in neurosurgery. World Neurosurg. 79(2 Suppl):17–913, 2013.
Lan, Q. Clinical application of keyhole techniques in minimally invasive neurosurgery. Chin. Med. J. 119(16):1327–1330, 2006.
Van Niekerk, M., P. Goussard, R. Van Toorn, and R. Solomons. Giant cerebral tuberculoma mimicking a high-grade tumour in a child. BMJ Case Rep.15(4):248545, 2022.
Roediger, J., T. A. Dembek, J. Achtzehn, J. L. Busch, A. P. Kramer, K. Faust, G. H. Schneider, P. Krause, A. Horn, and A. A. Kuhn. Automated deep brain stimulation programming based on electrode location: a randomised, crossover trial using a data-driven algorithm. Lancet Digital Health. 5(2):59–70, 2023.
Zhan, W., and C. H. Wang. Convection enhanced delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs into brain tumour. J. Controlled Release. 271:74–87, 2018.
Virdyawan, V., and F. Baena. Vessel pose estimation for obstacle avoidance in needle steering surgery using multiple forward looking sensors. In: 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 3845–3852, 2018.
Pinzi, M., T. Watts, R. Secoli, S. Galvan, and F. R. Y. Baena. Path replanning for orientation-constrained needle steering. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 68(5):1459–1466, 2021.
Segato, A., M. Di Marzo, S. Zucchelli, S. Galvan, R. Secoli, and E. De Momi. Inverse reinforcement learning intra-operative path planning for steerable needle. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 69(6):1995–2005, 2022.
Pinzi, M., S. Galvan, and Y. B. F. Rodriguez. The adaptive hermite fractal tree (AHFT): a novel surgical 3d path planning approach with curvature and heading constraints. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 14(4):659–670, 2019.
Caborni, C., S. Y. Ko, E. De Momi, G. Ferrigno, and F. Baena. Risk-based path planning for a steerable flexible probe for neurosurgical intervention. In: 4th IEEE RAS and EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob)/Symposium on Surgical Robotics, pp. 866–871, 2012.
Siegel, R. L., K. D. Miller, H. E. Fuchs, and A. Jemal. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 72(1):7–33, 2022.
Navani, N., M. Nankivell, D. R. Lawrence, S. Lock, H. Makker, D. R. Baldwin, R. J. Stephens, M. K. Parmar, S. G. Spiro, S. Morris, S. M. Janes, and B. T. I. Lung. Lung cancer diagnosis and staging with endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration compared with conventional approaches: an open-label, pragmatic, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 3(4):282–289, 2015.
Memoli, J. S. W., P. J. Nietert, and G. A. Silvestri. Meta-analysis of guided bronchoscopy for the evaluation of the pulmonary nodule. Chest. 142(2):385–393, 2012.
Fan, Y., A.-M. Zhang, X.-L. Wu, Z.-S. Huang, K. Kontogianni, K. Sun, W.-L. Fu, N. Wu, W. M. Kuebler, and F. J. F. Herth. Transbronchial needle aspiration combined with cryobiopsy in the diagnosis of mediastinal diseases: a multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 11(3):256–264, 2023.
Shahriari, N., W. Heerink, T. Katwijk, E. Hekman, M. Oudkerk, and S. Misra. Computed tomography (CT)-compatible remote center of motion needle steering robot: fusing CT images and electromagnetic sensor data. Med. Eng. Phys. 45:71–77, 2017.
Moreira, P., M. Abayazid, and S. Misra. Towards physiological motion compensation for flexible needle interventions. In: 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 831–836, 2015.
Fried, I., J. Hoelscher, M. Fu, M. Emerson, T. E. Ertop, M. Rox, J. Granna, A. Kuntz, J. A. Akulian, I. Webster, J. Robert, and R. Alterovitz. Design considerations for a steerable needle robot to maximize reachable lung volume. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1418–1425, 2021.
Lee, S. Y., J. M. Pakela, K. Na, J. Shi, B. J. McKenna, D. M. Simeone, E. Yoon, J. M. Scheiman, and M.-A. Mycek. Needle-compatible miniaturized optoelectronic sensor for pancreatic cancer detection. Sci. Adv. 6(47):1746, 2020.
Fu, M., K. Solovey, O. Salzman, and R. Alterovitz. Resolution-optimal motion planning for steerable needles. In: 2022 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), vol. 2022, pp. 9652–9659.
Kuntz, A., L. G. Torres, R. H. Feins, I. Webster, J. Robert, and R. Alterovitz, Motion planning for a three-stage multilumen transoral lung access system. In: 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 3255–3261, 2015.
Vogel, A., T. Meyer, G. Sapisochin, R. Salem, and A. Saborowski. Hepatocellular carcinoma. The Lancet. 400(10360):1345–1362, 2022.
Yang, J. D., P. Hainaut, G. J. Gores, A. Amadou, A. Plymoth, and L. R. Roberts. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16(10):589–604, 2019.
Childs, A., N. Zakeri, Y. T. Ma, J. O’Rourke, P. Ross, E. Hashem, R. A. Hubner, K. Hockenhull, C. Iwuji, S. Khan, D. H. Palmer, J. Connor, D. Swinson, S. Darby, C. Braconi, T. Roques, D. Yu, T. V. Luong, and T. Meyer. Biopsy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a multicentre uk audit. Br. J. Cancer. 125(10):1350–1355, 2021.
Izzo, F., V. Granata, R. Grassi, R. Fusco, R. Palaia, P. Delrio, G. Carrafiello, D. Azoulay, A. Petrillo, and S. A. Curley. Radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation in liver tumors: an update. Oncologist. 24(10):990–1005, 2019.
Kim, G. M., J. Y. Won, M. D. Kim, S. I. Park, Y. do Lee, W. Shin, M. Shin, K. H. Han, Y. do Kim, and S. U. Kim. Cryoablation of hepatocellular carcinoma with high-risk for percutaneous ablation: safety and efficacy. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 39(10):1447–1454, 2016.
Konh, B., B. Padasdao, Z. Batsaikhan, and S. Y. Ko. Integrating robot-assisted ultrasound tracking and 3d needle shape prediction for real-time tracking of the needle tip in needle steering procedures. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 17(4):e2272, 2021.
Baksic, P., H. Courtecuisse, C. Duriez, and B. Bayle. Robotic needle insertion in moving soft tissues using constraint-based inverse finite element simulation. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2407–2413, 2020.
Adebar, T. K., A. E. Fletcher, and A. M. Okamura. 3-d ultrasound-guided robotic needle steering in biological tissue. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61(12):2899–2910, 2014.
Rucker, D. C., J. Das, H. B. Gilbert, P. J. Swaney, M. I. Miga, N. Sarkar, I. Robert, and J. Webster. Sliding mode control of steerable needles. IEEE Trans. Robot. 29(5):1289–1299, 2013.
Alexander, R. T., B. R. Hemmelgarn, N. Wiebe, A. Bello, C. Morgan, S. Samuel, S. W. Klarenbach, G. C. Curhan, and M. Tonelli. Kidney stones and kidney function loss: a cohort study. BMJ. 345:5287, 2012.
De, S., R. Autorino, F. J. Kim, H. Zargar, H. Laydner, R. Balsamo, F. C. Torricelli, C. Di Palma, W. R. Molina, M. Monga, and M. De Sio. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy versus retrograde intrarenal surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 67(1):125–137, 2015.
Zhu, W., Z. Huang, and F. Zeng. Miniaturization in percutaneous nephrolithotomy: what is new? Asian J. Urol. 10(3):275–280, 2023.
Knoll, T., F. Daels, J. Desai, A. Hoznek, B. Knudsen, E. Montanari, C. Scoffone, A. Skolarikos, and K. Tozawa. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy: technique. World J. Urol. 35:1361–1368, 2017.
Zhang, D., Z. Li, K. Chen, J. Xiong, X. Zhang, and L. Wang. An optical tracker based robot registration and servoing method for ultrasound guided percutaneous renal access. Biomed. Eng. Online. 12:1–16, 2013.
Wood, N. A., K. Shahrour, M. C. Ost, and C. N. Riviere. Needle steering system using duty-cycled rotation for percutaneous kidney access, 2010.
Wilz, O., B. Kent, B. Sainsbury, and C. Rossa. Multiobjective trajectory tracking of a flexible tool during robotic percutaneous nephrolithotomy. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6(4):8110–8117, 2021.
Gomez-Iturriaga, A., M. Keyes, J. Martin, and D. E. Spratt. Should brachytherapy be added to external beam radiotherapy for prostate cancer? Lancet Oncol. 23(1):23–25, 2022.
Maghsoudi, A., and M. Jahed. Needle dynamics modelling and control in prostate brachytherapy. IET Control Theory Appl. 6(11):1671–1681, 2012.
Varnamkhasti, Z. K., and B. Konh. Compact 3d-printed active flexible needle for percutaneous procedures. Surg. Innov. 27(4):402–405, 2020.
Lehmann, T., R. Sloboda, N. Usmani, and M. Tavakoli. Human-machine collaboration modalities for semi-automated needle insertion into soft tissue. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3(1):477–483, 2018.
Carriere, J., M. Khadem, C. Rossa, N. Usmani, R. Sloboda, and M. Tavakoli. Surgeon-in-the-loop 3-d needle steering through ultrasound-guided feedback control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3(1):469–476, 2018.
Rossa, C., N. Usmani, R. Sloboda, and M. Tavakoli. A hand-held assistant for semiautomated percutaneous needle steering. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64(3):637–648, 2017.
Vries, M., S. L. Wilby, A. L. Palmer, W. Polak, I. O’Hea, D. Hodgson, and J. J. Dobbelsteen. Overcoming pubic arch interference in prostate brachytherapy using steerable needles. J. Contemp. Brachyther. 14(5):495–500, 2022.
Khadem, M., C. Rossa, N. Usmani, R. S. Sloboda, and M. Tavakoli. Roboticassisted needle steering around anatomical obstacles using notched steerable needles. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 22(6):1917–1928, 2018.
Fallahi, B., M. Waine, C. Rossa, R. Sloboda, N. Usmani, and M. Tavakoli. An integrator-backstepping control approach for three-dimensional needle steering. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 24(5):2204–2214, 2019.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province [Grant No. BK20210294], the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities [Grant No. NS2022051], Knowledge Innovation Program of Wuhan-Shuguang Project [Grant No. 2023010201020252], and Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation [Grant No. 2023A1515110156].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare and the authors also declare no compensation from any commercial entity that has been obtained for this work.
Additional information
Associate Editor Lyndia (Chun) Wu oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, Y., Ling, J., Feng, Z. et al. A Survey of Needle Steering Approaches in Minimally Invasive Surgery. Ann Biomed Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-024-03494-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-024-03494-0