Abstract
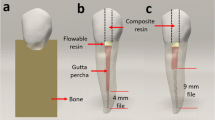
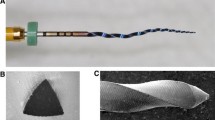
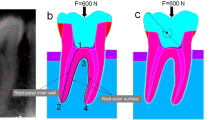
It is very important for clinicians to provide restorative treatments that provide durability for endodontically treated teeth. Trauma, occlusal premature contact, and features of teeth are some of the issues that can cause vertical root fractures (VRFs) in root canal-treated teeth. The aim of this 3-D study was to compare stress distribution on mandibular premolar teeth when using a variety of post designs instrumented with different rotary systems. Six mandibular premolar teeth were instrumented with the following tools: ProTaper Next, WaveOne (WO), Reciproc (R), ReciprocBlue (RB), F6-Skytaper, and TF-Adaptive. Teeth were scanned using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and the images were transferred to the Catia V5R25 software. Data were recorded in a stereolithography (STL) format. Four different post systems were used, fabricated from metal, fiber, zirconia, and titanium, respectively. Dentin, gutta, post, core, and crown models were added to the solid model. ANSYS V17.2 finite element analysis (FEA) software was used to determine stress distribution on each assembly. Finite analysis models were created that allowed for the calculation of stress distribution of 250-N loading at a 45° angle and vertical in relation to the roots. The maximum principal stress and von Mises values were higher under oblique loading on the roots. The F6-Skytaper and WO systems showed lower stress than other systems. The TF-Adaptive instrument showed higher stress distribution than the other models. Fiber and titanium posts showed lower stress than others. The F6-Skytaper, R, and RB instruments were found to be most effective in terms of displacement of the crown, resulting in the lowest stress values. Fiber and titanium posts showed better results than other post systems, while root canals instrumented with the F6-Skytaper and WO instruments were less likely to result in root fractures.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck, N., F. Graef, M. Wichmann, and M. Karl. In vitro fracture resistance of copy-milled zirconia ceramic posts. J. Prosth. Dent. 103:40–44, 2010
Belli, S., O. Eraslan, and G. Eskitaçcıoğlu. Effect of different treatment options on biomechanics of immature teeth: a finite element stress analysis study. J. Endod. 44:475–479, 2018
Bürklein, S., K. Hinschitza, T. Dammaschke, and E. Schafer. Shaping ability and cleaning effectiveness of two single-file systems in severely curved root canals of extracted teeth: Reciproc and WaveOne vs. MTwo and ProTaper. Int. Endod. J. 45:449–461, 2012
Chen, A., X. Feng, Y. Zhang, R. Liu, and L. Shao. Finite element analysis of stress distribution in four different endodontic post systems in a model canine. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 26:629–635, 2015
Cheng, R., X. D. Zhou, Z. Liu, H. Yang, Q. H. Gao, and T. Hu. Finite element analysis of the effects of three preparation techniques on stresses within roots having curved canals. Int. Endod. J. 42:220–226, 2009
Chien, P. H. Y., L. J. Walsh, and O. A. Peters. Finite element analysis of rotary nickel–titanium endodontic instruments: a critical review of the methodology. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 129(5):12802, 2021
De-Deus, G., E. Neves, E. J. Silva, et al. Apically extruded dentin debris by reciprocating single-file and multi-file rotary system. Clin. Oral Investig. 19:357–361, 2015
Dejak, B., and A. Młotkowski. Finite element analysis of strength and adhesion of cast posts compared to glass fiber-reinforced composite resin posts in anterior teeth. J. Prosthet. Dent. 105:115–126, 2011
Durmuş, G., and P. Oyar. Effects of post core materials on stress distribution in the restoration of mandibular second premolars: a finite element analyses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 112:547–554, 2014
Eken, R., O. G. Şen, G. Eskitaşçıoğlu, and S. Belli. Evaluation of the effect of rotary systems on stresses in a new testing model using a 3-dimensional printed simulated resin root with an oval-shaped canal: a finite element analysis study. J. Endod. 42:1273–1278, 2016
Elnaghy, A. M., and B. M. Elsaka. Evaluation of root canal transportation, centering ratio, and remaining dentin thickness associated with ProTaper Next instruments with and without glide path. J. Endod. 40:2053–2056, 2014
Fuss, Z., J. Lustig, A. Katz, and A. Tamse. An evaluation of endodontically treated vertical root fractured teeth: impact of operative procedures. J. Endod. 27:46–48, 2001
Goracci, C., and M. Ferrari. Current perspectives on post systems: a literature review. Aust. Dent. J. 56:77–83, 2011
Hin, E. S., M. K. Wu, P. R. Wesselink, and H. Shemesh. Effects of self-adjusting file, MTwo and ProTaper on the root canal wall. J. Endod. 39:262–264, 2013
Kim, H. C., M. H. Lee, J. Yum, A. Versluis, C. J. Lee, and B. M. Kim. Potential relationship between design of nickel–titanium rotary instruments and vertical root fracture. J. Endod. 36:1195–1199, 2010
Li, L., Z. Y. Wang, Z. C. Bai, Y. Mao, B. Gao, H. T. Xin, B. Zhao, Y. Zhang, and B. Liu. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of weakened roots restored with ifferent cements in combination with titanium alloy posts. Chin. Med. J. 119:305–311, 2006
Necchi, S., S. Taschieri, L. Petrini, and F. Migliavacca. Mechanical behaviour of nickel–titanium rotary endodontic instruments in simulated clinical conditions: a computational study. Int. Endod. J. 41:939–949, 2008
Nur, B. G., E. Ok, M. Altunsoy, et al. Fracture strength of roots instrumented with three different single file systems in curved root canals. Eur. J. Dent. 9:189–193, 2015
Rundquist, B. D., and A. Versluis. How does canal taper affect root stresses? Int. Endod. J. 39:226–237, 2006
Saber, S. M., D. M. Hayaty, N. N. Nawar, and H. C. Kim. The effect of access cavity designs and sizes of root canal preparations on the biomechanical behavior of an endodontically treated mandibular first molar: a finite element analysis. J. Endod. 46(22):1675–1681, 2020
Santos-Filho, P. C. F., C. Verissimo, L. H. A. Raposo, P. Y. N. Meceng, and L. R. M. Martins. Influence of ferrule, post system, and length on stress distribution of weakened root-filled teeth. J. Endod. 40:1874–1878, 2014
Shen, Y., J. M. Coil, A. J. Mo, Z. Wang, et al. WaveOne rotary instruments after clinical use. J. Endod. 42:186–189, 2016
Toksavul, S., M. Zor, M. Toman, M. A. Güngör, I. Nergiz, and C. Artunç. Analysis of dentinal stress distribution of maxillary central incisors subjected to various post-and-core applications. Oper. Dent. 31:89–96, 2006
Toparli, M., and S. Sasaki. Finite element analysis of the temperature and thermal stress in a postrestored tooth. J. Oral. Rehabil. 30:921–926, 2003
Valdivia, A. D., L. H. Raposo, P. C. Simamoto-Junior, V. R. Novais, and C. J. Soares. The effect of fiber post presence and restorative technique on the biomechanical behaviour of endodontically treated maxillary incisors: an in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 108:147–157, 2012
VDW. VDW Dental Brochure. Reciproc Blue Instruments. Munich: VDW, 2016.
Yuan, K., C. Niu, Q. Xie, J. Wenxin, L. Gao, Z. Huang, and R. Ma. Comparative evaluation of the impact of minimally invasive preparation vs. conventional straight-line preparation on tooth biomechanics: a finite element analysis. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 124(6):591–596, 2016
Zandbiglari, T., H. Davids, and E. Schafer. Influence of instrument taper on the resistance to fracture of endodontically treated roots. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 101:126–131, 2006
Zelic, K., A. Vukicevic, G. Jovicic, S. Aleksandrovic, N. Filipovic, and M. Djuric. Mechanical weakening of devitalized teeth: three-dimensional Finite Element Analysis and prediction of tooth fracture. Int. Endod. J. 48:850–863, 2015
Zorane, F., R. Sorrentino, D. Apicella, B. Valentino, M. Ferrari, R. Aversa, et al. Evaluation of the biomechanical behavior of maxillary central incisors restored by means of endocrowns compared to a natural tooth: a 3D static linear finite elements analysis. Dent. Mater. J. 22:1035–1044, 2006
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Professor Sema Belli for her expert advice and encouragement throughout this project.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Eiji Tanaka oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ince Yusufoglu, S., Saricam, E. & Ozdogan, M.S. Finite Element Analysis of Stress Distribution in Root Canals When Using a Variety of Post Systems Instrumented with Different Rotary Systems. Ann Biomed Eng 51, 1436–1448 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03145-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03145-w