Abstract
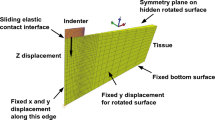
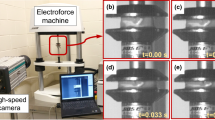
This study characterizes the mechanical properties of human brain tissue resected during the course of surgery under multistep indentation loading up to 30% strain. The experimental characterization using fresh, post-operative, human brain tissue is highly advantageous since postmortem times can affect its biomechanical behavior. Although the quasilinear theory of viscoelasticity (QLV) approach has been widely used to model brain tissue mechanical properties, our analysis concluded that the linear viscoelastic approach provided a better fit to the experimental data overall. The only statistically significant regional difference in observed stiffness was between the cortex gray and dentate gyrus. There were no statistically significant age or sex dependent differences, although the data suggested that the cortex white matter in males was stiffer than that in females. Our results can help improve the accuracy of finite element models of brain tissue deformation to predict its response to traumatic brain injury.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abba, M. T. and S. R. Kalidindi, Protocols for studying the time-dependent mechanical response of viscoelastic materials using spherical indentation stress-strain curves. Mechanics of Time-Dependent Materials, 2020.
Alhilali, L. M., J. A. Delic, S. Gumus, and S. Fakhran. Evaluation of white matter injury patterns underlying neuropsychiatric symptoms after mild traumatic brain injury. Radiology. 277(3):793–800, 2015.
Bayly, P. V., L. A. Taber, and C. D. Kroenke. Mechanical forces in cerebral cortical folding: a review of measurements and models. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 29:568–581, 2014.
Bentil, S. A., and R. B. Dupaix. Exploring the mechanical behavior of degrading swine neural tissue at low strain rates via the fractional Zener constitutive model. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 30:83–90, 2014.
Budday, S., R. Nay, R. de Rooij, P. Steinmann, T. Wyrobek, T. C. Ovaert, and E. Kuhl. Mechanical properties of gray and white matter brain tissue by indentation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 46:318–330, 2015.
Budday, S., G. Sommer, C. Birkl, C. Langkammer, J. Haybaeck, J. Kohnert, M. Bauer, F. Paulsen, P. Steinmann, E. Kuhl, and G. A. Holzapfel. Mechanical characterization of human brain tissue. Acta Biomater. 48:319–340, 2017.
Chatelin, S., J. Vappou, S. Roth, J. S. Raul, and R. Willinger. Towards child versus adult brain mechanical properties. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 6:166–173, 2012.
Christ, A. F., K. Franze, H. Gautier, P. Moshayedi, J. Fawcett, R. J. Franklin, R. T. Karadottir, and J. Guck. Mechanical difference between white and gray matter in the rat cerebellum measured by scanning force microscopy. J. Biomech. 43(15):2986–2992, 2010.
Dolle, J. P., A. Jaye, S. A. Anderson, H. Ahmadzadeh, V. B. Shenoy, and D. H. Smith. Newfound sex differences in axonal structure underlie differential outcomes from in vitro traumatic axonal injury. Exp. Neurol. 300:121–134, 2018.
Donohue, B. R., A. Ambrus, and S. R. Kalidindi. Critical evaluation of the indentation data analyses methods for the extraction of isotropic uniaxial mechanical properties using finite element models. Acta Mater. 60(9):3943–3952, 2012.
Elkin, B. S., A. Ilankova, and B. Morrison. Dynamic, regional mechanical properties of the porcine brain: indentation in the coronal plane. J. Biomech. Eng. 133(7):071009, 2011.
Elkin, B. S., A. Ilankovan, and B. Morrison. Age-dependent regional mechanical properties of the rat hippocampus and cortex. J. Biomech. Eng. 132(1):011010, 2010.
Elkin, B. S., A. I. Ilankovan, and B. Morrison 3rd. A detailed viscoelastic characterization of the P17 and adult rat brain. J. Neurotrauma. 28(11):2235–2244, 2011.
Elkin, B. S., and B. Morrison III. Viscoelastic properties of the P17 and adult rat brain from indentation in the coronal plane. J. Biomech. Eng. 135:114507, 2013.
Faul, M. and V. Coronado, Traumatic Brain Injury in The United States, U.D.o.H.a.H. Services, Editor. 2010.
Finan, J. D., B. S. Elkin, E. M. Pearson, I. L. Kalbian, and B. Morrison 3rd. Viscoelastic properties of the rat brain in the sagittal plane: effects of anatomical structure and age. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40(1):70–78, 2012.
Finan, J. D., P. M. Fox, and B. Morrison 3rd. Non-ideal effects in indentation testing of soft tissues. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 13:573–584, 2014.
Finan, J. D., S. N. Sundaresh, B. S. Elkin, G. M. McKhann 2nd., and B. Morrison 3rd. Regional mechanical properties of human brain tissue for computational models of traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater. 55:333–339, 2017.
Galanaud, D., V. Perlbarg, R. Gupta, R. D. Stevens, P. Sanchez, E. Tollard, N. M. de Champfleur, J. Dinkel, S. Faivre, G. Soto-Ares, B. Veber, V. Cottenceau, F. Masson, T. Tourdias, E. Andre, G. Audibert, E. Schmitt, D. Ibarrola, F. Dailler, A. Vanhaudenhuyse, L. Tshibanda, J. F. Payen, J. F. Le Bas, A. Krainik, N. Bruder, N. Girard, S. Laureys, H. Benali, L. Puybasset, Neuro Imaging for Coma, and C. Recovery. Assessment of white matter injury and outcome in severe brain trauma: a prospective multicenter cohort. Anesthesiology. 117(6):1300–1310, 2012.
Garo, A., M. Hrapko, J. A. van Dommelen, and G. W. Peters. Towards a reliable characterisation of the mechanical behaviour of brain tissue: the effects of post-mortem time and sample preparation. Biorheology. 44(1):51–58, 2007.
Gennatas, E. D., B. B. Avants, D. H. Wolf, T. D. Satterthwaite, K. Ruparel, R. Ciric, H. Hakonarson, R. E. Gur, and R. C. Gur. Age-related effects and sex differences in gray matter density, volume, mass, and cortical thickness from childhood to young adulthood. J. Neurosci. 37(20):5065–5073, 2017.
Gessel, L. M., S. K. Fields, C. L. Collins, R. W. Dick, and R. D. Comstock. Concussions among United States high school and collegiate athletes. J. Athl. Train. 42(4):495–503, 2007.
Gupte, R., W. Brooks, R. Vukas, J. Pierce, and J. Harris. Sex differences in traumatic brain injury: what we know and what we should know. J. Neurotrauma. 36(22):3063–3091, 2019.
Gur, R. C., and R. E. Gur. Complementarity of sex differences in brain and behavior: From laterality to multimodal neuroimaging. J.Neurosci. Res. 95(1–2):189–199, 2017.
Gur, R. C., B. I. Turetsky, M. Matsui, M. Yan, W. Bilker, P. Hughett, and R. E. Gur. Sex differences in brain gray and white matter in healthy young adults: correlations with cognitive performance. J. Neurosci. 19(10):4065–4072, 1999.
Harding, J. W., and I. N. Sneddon. The elastic stresses produced by the indentation of the plane surface of a semi-infinite elastic solid by a rigid punch. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 41(1):16–26, 1945.
Hayes, W. C., L. M. Keer, G. Herrmann, and L. F. Mockros. A mathematical analysis for indentation tests of articular cartilage. J. Biomech. 5:541–551, 1972.
Jin, X., F. Zhu, H. Mao, M. Shen, and K. H. Yang. A comprehensive experimental study on material properties of human brain tissue. J. Biomech. 46(16):2795–2801, 2013.
Kalidindi, S. R., and S. Pathak. Determination of the effective zero-point and the extraction of spherical nanoindentation stress-strain curves. Acta Mater. 56(14):3523–3532, 2008.
Laksari, K., M. Shafieian, and K. Darvish. Constitutive model for brain tissue under finite compression. J. Biomech. 45(4):642–646, 2012.
Levin, H. S., and R. R. Diaz-Arrastia. Diagnosis, prognosis, and clinical management of mild traumatic brain injury. Lancet Neurol. 14(5):506–517, 2015.
Macmanus, D. B., A. Menichetti, B. Depreitere, N. Famaey, J. V. Sloten, and M. Gilchrist. Towards animal surrogates for characterising large strain dynamic mechanical properties of human brain tissue. Brain Multiphys. 1:100018, 2020.
MacManus, D. B., J. G. Murphy, and M. D. Gilchrist. Mechanical characterisation of brain tissue up to 35% strain at 1, 10, and 100/s using a custom-built micro-indentation apparatus. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 87:256–266, 2018.
MacManus, D. B., B. Pierrat, J. G. Murphy, and M. D. Gilchrist. Mechanical characterization of the P56 mouse brain under large-deformation dynamic indentation. Sci. Rep. 6:21569, 2016.
MacManus, D. B., B. Pierrat, J. G. Murphy, and M. D. Gilchrist. A viscoelastic analysis of the P56 mouse brain under large-deformation dynamic indentation. Acta Biomater. 48:309–318, 2017.
Marar, M., N. M. McIlvain, S. K. Fields, and R. D. Comstock. Epidemiology of concussions among United States high school athletes in 20 sports. Am. J. Sports Med. 40(4):747–755, 2012.
Nicolle, S., M. Lounis, R. Willinger, and J. F. Palierne. Shear linear behavior of brain tissue over a large frequency range. Biorheology. 42(3):209–223, 2005.
Pathak, S., S. R. Kalidindi, C. Klemenz, and N. Orlovskaya. Analyzing indentation stress-strain response of LaGaO3 single crystals using spherical indenters. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28(11):2213–2220, 2008.
Pervin, F., and W. W. Chen. Dynamic mechanical response of bovine gray matter and white matter brain tissues under compression. J. Biomech. 42(6):731–735, 2009.
Prange, M. T., and S. S. Margulies. Regional, directional, and age-dependent properties of the brain undergoing large deformation. J. Biomech. Eng. 124(2):244–252, 2002.
Rashid, B., M. Destrade, and M. D. Gilchrist. Mechanical characterization of brain tissue in tension at dynamic strain rates. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 33:43–54, 2014.
Takhounts, E. G., J. R. Crandall, and K. Darvish. On the importance of nonlinearity of brain tissue under large deformations. Stapp Car Crash J. 47:79, 2003.
Thibault, K. L., and S. S. Margulies. Age-dependent material properties of the porcine cerebrum: effect on pediatric inertial head injury criteria. J. Biomech. 31(12):1119–1126, 1998.
Van Dommelen, J., T. Van der Sande, M. Hrapko, and G. Peters. Mechanical properties of brain tissue by indentation: interregional variation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 3(2):158–166, 2010.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. A.A. Sosunov at the Columbia University Medical Center and the patients for providing the human brain tissue samples. The authors acknowledge the computing resources from Columbia University's Shared Research Computing Facility project, which is supported by NIH Research Facility Improvement Grant 1G20RR030893-01, and associated funds from the New York State Empire State Development, Division of Science Technology and Innovation (NYSTAR) Contract C090171, both awarded on April 15, 2010. This study was supported in part by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) (Project No. DTNH22-08-C-00088), a grant from the Paul Allen Family Foundation, and funding from Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Stefan M. Duma oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundaresh, S.N., Finan, J.D., Elkin, B.S. et al. Region-Dependent Viscoelastic Properties of Human Brain Tissue Under Large Deformations. Ann Biomed Eng 50, 1452–1460 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-022-02910-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-022-02910-7