Abstract
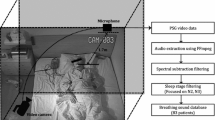
Snore sound (SnS) classification can support a targeted surgical approach to sleep related breathing disorders. Using machine listening methods, we aim to find the location of obstruction and vibration within a subject’s upper airway. Wavelet features have been demonstrated to be efficient in the recognition of SnSs in previous studies. In this work, we use a bag-of-audio-words approach to enhance the low-level wavelet features extracted from SnS data. A Naïve Bayes model was selected as the classifier based on its superiority in initial experiments. We use SnS data collected from 219 independent subjects under drug-induced sleep endoscopy performed at three medical centres. The unweighted average recall achieved by our proposed method is 69.4%, which significantly (\(p<0.005,\) one-tailed z-test) outperforms the official baseline (58.5%), and beats the winner (64.2%) of the INTERSPEECH ComParE Challenge 2017 Snoring sub-challenge. In addition, the conventionally used features like formants, mel-scale frequency cepstral coefficients, subband energy ratios, spectral frequency features, and the features extracted by the openSMILE toolkit are compared with our proposed feature set. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in SnS classification.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiriparian, S., M. Gerczuk, S. Ottl, N. Cummins, M. Freitag, S. Pugachevskiy, A. Baird, and B. Schuller. Snore sound classification using image-based deep spectrum features. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, 2017, Stockholm, Sweden, pp. 3512–3516.
Arthur, D. and S. Vassilvitskii. K-means++: the advantages of careful seeding. In: Proceedings of ACM–SIAM SODA, 2007, New Orleans, LA, USA, pp. 1027–1035.
Azarbarzin, A. and Moussavi, Z. Automatic and unsupervised snore sound extraction from respiratory sound signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58(5):1156–1162, 2011.
Coifman, R. R., Y. Meyer, S. Quake, and V. Wickerhauser. Signal processing and compression with wavelet packets. In: Wavelets and Their Applications, edited by J. S. Byrnes, J. L. Byrnes, K. A. Hargreaves, and K. Berry. Dordrecht: Springer, 1994, pp. 363–379.
Coifman, R. R. and M. V. Wickerhauser. Entropy-based algorithms for best basis selection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 38(2):713–718, 1992.
De Bruijn, N. Uncertainty principles in Fourier analysis. In: Inequalities (Proceedings of Symposium of Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio, 1965). New York: Academic , 1967, pp. 57–71.
Deller Jr., J. R., J. H. L. Hansen, and J. G. Proakis. Discrete Time Processing of Speech Signals. New York: Wiley-IEEE Press, 1999.
Demin, H., Y. Jingying, W. J. Y. Qingwen, L. Yuhua, and W. Jiangyong. Determining the site of airway obstruction in obstructive sleep apnea with airway pressure measurements during sleep. Laryngoscope 112(11):2081–2085, 2002.
Dietterich, T. G. Approximate statistical tests for comparing supervised classification learning algorithms. Neural Comput. 10(7):1895–1923, 1998.
Elwali, A. and Z. Moussavi. Obstructive sleep apnea screening and airway structure characterization during wakefulness using tracheal breathing sounds. Ann. Biomed. Eng., 45(3):839–850, 2017.
Eyben, F. Real-time Speech and Music Classification by Large Audio Feature Space Extraction. Doctoral Thesis, Springer, Cham, 2015.
Eyben, F., F. Weninger, F. Groß, and B. Schuller. Recent developments in openSMILE, the Munich open-source multimedia feature extractor. In: Proceedings of ACM MM, Barcelona, Catalunya, Spain. ACM, 2013, pp. 835–838.
Freitag, M., S. Amiriparian, N. Cummins, M. Gerczuk, and B. Schuller. An end-to-evolution hybrid approach for snore sound classification. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, Stockholm, Sweden, 2017, pp. 3507–3511.
Gosztolya, G., R. Busa-Fekete, T. Grósz, and L. Tóth. DNN-based feature extraction and classifier combination for child-directed speech, cold and snoring identification. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, Stockholm, Sweden, 2017, pp. 3522–3526.
Hall, M., E. Frank, G. Holmes, B. Pfahringer, P. Reutemann, and I. H. Witten. The WEKA data mining software: an update. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 11(1):10–18, 2009.
Janott, C., M. Schmitt, Y. Zhang, K. Qian, V. Pandit, Z. Zhang, C. Heiser, W. Hohenhorst, M. Herzog, W. Hemmert, and B. Schuller. Snoring classified: the Munich Passau Snore Sound Corpus. Comput. Biol. Med. 94:106–118, 2018.
Janott, C., B. Schuller, and C. Heiser. Acoustic information in snoring noise. HNO 65(2):107–116, 2017.
Kaya, H. and K. A. Alexey. Introducing weighted kernel classifiers for handling imbalanced paralinguistic corpora: snoring, addressee and cold. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, Stockholm, Sweden, 2017, pp. 3527–3531.
Kezirian, E. J., W. Hohenhorst, and N. de Vries. Drug-induced sleep endoscopy: the VOTE classification. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 268(8):1233–1236, 2011.
Khushaba, R. N., S. Kodagoda, S. Lal, and G. Dissanayake. Driver drowsiness classification using fuzzy wavelet-packet-based feature-extraction algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58(1):121–131, 2011.
LeCun, Y., Y. Bengio, and G. Hinton. Deep learning. Nature 521(7553):436–444, 2015.
Li, K. K. Surgical therapy for adult obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med. Rev. 9(3):201–209, 2005.
Lin, H.-C., M. Friedman, H.-W. Chang, and B. Gurpinar. The efficacy of multilevel surgery of the upper airway in adults with obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Laryngoscope 118(5):902–908, 2008.
Mallat, S. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing: The Sparse Way. Burlington: Elsevier, 2009.
MathWorks. Matlab Wavelet Toolbox. https://www.mathworks.com/products/wavelet.html, 2018.
Mlynczak, M., E. Migacz, M. Migacz, and W. Kukwa. Detecting breathing and snoring episodes using a wireless tracheal sensor-a feasibility study. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 21(6):1504–1510, 2017.
Mokhlesi, B., S. Ham, and D. Gozal. The effect of sex and age on the comorbidity burden of OSA: an observational analysis from a large nationwide US health claims database. Eur. Respir. J. 47(4):1162–1169, 2016.
Montazeri, A., E. Giannouli, and Z. Moussavi. Assessment of obstructive sleep apnea and its severity during wakefulness. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40(4):916–924, 2012.
Murty, M. N. and V. S. Devi. Pattern Recognition: An Algorithmic Approach. Dordrecht: Springer, 2011.
Ng, A. K., T. San Koh, U. R. Abeyratne, and K. Puvanendran. Investigation of obstructive sleep apnea using nonlinear mode interactions in nonstationary snore signals. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 37(9):1796–1806, 2009a.
Ng, A. K., T. San Koh, E. Baey, T. H. Lee, U. R. Abeyratne, and K. Puvanendran. Could formant frequencies of snore signals be an alternative means for the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea? Sleep Med. 9(8):894–898, 2008.
Ng, A. K., T. San Koh, E. Baey, and K. Puvanendran. Role of upper airway dimensions in snore production: acoustical and perceptual findings. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 37(9):1807–1817, 2009b.
Nwe, L. T., D. H. Tran, T. Z. W. Ng, and B. Ma. An integrated solution for snoring sound classification using Bhattacharyya distance based GMM supervectors with SVM, feature selection with random forest and spectrogram with CNN. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, Stockholm, Sweden, 2017, pp. 3467–3471.
O’Shaughnessy, D. Speech Communication: Human and Machine. New York: Addison-Wesley, 1987.
Pancoast, S. and M. Akbacak. Bag-of-audio-words approach for multimedia event classification. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, Portland, OR, USA, 2012, pp. 2105–2108.
Peppard, P. E., T. Young, J. H. Barnet, M. Palta, E. W. Hagen, and K. M. Hla. Increased prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 177(9):1006–1014, 2013.
Pevernagie, D., R. M. Aarts, and M. De Meyer. The acoustics of snoring. Sleep Med. Rev. 14(2):131–144, 2010.
Pishro-Nik, H. Introduction to Probability, Statistics, and Random Processes. Electrical and Computer Engineering Educational Materials, 2014. http://scholarworks.umass.edu/ece_ed_materials/1.
Qian, K., C. Janott, V. Pandit, Z. Zhang, C. Heiser, W. Hohenhorst, M. Herzog, W. Hemmert, and B. Schuller. Classification of the excitation location of snore sounds in the upper airway by acoustic multi-feature analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64(8):1731–1741, 2017.
Qian, K., C. Janott, Z. Zhang, J. Deng, A. Baird, C. Heiser, W. Hohenhorst, M. Herzog, W. Hemmert, and B. Schuller. Teaching machines on snoring: a benchmark on computer audition for snore sound excitation localisation. Arch. Acoust. 43(3):465–475, 2018.
Qian, K., C. Janott, Z. Zhang, C. Heiser, and B. Schuller. Wavelet features for classification of VOTE snore sounds. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, Shanghai, China, 2016, pp. 221–225.
Rao, M. V. A., S. Yadav, and P. Ghosh, Kumar. A dual source-filter model of snore audio for snorer group classification. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, Stockholm, Sweden, 2017, pp. 3502–3506.
Rawat, S., P. F. Schulam, S. Burger, D. Ding, Y. Wang, and F. Metze. Robust audio-codebooks for large-scale event detection in consumer videos. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, Lyon, France, 2013, pp. 2929–2933.
Reda, M., G. J. Gibson, and J. A. Wilson. Pharyngoesophageal pressure monitoring in sleep apnea syndrome. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 125(4):324–331, 2001.
Schmitt, M., C. Janott, V. Pandit, K. Qian, C. Heiser, W. Hemmert, and B. Schuller. A bag-of-audio-words approach for snore sounds excitation localisation. In: Proceedings of ITG Speech Communication, Paderborn, Germany, 2016a, pp. 230–234.
Schmitt, M., F. Ringeval, and B. Schuller. At the border of acoustics and linguistics: bag-of-audio-words for the recognition of emotions in speech. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016b, pp. 495–499.
Schmitt, M. and B. W. Schuller. openXBOW-introducing the Passau open-source crossmodal bag-of-words toolkit. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 18(96):1–5, 2017.
Schuller, B., S. Steidl, and A. Batliner. The INTERSPEECH 2009 emotion challenge. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, Brighton, UK, 2009, pp. 312–315.
Schuller, B., S. Steidl, A. Batliner, E. Bergelson, J. Krajewski, C. Janott, A. Amatuni, M. Casillas, A. Seidl, M. Soderstrom, S. A. Warlaumont, G. Hidalgo, S. Schnieder, C. Heiser, W. Hohenhorst, M. Herzog, M. Schmitt, K. Qian, Y. Zhang, G. Trigeorgis, P. Tzirakis, and S. Zafeiriou. The INTERSPEECH 2017 computational paralinguistics challenge: addressee, cold and snoring. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, Stockholm, Sweden, 2017, pp. 3442–3446.
Schuller, B., S. Steidl, A. Batliner, A. Vinciarelli, K. Scherer, F. Ringeval, M. Chetouani, F. Weninger, F. Eyben, E. Marchi, M. Mortillaro, H. Salamin, A. Polychroniou, F. Valente, and S. Kim. The INTERSPEECH 2013 computational paralinguistics challenge: social signals, conflict, emotion, autism. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, Lyon, France, 2013, pp. 148–152.
Snell, R. C. and F. Milinazzo. Formant location from LPC analysis data. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process., 1(2):129–134, 1993.
Strollo Jr., P. J. and R. M. Rogers. Obstructive sleep apnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 334(2):99–104, 1996.
Stuck, B. A. and J. T. Maurer. Airway evaluation in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med. Rev. 12(6):411–436, 2008.
Tavarez, D., X. Sarasola, A. Alonso, J. Sanchez, L. Serrano, E. Navas, and I. Hernáez. Exploring fusion methods and feature space for the classification of paralinguistic information. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, Stockholm, Sweden, 2017, pp. 3517–3521.
Vroegop, A. V., O. M. Vanderveken, A. N. Boudewyns, J. Scholman, V. Saldien, K. Wouters, M. J. Braem, P. H. Van de Heyning, and E. Hamans. Drug-induced sleep endoscopy in sleep-disordered breathing: report on 1,249 cases. Laryngoscope 124(3):797–802, 2014.
Yadollahi, A., A. Montazeri, A. Azarbarzin, and Z. Moussavi. Respiratory flow-sound relationship during both wakefulness and sleep and its variation in relation to sleep apnea. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 41(3):537–546, 2013.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the China Scholarship Council (CSC), and the European Union’s Seventh Framework under Grant Agreements No. 338164 (ERC StG iHEARu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Ka-Wai Kwok oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, K., Schmitt, M., Janott, C. et al. A Bag of Wavelet Features for Snore Sound Classification. Ann Biomed Eng 47, 1000–1011 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-019-02217-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-019-02217-0