Abstract
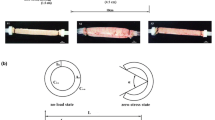
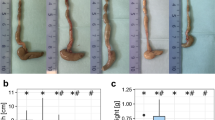
Short-term feeding with low-fiber diet remodels the mechanomorphological properties in the rabbit small intestine. The aims were to study the effect of feeding low-fiber diet for 5 months on mechanomorphological properties including the collagen fraction in the rabbit intestines. Fifteen rabbits were divided into an Intervention group (IG, n = 10) fed a low-fiber diet and a Control group (CG, n = 5) fed a normal diet for 5 months. Five months later, four 10-cm-long segments obtained from the duodenum, jejunum, ileum and large intestine were used for histological and mechanical analysis, respectively. The wall thickness, wall area, mucosa and muscle layer thickness decreased whereas the submucosa layer thickness increased in the IG (p < 0.05). The collagen fraction decreased in all layers and segments in the IG (p < 0.05). The opening angle increased in the large intestine and decreased in the ileum in the IG (p < 0.05). The intestinal stress–strain curves for IG shifted to the right, indicating softening. The creep did not change in the four segments. The wall stiffness was associated with wall thickness and collagen fraction in the submucosa layer. Long-term low-fiber diet in rabbits induced histomorphometric and biomechanical remodelling of the intestines.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosini, G. L. Childhood dietary patterns and later obesity: a review of the evidence. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 73:137–146, 2014.
Chen, P., J. Zhao, V. H. Nielsen, T. Clausen, and H. Gregersen. Intestinal remodelling in mink fed with reduced protein content. J. Biomech. 42:443–448, 2009.
Damjanovic, M., and M. Barton. Fat intake and cardiovascular response. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 10:25–31, 2008.
Dickstein, L. P., K. N. Franco, E. S. Rome, and M. Auron. Recognizing, managing medical consequences of eating disorders in primary care. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 81:255–263, 2014.
Dou, Y., S. Gregersen, J. Zhao, F. Zhuang, and H. Gregersen. Morphometric and biomechanical intestinal remodeling induced by fasting in rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 47:1158–1168, 2002.
El-salhy, M. Core tip: there are several factors that play a major role in the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome Recent developments in the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 21:7621–7636, 2015.
Fung, Y. C. Biomechanics: Mechanical Properties of Living Tissues (2nd ed.). New York: Springer, 1994.
Gao, C., and H. Gregersen. Biomechanical and morphological properties in rat large intestine. J. Biomech. 33:1089–1097, 2000.
Gregersen, H., G. S. Kassab, and Y. C. Fung. The zero-stress state of the gastrointestinal tract: biomechanical and functional implications. Dig. Dis. Sci. 45:2271–2281, 2000.
Gregersen, H., L. Lundby, and J. Overgaard. Early and late effects of irradiation on morphometry and residual strain of mouse rectum. Dig. Dis. Sci. 47:1472–1479, 2002.
Hamilton, M. K., G. Boudry, D. G. Lemay, and H. E. Raybould. Changes in intestinal barrier function and gut microbiota in high-fat diet fed rats are dynamic and region-dependent. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 308:G840–G851, 2015.
Kaline, K., S. R. Bornstein, A. Bergmann, H. Hauner, and P. E. H. Schwarz. The importance and effect of dietary fiber in diabetes prevention with particular consideration of whole grain products. Hormone Metab. Res. 39:687–693, 2007.
Liu, Y., J. Zhao, L. Donghua, L. Bao, and H. Gregersen. Low-residue diet fed to rabbits induces histomorphological and biomechanical remodeling of small intestine. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016. doi:10.1111/nmo.12983.
Mia, M. A. R., M. N. I. Siddiqui, M. S. Haque, M. N. Islam, M. Rukunzzaman, and K. Deb. Dietary fibre and coronary heart disease. Mymensingh Med. J. 11:133–135, 2002.
Paulo, A. Z., O. M. S. Amancio, M. B. de Morais, and K. M. M. D. Tabacow. Low-dietary fiber intake as a risk factor for recurrent abdominal pain in children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 60:823–827, 2006.
Roy, M., P. Gaudreau, and H. Payette. A scoping review of anorexia of aging correlates and their relevance to population health interventions. Appetite 105:688–699, 2016.
Slattery, M. L. Diet, lifestyle, and colon cancer. Semin. Gastrointest. Dis. 11:142–146, 2000.
Sokolis, D. P., and S. G. Sassani. Microstructure-based constitutive modeling for the large intestine validated by histological observations. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 21:149–166, 2013.
Spiller, R. C. Changing views on diverticular disease: impact of aging, obesity, diet, and microbiota. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 27:305–312, 2015.
Timmons, J., E. T. Chang, J.-Y. Wang, and J. N. Rao. Polyamines and gut mucosal homeostasis. J. Gastrointest. Dig. Syst. 2012. doi:10.4172/2161-069X.S7-001.
Vereecken, C. A., J. Todd, C. Roberts, C. Mulvihill, and L. Maes. Television viewing behaviour and associations with food habits in different countries. Public Health Nutr. 9:244–250, 2006.
Yang, J., J. Zhao, P. Chen, T. Nakaguchi, D. Grundy, and H. Gregersen. Interdependency between mechanical parameters and afferent nerve discharge in hypertrophic intestine of rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 310:G376–G386, 2016.
Zarrinpar, A., A. Chaix, and S. Panda. Daily eating patterns and their impact on health and disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 27:69–83, 2016.
Zhao, J., D. Liao, and H. Gregersen. Biomechanics of the gastrointestinal tract in health and disease. In: Biomechanics: Principles, Trends and Applications, edited by J. Zhao, D. Liao, and H. Gregersen. Nova: New York, 2010, pp. 163–206.
Zhao, J., J. Yang, and H. Gregersen. Biomechanical and morphometric intestinal remodelling during experimental diabetes in rats. Diabetologia 46:1688–1697, 2003.
Acknowledgments
The studies were financially supported by Grants from Chongqing Science and Technology Commission (cstc2013kjrc-ljrccj10003), National “111 Plan” Base (B06023) and Danish Karen Elise Jensen foundation. Yue Liu was partially supported by “The Short-term International Academic fund” of Chongqing University 2015 Overseas Visiting Student Project. These contributions did not constitute conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Elena S. Di Martino oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhao, J., Liao, D. et al. Intestinal Mechanomorphological Remodeling Induced by Long-Term Low-Fiber Diet in Rabbits. Ann Biomed Eng 45, 2867–2878 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1922-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1922-5