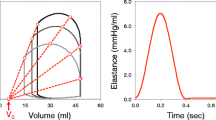
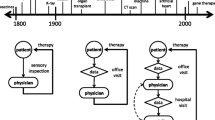
Abstract
Computational modelling of the heart is rapidly advancing to the point of clinical utility. However, the difficulty of parameterizing and validating models from clinical data indicates that the routine application of truly predictive models remains a significant challenge. We argue there is significant value in an intermediate step towards prediction. This step is the use of biophysically based models to extract clinically useful information from existing patient data. Specifically in this paper we review methodologies for applying modelling frameworks for this goal in the areas of quantifying cardiac anatomy, estimating myocardial stiffness and optimizing measurements of coronary perfusion. Using these indicative examples of the general overarching approach, we finally discuss the value, ongoing challenges and future potential for applying biophysically based modelling in the clinical context.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Saadi, N., E. Nagel, M. Gross, A. Bornstedt, B. Schnackenburg, C. Klein, W. Klimek, H. Oswald, and E. Fleck. Noninvasive detection of myocardial ischemia from perfusion reserve based on cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Circulation 101:1379–1383, 2000.
Ashikaga, H., H. Arevalo, F. Vadakkumpadan, R. C. Blake, J. D. Bayer, S. Nazarian, M. Muz Zviman, H. Tandri, R. D. Berger, H. Calkins, D. A. Herzka, N. A. Trayanova, and H. R. Halperin. Feasibility of image-based simulation to estimate ablation target in human ventricular arrhythmia. Hear. Rhythm 10:1109–1116, 2013.
Audoly, S., G. Bellu, L. D’Angiò, M. P. Saccomani, and C. Cobelli. Global identifiability of nonlinear models of biological systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 48:55–65, 2001.
Augenstein, K. F., B. R. Cowan, I. J. LeGrice, P. M. F. Nielsen, and A. A. Young. Method and apparatus for soft tissue material parameter estimation using tissue tagged magnetic resonance imaging. J. Biomech. Eng. 127:148, 2005.
Bermejo, J., R. Yotti, C. Pérez del Villar, J. C. del Álamo, D. Rodríguez-Pérez, P. Martínez-Legazpi, Y. Benito, J. C. Antoranz, M. M. Desco, A. González-Mansilla, A. Barrio, J. Elízaga, and F. Fernández-Avilés. Diastolic chamber properties of the left ventricle assessed by global fitting of pressure-volume data: improving the gold standard of diastolic function. J. Appl. Physiol. 115:556–568, 2013.
Borlaug, B. A., and W. J. Paulus. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Eur. Hear. J. 32:670–679, 2011.
Butterworth, E., B. E. Jardine, G. M. Raymond, M. L. Neal, and J. B. Bassingthwaighte. JSim, an open-source modeling system for data analysis. F1000 Res 2:288, 2013.
Cebral, J. R., M. A. Castro, J. E. Burgess, R. S. Pergolizzi, M. J. Sheridan, and C. M. Putman. Characterization of cerebral aneurysms for assessing risk of rupture by using patient-specific computational hemodynamics models. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 26:2550–2559, 2005.
Chapelle, D., J.-F. Gerbeau, J. Sainte-Marie, and I. Vignon-Clementel. A poroelastic model valid in large strains with applications to perfusion in cardiac modeling. Comput. Mech. 46:91–101, 2010.
Clayton, R. H., O. Bernus, E. M. Cherry, H. Dierckx, F. H. Fenton, L. Mirabella, A. V. Panfilov, F. B. Sachse, G. Seemann, and H. Zhang. Models of cardiac tissue electrophysiology: progress, challenges and open questions. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 104:22–48, 2011.
Cohn, J. N., R. Ferrari, and N. Sharpe. Cardiac remodeling-concepts and clinical implications: a consensus paper from an International Forum on Cardiac Remodeling. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 35:569–582, 2000.
Cookson, A. N., J. Lee, C. Michler, R. Chabiniok, E. R. Hyde, D. A. Nordsletten, M. Sinclair, M. Siebes, and N. P. Smith. A novel porous mechanical framework for modelling the interaction between coronary perfusion and myocardial mechanics. J. Biomech. 45:850–855, 2012.
Cookson, A. N., J. Lee, C. Michler, R. Chabiniok, E. Hyde, D. Nordsletten, and N. P. Smith. A spatially-distributed computational model to quantify behaviour of contrast agents in MR perfusion imaging. Med. Image Anal. 18:1200–1216, 2014.
Cookson, A. N., J. Lee, D. Nordsletten, and N. P. Smith. Contrast agent transport in a multiscale poroelastic model of myocardial perfusion. J. Comput. Phys. Submitted, 2015.
Cootes, T., A. Hill, C. Taylor, and J. Haslam. Use of active shape models for locating structures in medical images. Image Vis. Comput. 12:355–365, 1994.
Cullen, J. H., M. A. Horsfield, C. R. Reek, G. R. Cherryman, D. B. Barnett, and N. J. Samani. A myocardial perfusion reserve index in humans using first-pass contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 33:1386–1394, 1999.
DiFrancesco, D., and D. Noble. A model of cardiac electrical activity incorporating ionic pumps and concentration changes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. L. B Biol. Sci. 307:353–398, 1985.
Fedak, P. W. M., S. Verma, R. D. Weisel, and R.-K. Li. Cardiac remodeling and failure: from molecules to man (Part I). Cardiovasc. Pathol. 14:1–11, 2005.
Finegold, J. A., P. Asaria, and D. P. Francis. Mortality from ischaemic heart disease by country, region, and age: statistics from World Health Organisation and United Nations. Int. J. Cardiol. 168:934–945, 2013.
Firstenberg, M. S., P. M. Vandervoort, N. L. Greenberg, N. G. Smedira, P. M. McCarthy, M. J. Garcia, and J. D. Thomas. Noninvasive estimation of transmitral pressure drop across the normal mitral valve in humans: Importance of convective and inertial forces during left ventricular filling. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 36:1942–1949, 2000.
Fonseca, C. G., M. Backhaus, D. A. Bluemke, R. D. Britten, J. D. Chung, B. R. Cowan, I. D. Dinov, J. P. Finn, P. J. Hunter, A. H. Kadish, D. C. Lee, J. A. C. Lima, P. Medrano-Gracia, K. Shivkumar, A. Suinesiaputra, W. Tao, and A. A. Young. The cardiac Atlas Project-an imaging database for computational modeling and statistical atlases of the heart. Bioinformatics 27:2288–2295, 2011.
Gaddum, N. R., L. Keehn, A. Guilcher, A. Gomez, S. Brett, P. Beerbaum, T. Schaeffter, and P. Chowienczyk. Altered dependence of aortic pulse wave velocity on transmural pressure in hypertension revealing structural change in the aortic wall. Hypertension 65:362–369, 2015.
Garny, A., D. Noble, and P. Kohl. Dimensionality in cardiac modelling. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 87:47–66, 2005.
Gonzalez, G., D. Nolte, A. Lewandowski, P. Leeson, N. Smith, and P. Lamata. Improving the stratification power of cardiac ventricular shape. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 17:O77, 2015.
Grenander, U., and M. I. Miller. Computational anatomy: an emerging discipline. Q. Appl. Math. 56:617–694, 1998.
Hadjicharalambous, M., R. Chabiniok, L. Asner, E. Sammut, J. Wong, G. Carr-White, J. Lee, R. Razavi, N. Smith, and D. Nordsletten. Analysis of passive cardiac constitutive laws for parameter estimation using 3D tagged MRI. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2014. doi:10.1007/s10237-014-0638-9.
Hautvast, G. L. T. F., A. Chiribiri, T. Lockie, M. Breeuwer, E. Nagel, and S. Plein. Quantitative analysis of transmural gradients in myocardial perfusion magnetic resonance images. Magn. Reson. Med. 66:1477–1487, 2011.
Heimann, T., and H.-P. Meinzer. Statistical shape models for 3D medical image segmentation: a review. Med. Image Anal. 13:543–563, 2009.
Helm, P. A., L. Younes, M. F. Beg, D. B. Ennis, C. Leclercq, O. P. Faris, E. McVeigh, D. Kass, M. I. Miller, and R. L. Winslow. Evidence of structural remodeling in the dyssynchronous failing heart. Circ. Res. 98:125–132, 2006.
Hunter, P. J., and T. K. Borg. Integration from proteins to organs: the Physiome Project. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:237–243, 2003.
Hyde, E. R., A. N. Cookson, J. Lee, C. Michler, A. Goyal, T. Sochi, R. Chabiniok, M. Sinclair, D. A. Nordsletten, J. Spaan, J. P. van den Wijngaard, M. Siebes, and N. P. Smith. Multi-scale parameterisation of a myocardial perfusion model using whole-organ arterial networks. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 42:797–811, 2014.
Hyde, E. R., C. Michler, J. Lee, A. N. Cookson, R. Chabiniok, D. A. Nordsletten, and N. P. Smith. Parameterisation of multi-scale continuum perfusion models from discrete vascular networks. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 51:557–570, 2012.
Ishida, M., G. Morton, A. Schuster, E. Nagel, and A. Chiribiri. Quantitative assessment of myocardial perfusion MRI. Curr. Cardiovasc. Imaging Rep. 3:65–73, 2010.
Jerosch-Herold, M., R. T. Seethamraju, C. M. Swingen, N. M. Wilke, and A. E. Stillman. Analysis of myocardial perfusion MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 19:758–770, 2004.
Jerosch-Herold, M., N. Wilke, and A. E. Stillman. Magnetic resonance quantification of the myocardial perfusion reserve with a Fermi function model for constrained deconvolution. Med. Phys. 25:73–84, 1998.
Kirk, J. A., M. P. Saccomani, and S. G. Shroff. A priori identifiability analysis of cardiovascular models. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 4:500–512, 2013.
Lamata, P., R. Casero, V. Carapella, S. A. Niederer, M. J. Bishop, J. E. Schneider, P. Kohl, and V. Grau. Images as drivers of progress in cardiac computational modelling. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 115:198–212, 2014.
Lamata, P., S. Niederer, D. Nordsletten, D. C. Barber, I. Roy, D. Hose, and N. Smith. An accurate, fast and robust method to generate patient-specific cubic Hermite meshes. Med. Image Anal. 15:801–813, 2011.
Lamata, P., A. Pitcher, S. Krittian, D. Nordsletten, M. M. Bissell, T. Cassar, A. J. Barker, M. Markl, S. Neubauer, and N. P. Smith. Aortic relative pressure components derived from four-dimensional flow cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Magn. Reson. Med. 72:1162–1169, 2014.
Lamata, P., M. Sinclair, E. Kerfoot, A. Lee, A. Crozier, B. Blazevic, S. Land, A. J. Lewandowski, D. Barber, S. Niederer, and N. Smith. An automatic service for the personalization of ventricular cardiac meshes. J. R. Soc. Interface 11(91):20131023, 2014.
Lee, J., D. Nordsletten, A. Cookson, S. Rivolo, and N. Smith. In silico coronary wave intensity analysis: application of an integrated one-dimensional and poromechanical model of cardiac perfusion. J. Physiol. Under revi, 2014.
Lewandowski, A. J., D. Augustine, P. Lamata, E. F. Davis, M. Lazdam, J. Francis, K. McCormick, A. R. Wilkinson, A. Singhal, and A. Lucas. Preterm heart in adult life: cardiovascular magnetic resonance reveals distinct differences in left ventricular mass, geometry, and function. Circulation 127:197–206, 2013.
Li, L., S. A. Niederer, W. Idigo, Y. H. Zhang, P. Swietach, B. Casadei, and N. P. Smith. A mathematical model of the murine ventricular myocyte: a data-driven biophysically based approach applied to mice overexpressing the canine NCX isoform. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 299:H1045–H1063, 2010.
Maeder, M. T., and D. M. Kaye. Heart failure with normal left ventricular ejection fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 53:905–918, 2009.
Medrano-Gracia, P., B. Cowan, J. P. Finn, A. Kadish, D. Lee, J. Lima, A. Suinesiaputra, and A. Young. Atlas-based analysis of cardiac shape and function: correction of regional shape bias due to imaging protocol for population studies. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 15:80, 2013.
Members, A. F., et al. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 14:803–869, 2012.
Michler, C., A. N. Cookson, R. Chabiniok, E. Hyde, J. Lee, M. Sinclair, T. Sochi, A. Goyal, G. Vigueras, D. A. Nordsletten, and N. P. Smith. A computationally efficient framework for the simulation of cardiac perfusion using a multi-compartment Darcy porous-media flow model. Int. J. Numer. Method. Biomed. Eng. 29:217–232, 2013.
Min, J. K., J. Leipsic, M. J. Pencina, D. S. Berman, B.-K. Koo, C. van Mieghem, A. Erglis, F. Y. Lin, A. M. Dunning, P. Apruzzese, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of fractional flow reserve from anatomic CT angiography. Jama 308:1237–1245, 2012.
Morris, P. D., D. Ryan, A. C. Morton, R. Lycett, P. V. Lawford, D. R. Hose, and J. P. Gunn. Virtual fractional flow reserve from coronary angiography: modeling the significance of coronary lesions: results from the VIRTU-1 (VIRTUal Fractional Flow Reserve From Coronary Angiography) study. JACC. Cardiovasc. Interv. 6:149–157, 2013.
Motwani, M., A. Kidambi, S. Sourbron, T. A. Fairbairn, A. Uddin, S. Kozerke, J. P. Greenwood, and S. Plein. Quantitative three-dimensional cardiovascular magnetic resonance myocardial perfusion imaging in systole and diastole. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 16:19, 2014.
Nagel, E., C. Klein, I. Paetsch, S. Hettwer, B. Schnackenburg, K. Wegscheider, and E. Fleck. Magnetic resonance perfusion measurements for the noninvasive detection of coronary artery disease. Circulation 108:432–437, 2003.
Nasopoulou, A., B. Blazevic, A. Crozier, W. Shi, A. Shetty, C. A. Rinaldi, P. Lamata, and S. Niederer. Myocardial stiffness estimation: a novel cost function for unique parameter identification. In: Functional imaging and modeling of the heart SE—41, edited by H. van Assen, P. Bovendeerd, and T. Delhaas. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2015, pp. 355–363.
Niederer, S. A., M. Fink, D. Noble, and N. P. Smith. A meta-analysis of cardiac electrophysiology computational models. Exp. Physiol. 94:486–495, 2009.
Niederer, S. A., G. Plank, P. Chinchapatnam, M. Ginks, P. Lamata, K. S. Rhode, C. A. Rinaldi, R. Razavi, and N. P. Smith. Length-dependent tension in the failing heart and the efficacy of cardiac resynchronization therapy. Cardiovasc. Res. 89:336–343, 2010.
Nolte, F., E. R. Hyde, C. Rolandi, J. Lee, P. van Horssen, K. Asrress, J. P. H. M. van den Wijngaard, A. N. Cookson, T. van de Hoef, R. Chabiniok, R. Razavi, C. Michler, G. L. T. F. Hautvast, J. J. Piek, M. Breeuwer, M. Siebes, E. Nagel, N. P. Smith, and J. A. E. Spaan. Myocardial perfusion distribution and coronary arterial pressure and flow signals: clinical relevance in relation to multiscale modeling, a review. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 51:1271–1286, 2013.
Opie, L. H., P. J. Commerford, B. J. Gersh, and M. A. Pfeffer. Controversies in ventricular remodelling. Lancet 367:356–367, 2006.
Pathmanathan, P., and R. A. Gray. Ensuring reliability of safety-critical clinical applications of computational cardiac models. Front. Physiol. 4:358, 2013.
Rappaport, D., E. Konyukhov, L. Shulman, Z. Friedman, P. Lysyansky, A. Landesberg, and D. Adam. Detection of the cardiac activation sequence by novel echocardiographic tissue tracking method. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 33:880–893, 2007.
Relan, J., P. Chinchapatnam, M. Sermesant, K. Rhode, M. Ginks, H. Delingette, C. A. Rinaldi, R. Razavi, and N. Ayache. Coupled personalization of cardiac electrophysiology models for prediction of ischaemic ventricular tachycardia. Interface Focus 1:396–407, 2011.
Schileo, E., F. Taddei, L. Cristofolini, and M. Viceconti. Subject-specific finite element models implementing a maximum principal strain criterion are able to estimate failure risk and fracture location on human femurs tested in vitro. J. Biomech. 41:356–367, 2008.
Sermesant, M., R. Chabiniok, P. Chinchapatnam, T. Mansi, F. Billet, P. Moireau, J. M. Peyrat, K. Wong, J. Relan, K. Rhode, M. Ginks, P. Lambiase, H. Delingette, M. Sorine, C. A. Rinaldi, D. Chapelle, R. Razavi, and N. Ayache. Patient-specific electromechanical models of the heart for the prediction of pacing acute effects in CRT: a preliminary clinical validation. Med. Image Anal. 16:201–215, 2012.
Sermesant, M., P. Moireau, O. Camara, J. Sainte-Marie, R. Andriantsimiavona, R. Cimrman, D. L. G. Hill, D. Chapelle, and R. Razavi. Cardiac function estimation from MRI using a heart model and data assimilation: advances and difficulties. Med Image Anal 10:642–656, 2006.
Shi, W., X. Zhuang, H. Wang, S. Duckett, D. Luong, C. Tobon-Gomez, K. Tung, P. Edwards, K. S. Rhode, R. S. Razavi, S. Ourselin, and D. Rueckert. A comprehensive cardiac motion estimation framework using both untagged and 3D tagged MR images based on nonrigid registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 31:1263–1275, 2012.
Smith, N. P. A computational study of the interaction between coronary blood flow and myocardial mechanics. Physiol. Meas. 25:863–877, 2004.
Smith, N. P., E. J. Crampin, S. A. Niederer, J. B. Bassingthwaighte, and D. A. Beard. Computational biology of cardiac myocytes: proposed standards for the physiome. J. Exp. Biol. 210(9):1576–1583, 2007.
Smith, N., A. de Vecchi, M. McCormick, D. Nordsletten, O. Camara, A. F. Frangi, H. Delingette, M. Sermesant, J. Relan, N. Ayache, M. W. Krueger, W. H. W. Schulze, R. Hose, I. Valverde, P. Beerbaum, C. Staicu, M. Siebes, J. Spaan, P. Hunter, J. Weese, H. Lehmann, D. Chapelle, and R. Rezavi. euHeart: personalized and integrated cardiac care using patient-specific cardiovascular modelling. Interface Focus 1:349–364, 2011.
Sourbron, S. A tracer-kinetic field theory for medical imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33:935–946, 2014.
Spaan, J. A., N. P. Breuls, and J. D. Laird. Diastolic-systolic coronary flow differences are caused by intramyocardial pump action in the anesthetized dog. Circ. Res. 49:584–593, 1981.
Tofts, P. S., G. Brix, D. L. Buckley, J. L. Evelhoch, E. Henderson, M. V. Knopp, H. B. Larsson, T.-Y. Lee, N. A. Mayr, G. J. Parker, R. E. Port, J. Taylor, and R. M. Weisskoff. Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: standardized quantities and symbols. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 10:223–232, 1999.
Wang, V. Y., H. I. Lam, D. B. Ennis, B. R. Cowan, A. A. Young, and M. P. Nash. Modelling passive diastolic mechanics with quantitative MRI of cardiac structure and function. Med. Image Anal. 13:773–784, 2009.
Winslow, R., L. N. Trayanova, D. Geman, and M. I. Miller. Computational medicine: translating models to clinical care. Sci. Transl. Med. 4:158rv11, 2012.
Wong, K. C. L., M. Sermesant, K. Rhode, M. Ginks, C. A. Rinaldi, R. Razavi, H. Delingette, and N. Ayache. Velocity-based cardiac contractility personalization from images using derivative-free optimization. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 43:35–52, 2015.
Xi, J., P. Lamata, J. Lee, P. Moireau, D. Chapelle, and N. Smith. Myocardial transversely isotropic material parameter estimation from in silico measurements based on a reduced-order unscented Kalman filter. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 4:1090–1102, 2011.
Xi, J., P. Lamata, S. Niederer, S. Land, W. Shi, X. Zhuang, S. Ourselin, S. G. Duckett, A. K. Shetty, C. A. Rinaldi, D. Rueckert, R. Razavi, and N. P. Smith. The estimation of patient-specific cardiac diastolic functions from clinical measurements. Med. Image Anal. 17:133–146, 2013.
Xi, J., W. Shi, D. Rueckert, R. Razavi, N. Smith, and P. Lamata. Understanding the need of ventricular pressure for the estimation of diastolic biomarkers. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 13:747–757, 2014.
Zierler, K. L. Theoretical basis of indicator-dilution methods for measuring flow and volume. Circ. Res. 10:393–407, 1962.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge funding from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EP/G0075727/2), the Wellcome Trust Medical Engineering Centre at King’s College London (WT 088641/Z/09/Z). PL holds a Sir Henry Dale Fellowship funded jointly by the Wellcome Trust and the Royal Society (Grant No. 099973/Z/12/Z). This research was supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London. The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Karol Miller oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamata, P., Cookson, A. & Smith, N. Clinical Diagnostic Biomarkers from the Personalization of Computational Models of Cardiac Physiology. Ann Biomed Eng 44, 46–57 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1439-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1439-8