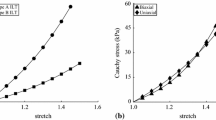
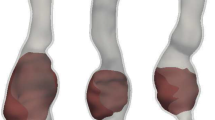
Abstract
It has been recognized that the intraluminal thrombus (ILT) is a biologically active material contributing in the progression and rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs). To advance our understanding of the potential role of ILT in the natural history of AAAs, the structural, mechanical, and histological characteristics of ILTs have been studied with great interest over the past decade. Given that the ILT is evolving and changing its composition during AAA progression, attention has been paid to exploring the chemomechanical effects of ILT on the underlying wall properties. Various biomechanical and chemomechanical data, and related models have provided advanced insights into AAA pathogenesis which have served as a basis for clinical diagnosis. The goal of this review is to describe and summarize recent advances in the research of ILT found in the aorta in terms of structure, mechanics, and histology on a patient-specific basis. We point to some possible future studies which hopefully stimulate multidisciplinary research to address open problems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolph, R., D. A. Vorp, D. L. Steed, M. W. Webster, M. V. Kameneva, and S. C. Watkins. Cellular content and permeability of intraluminal thrombus in abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 25:916–926, 1997.
Arzani, A., G. Y. Suh, R. L. Dalman, and S. C. Shadden. A longitudinal comparison of hemodynamics and intraluminal thrombus deposition in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 307:H1786-H1795, 2014. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00461.2014.
Ashton, J. H., J. P. Vande Geest, B. R. Simon, and D. G. Haskett. Compressive mechanical properties of the intraluminal thrombus in abdominal aortic aneurysms and fibrin-based thrombus mimics. J. Biomech. 42:197–201, 2009.
Basciano, C., C. Kleinstreuer, S. Hyun, and E. A. Finol. A relation between near-wall particle-hemodynamics and onset of thrombus formation in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 39:2010–2026, 2011.
Bluestein, D., K. Dumont, M. De Beule, J. Ricotta, P. Impellizzeri, B. Verhegghe et al. Intraluminal thrombus and risk of rupture in patient specific abdominal aortic aneurysm—FSI modelling. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 12:73–81, 2009.
Brown, L. C. and J. T. Powell. Risk factors for aneurysm rupture in patients kept under ultrasound surveillance. UK Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Ann. Surg. 230:289–296, 1999.
Brown, E. A., R. I. Litvinov, D. E. Disher, P. K. Purohit, and J. W. Weisel. Multiscale mechanics of fibrin polymer: gel stretching with protein unfolding and loss of water. Science. 325:741–744, 2009.
Carmo, M., L. Colombo, A. Bruno, F. R. Corsi, L. Roncoroni, M. S. Cuttin et al. Alteration of elastin, collagen and their cross-links in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 23:543–549, 2002.
Carrell, T. W., K. G. Burnand, N. A. Booth, J. Humphries, and A. Smith. Intraluminal thrombus enhances proteolysis in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Vascular. 14:9–16, 2006.
Chen, C. Y., R. Antón, M. Y. Hung, P. Menon, E. A. Finol, and K. Pekkan. Effects of intraluminal thrombus on patient-specific abdominal aortic aneurysm hemodynamics via stereoscopic particle image velocity and computational fluid dynamics modeling. J. Biomech. Eng. 136:031001, 2014.
da Silva, E. S., A. J. Rodrigues, E. Magalhaes Castro de Tolosa, C. J. Rodrigus, G. Villas Boas do Prado, and J. C. Nakamoto. Morphology and diameter of infrarenal aortic aneurysms: a prospective autopsy study. Cardiovasc. Surg. 8:526–532, 2000.
Darling, R.C., C. R. Messina, D. C. Brewster, and L. W. Ottinger. Autopsy study of unoperated abdominal aortic aneurysms. Circulation. 56 (II suppl):161–164, 1977.
Di Achille, P., G. Tellides, C. A. Figueroa, and J. D. Humphrey. A haemodynamic predictor of intraluminal thrombus formation in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. 470:20140163, 2014.
Di Martino, E. S., S. Mantero, F. Inzoli, G. Melissano, D. Astore, R. Chiesa et al. Biomechanics of abdominal aortic aneurysm in the presence of endoluminal thrombus: experimental characterisation and structural static computational analysis. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 15:290–299, 1998.
Dobrin, P. B. Pathophysiology and pathogenesis of aortic aneurysms. Current concepts. Surg. Clin. North. Am. 69:687–703, 1989.
Dobrin, P. B., W. H. Baker, and W. C. Gley. Elastolytic and collagenolytic studies of arteries. Implications for the mechanical properties of aneurysms. Arch. Surg. 119:405–409, 1984.
Fineschi, V., E. Turillazzi, M. Neri, C. Pomara, and I. Riezzo. Histological age determination of venous thrombosis: a neglected forensic task in fatal pulmonary thrombo-embolism. Forensic Sci. Int. 186:22–28, 2009.
Fleming, C., E. P. Whitlock, T. L. Beil, and F. A. Lederle. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: a best-evidence systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 142:203–211, 2005.
Folkesson, M., A. Silveira, P. Eriksson, and J. Swedenborg. Protease activity in the multi-layered intra-luminal thrombus of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Atherosclerosis. 218:294–299, 2011.
Furie, B. and B. C. Furie. In vivo thrombus formation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 5 (Suppl 1):12–17, 2007.
Gasser, T. C., G. Görgülü, M. Folkesson, and J. Swedenborg. Failure properties of intraluminal thrombus in abdominal aortic aneurysm under static and pulsating mechanical loads. J. Vasc. Surg. 48:179–188, 2008.
Gasser, T. C., M. Auer, F. Labruto, J. Swedenborg, and J. Roy. Biomechanical rupture risk assessment of abdominal aortic aneurysms: model complexity versus predictability of finite element simulations. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 40:176–185, 2010.
Georgakarakos, E., C. V. Ioannou, S. Volanis, Y. Papaharilaou, J. Ekaterinaris, and A. N. Katsamouris. The influence of intraluminal thrombus on abdominal aortic aneurysm wall stress. Int. Angiol. 28:325–333, 2009.
Hans, S. S., O. Jareunpoon, M. Balasubramaniam, G. B. Zelenock. Size and location of thrombus in intact and ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 41:584–588, 2005.
Harter, L. P., B. H. Gross, R. A. Callen, and R. A. Barth. Ultrasonic evalution of abdominal aortic thrombus. J. Ultrasound Med. 1:315–318, 1982.
Hinnen, J. W., D. J. Rixen, O. H. Koning, J. H. van Bockel, and J. F. Hamming. Development of fibrinous thrombus analogue for in-vitro abdominal aortic aneurysm studies. J. Biomech. 40:289–295, 2007.
Holmes, D. R., S. Liao, W. C. Parks, and R. W. Thompson. Medial neovascularization in abdominal aortic aneurysms: a histopathological marker of aneurysmal degeneration with pathophysiologic implications. J. Vasc. Surg. 21:761–771, 1995.
Holzapfel, G. A. Nonlinear Solid Mechanics. A Continuum Approach for Engineering. Chichester: Wiley, 2000.
Holzapfel, G. A., J. Tong, T. Cohnert, and P. Regitnig. Recent advances in the biomechanics of abdominal aortic aneurysms. In: ESVB 2011 New Endovascular Technologies. From Bench Test to Clinical Practice, edited by N. Chakfé, B. Durand, and W. Meichelboeck. Strasbourg: Europrot, 2011, pp. 23–40.
Holzapfel, G. A., T. C. Gasser, and R. W. Ogden. A new constitutive framework for arterial wall mechanics and a comparative study of material models. J. Elast. 61:1–48, 2000.
Holzapfel, G. A., G. Sommer, C. T. Gasser, P. Regitnig. Determination of layer-specific mechanical properties of human coronary arteries with non-atherosclerotic intimal thickening, and related constitutive modeling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 289:H2048–H2058, 2005.
Humphrey, J. D. and C. A. Taylor. Intracranial and abdominal aortic aneurysms: similarities, differences, and need for a new class of computational models. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 10:221–246, 2008.
Humphrey, J. D. and G. A. Holzapfel. Mechanics, mechanobiology, and modeling of human abdominal aorta and aneurysms. J. Biomech. 45:805–814, 2012.
Inzoli, F., F. Boschetti, M. Zappa, T. Longo, and R. Fumero. Biomechanical factors in abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture. Eur. J. Vasc. Surg. 7:667–674, 1993.
Irniger, W. Histologische Altersbestimmung von Thrombosen und Embolien. Virchows Arch. Path. Anat. 336:220–237, 1963.
Kamocka, M. M., J. Mu, X. Liu, N. Chen, A. Zollman, B. Sturonas-Brown et al. Two-photon intravital imaging of thrombus development. J. Biomed. Opt. 15:016020, 2010.
Karšaj, I. and J. D. Humphrey. A mathematical model of evolving mechanical properties of intraluminal thrombus. Biorheology. 46:509–527, 2009.
Katz, D.J., J. C. Stanley, and G. B. Zelenock. Operative mortality rates for intact and ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms in Michigan: an eleven-year statewide experience. J. Vasc. Surg. 19:804–817, 1994.
Kazi, M., J. Thyberg, P. Religa, J. Roy, P. Eriksson, U. Hedin et al. Influence of intraluminal thrombus on structural and cellular composition of abdominal aortic aneurysm wall. J. Vasc. Surg. 38:1283–1292, 2003.
Kazi, M., C. Zhu, J. Roy, G. Paulsson-Berne, A. Hamsten, J. Swedenborg et al. Difference in matrix-degrading protease expression and activity between thrombus-free and thrombus-covered wall of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25:1341–1346, 2005.
Koole, D., H. J. Zandvoort, A. Schoneveld, A. Vink, J. A. Vos, L. L. van den Hoogen et al. Intraluminal abdominal aortic aneurysm thrombus is associated with disruption of wall integrity. J. Vasc. Surg. 57:77–83, 2013.
Lederle, F. A., S. E. Wilson, G. R. Johnson, D. B. Reinke, F. N. Littooy, C. W. Acher et al. Immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N. Engl. J. Med. 346:1437–1444, 2002.
Les, A.S., S. C. Shadden, C. A. Figueroa, J. M. Park, M. M. Tedesco, R. J. Herfkens et al. Quantification of hemodynamics in abdominal aortic aneurysms during rest and exercise using magnetic resonance imaging and computational fluid dynamics. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:1288–1313, 2010.
Liu, W., L. M. Jawerth, E. A. Sparks, M. R. Falvo, R. R. Hantgan, R. Superfine et al. Fibrin fibers have extraordinary extensibility and elasticity. Science. 313:634, 2006.
Maier, A., M. W. Gee, C. Reeps, H. H. Eckstein, and W. A. Wall. Impact of calcifications on patient-specific wall stress analysis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Biomech. Model Mechanobiol. 9:511–521, 2010.
Martinez-Pinna, R., J. Madrigal-Matute, C. Tarin, E. Burillo, M. Esteban-Salan, C. Pastor-Vargas et al. Proteomic analysis of intraluminal thrombus highlights complement activation in human abdominal aortic aneurysms. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 33:2013–2020, 2013.
Matusik, P., P. Mazur, E. Stepień, R. Pfitzner, J. Sadowski, and A. Undas. Architecture of intraluminal thrombus removed from abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis. 30:7–9, 2010.
Mower, W. R., L. J. Baraff, and J. Sneyd. Stress distributions in vascular aneurysms: factors affecting risk of aneurysm rupture. J. Surg. Res. 55:155–161, 1993.
Mower, W. R., W. J. Quinones, and S. S. Gambhir. Effect of intraluminal thrombus on abdominal aortic aneurysm wall stress. J. Vasc. Surg. 26:602–608, 1997.
Nicholls, S. C., J. B. Gardner, M. H. Meissner, and K. H. Johansen. Rupture in small abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 28:884–888, 1998.
Noel, A. A., P. Gloviczki, K. J. Cherry Jr, T. C. Bower, J. M. Panneton, G. I. Mozes et al. Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: the excessive mortality rate of conventional repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 34:41–46, 2001.
O’Leary, S. A., E. G. Kavanagh, P. A. Grace, T. M. McGloughlin, and B. J. Dolye. The biaxial mechanical behaviour of abdominal aortic aneurysm intraluminal thrombus: Classification of morphology and the determination of layer and region specific properties. J. Biomech. 47:1430–1437, 2014.
O’Rourke, M. J., J. P. McCullough, and S. Kelly. An investigation of the relationship between hemodynamics and thrombus deposition within patient-specific models of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 226:548–564, 2012.
Polzer, S., T. C. Gasser, J. Swedenborg, and J. Bursa. The impact of intraluminal thrombus failure on the mechanical stress in the wall of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 41:467–473, 2011.
Powell, J. T. and A. R. Brady. Detection, management, and prospects for the medical treatment of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24:241–245, 2004.
Raghavan, M. L. and D. A. Vorp. Toward a biomechanical tool to evaluate rupture potential of abdominal aortic aneurysm: identification of a finite strain constitutive model and evaluation of its applicability. J. Biomech. 33:475–482, 2000.
Salsac, A. V., S. R. Sparks, and J. C. Lasheras. Hemodynamic changes occurring during the progressive enlargement of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 18:14–21, 2004.
Satta, J., E. Läärä, and T. Juvonen. Intraluminal thrombus predicts rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 23:737–739, 1996.
Schurink, G. W. H., J. M. van Baalen, M. J. T Visser, J. H. van Bockel. Thrombus within an aortic aneurysm does not reduce pressure on the aneurysmal wall. J. Vasc. Surg. 31:501–506, 2000.
Shah, P. K. Inflammation, metalloproteinases, and increased proteolysis: an emerging pathophysiologic paradigm in aortic aneurysm. Circulation. 96:2228–2232, 1997.
Sommer, G., T. C. Gasser, P. Regitnig, M. Auer, and G. A. Holzapfel. Dissection of the human aortic media: an experimental study. J. Biomech. Eng. 130:021007, 2008
Speelman, L., G. W. H. Schurink, E. M. H. Bosboom, J. Buth, M. Breeuwer, F. N. van de Vosse et al. The mechanical role of thrombus on the growth rate of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 51:19–26, 2010.
Stenbaek, J., B. Kalin, and J. Swedenborg. Growth of thrombus may be a better predictor of rupture than diameter in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 20:466–499, 2000.
Swedenborg, J. and P. Eriksson. The intraluminal thrombus as a source of proteolytic activity. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1085:133–138, 2006.
Tong, J., T. Cohnert, P. Regitnig, and G. A. Holzapfel. Effects of age on the elastic properties of the intraluminal thrombus and the thrombus-covered wall in abdominal aortic aneurysms: biaxial extension behavior and material modeling. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 42:207–219, 2011.
Tong, J., G. Sommer, P. Regitnig, and G. A. Holzapfel. Dissection properties and mechanical strength of tissue components in human carotid bifurcations. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 39:1703–1719, 2011.
Tong, J., A. J. Schriefl, T. Cohnert, and G. A. Holzapfel. Gender differences in biomechanical properties, thrombus age, mass fraction and clinical factors of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 45:364–372, 2013.
Tong, J., T. Cohnert, P. Regitnig, J. Kohlbacher, R. Birner-Gruenberger, A. J. Schriefl et al. Variations of dissection properties and mass fractions with thrombus age in human abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Biomech. 47:14–23, 2014.
Touat, Z., V. Ollivier, J. Dai, M. G. Huisse, A. Bezeaud, U. Sebbag et al. Renewal of mural thrombus releases plasma markers and is involved in aortic abdominal aneurysm evolution. Am. J. Pathol. 168:1022–1030, 2010.
van Dam, E. A., S. D. Dams, G. W. Peters, M. C. Rutten, G. W. Schurink, J. Buth et al. Determination of linear viscoelastic behavior of abdominal aortic aneurysm thrombus. Biorheology. 43:695–707, 2006.
van Dam, E. A., S. D. Dams, G. W. M. Peters, M. C. M. Rutten, G. W. H Schurink, J. Buth et al. Non-linear viscoelastic behavior of abdominal aortic aneurysm thrombus. Biomech. Model Mechanobiol. 7:127–137, 2008.
Vande Geest, J. P., M. S. Sacks, and D. A. Vorp. A planar biaxial constitutive relation for the luminal layer of intra-luminal thrombus in abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Biomech. 39:2347–2354, 2006.
Vande Geest, J. P., D. H. J. Wang, S. R. Wisniewski, M. S. Makaroun, and D. A. Vorp. Towards a noninvasive method for determination of patient-specific wall strength distribution in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 34:1098–1106, 2006.
Vorp, D. A. Biomechanics of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Biomech. 40:1887–1902, 2007.
Vorp, D. A., J. Gorcsan, W. A. Mandarino, and M. W. Webster. The potential influence of intraluminal thrombus on abdominal aortic aneurysm as assessed by a noninvasive method. Cardiovasc. Surg. 4:732–739, 1996.
Vorp, D. A., P. C. Lee, D. H. Wang, M. S. Makaroun, E. M. Nemoto, S. Ogawa et al. Association of intraluminal thrombus in abdominal aortic aneurysm with local hypoxia and wall weakening. J. Vasc. Surg. 34:291–299, 2001.
Wang, D. H. J., M. S. Makaroun, M. W. Webster, and D. A. Vorp. Mechanical properties and microstructure of intraluminal thrombus from abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Biomech. Eng. 123:536–539, 2001.
Wang, D. H. J., M. S. Makaroun, M. W. Webster, and D. A. Vorp. Effect of intraluminal thrombus on wall stress in patient-specific models of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 36:598–604, 2002.
Weisel, J. W. The mechanical properties of fibrin for basic scientists and clinicians. Biophys. Chem. 112:267–276, 2004.
Weisel, J. W. Structure of fibrin: impact on clot stability. J. Thromb. Haemost. 5:116–124, 2007.
Wiernicki, I., E. Stachowska, K. Safranow, M. Cnotliwy, M. Rybicka, M. Kaczmarczyk et al. Enhanced matrix-degrading proteolytic activity within the thin thrombus-covered wall of human abdominal aortic aneurysms. Atherosclerosis. 212:161–165, 2010.
Wilson, J. S., L. Virag, P. Di Achille, I. Karšaj, and J. D. Humphrey. Biochemomechanics of intraluminal thrombus in abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Biomech. Eng. 135:021011, 2013.
Wolf, Y.G., W. S. Thomas, F. J. Brennan, W. G. Goff, M. J. Sise, and E. F. Bernstein. Computed tomography scanning findings associated with rapid expansion of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 20:529–535, 1994.
Xu, Z., N. Chen, M. M. Kamocka, E. D. Rosen, and M. Alber. A multiscale model of thrombus development. J. R. Soc. Interface. 5:705–722, 2008.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Estefanía Peña oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, J., Holzapfel, G.A. Structure, Mechanics, and Histology of Intraluminal Thrombi in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Ann Biomed Eng 43, 1488–1501 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1332-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1332-5