Abstract
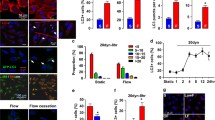
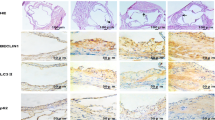
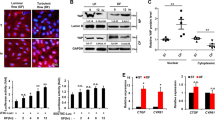
Vascular endothelial cell function responds to steady laminar shear stress; however, the underlying mechanisms are not fully elucidated. In the present study, we examined the effect of steady laminar shear stress on vascular endothelial cell autophagy and endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) expression using an ex vivo perfusion system. Human vascular endothelial cells and common arteries of New Zealand rabbits were pretreated with or without rapamycin or 3-MA for 30 min. These were then placed in an ex vivo cell perfusion system or an ex vivo organ perfusion system under static conditions (0 dynes/cm2) or steady laminar shear stress (5 or 15 dynes/cm2) for 1 h. In both ex vivo perfusion vascular endothelial cells and vascular vessel segment, steady laminar shear stress promoted autophagy and eNOS expression and inhibited ET-1 expression. Compared with steady laminar shear stress treatment alone, the pretreatment of autophagy inducer rapamycin obviously strengthened the expression of eNOS and decreased the expression of ET-1 in both the 5 and 15 dynes/cm2 treatment groups. Moreover, when pretreated with the autophagy inhibitor 3-MA, the eNOS expression was obviously inhibited and the ET-1 expression was reversed. These findings demonstrate that autophagy is upregulated under steady laminar shear stress, improving endothelial cell maintenance of vascular tone function.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, W., M. Bacanamwo, and D. G. Harrison. Activation of p300 histone acetyltransferase activity is an early endothelial response to laminar shear stress and is essential for stimulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase mRNA transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 283:16293–16298, 2008.
Cheng, C., D. Tempel, A. Oostlander, F. Helderman, F. Gijsen, J. Wentzel, R. van Haperen, D. B. Haitsma, P. W. Serruys, A. F. van der Steen, R. de Crom, and R. Krams. Rapamycin modulates the eNOS vs. shear stress relationship. Cardiovasc. Res. 78:123–129, 2008.
Corbin, F. Blaise GA, parent M, Chen H, Daloze PM. Effect of rapamycin on rat aortic ring vasomotion. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 24:813–817, 1994.
Diehl, K. J., D. L. Templeton, J. Ma, B. R. Weil, J. J. Greiner, B. L. Stauffer, and C. A. DeSouza. Impaired fasting blood glucose is associated with increased endothelin-1 vasoconstrictor tone. Atherosclerosis 229:130–133, 2013.
Eskelinen, E. L., and P. Saftig. Autophagy: a lysosomal degradation pathway with a central role in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1793:664–673, 2009.
Gijsen, F., A. van der Giessen, A. van der Steen, and J. Wentzel. Shear stress and advanced atherosclerosis in human coronary arteries. J. Biomech. 46:240–247, 2013.
Heo, K. S., K. Fujiwara, and J. Abe. Disturbed-flow-mediated vascular reactive oxygen species induce endothelial dysfunction. Circ. J. 75:2722–2730, 2011.
Herranz, B., S. Marquez, B. Guijarro, E. Aracil, C. Aicart-Ramos, I. Rodriguez-Crespo, I. Serrano, M. Rodríguez-Puyol, C. Zaragoza, and M. Saura. Integrin-linked kinase regulates vasomotor function by preventing endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling: role in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 110:439–449, 2012.
Hou, J., Z. P. Han, Y. Y. Jing, X. Yang, S. S. Zhang, K. Sun, C. Hao, Y. Meng, F. H. Yu, X. Q. Liu, Y. F. Shi, M. C. Wu, L. Zhang, and L. X. Wei. Autophagy prevents irradiation injury and maintains stemness through decreasing ROS generation in mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 4:e844, 2013.
Jeon, H., and Y. C. Boo. Laminar shear stress enhances endothelial cell survival through a NADPH oxidase 2-dependent mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 430:460–465, 2013.
Kim, J., Y. C. Kim, C. Fang, R. C. Russell, J. H. Kim, W. Fan, R. Liu, Q. Zhong, and K. L. Guan. Differential regulation of distinct Vps34 complexes by AMPK in nutrient stress and autophagy. Cell 152(1–2):290–303, 2013.
Kim, J., M. Kundu, and B. Viollet. Guan KL.AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat. Cell Biol. 13:132–141, 2011.
Kim, H. S., V. Montana, H. J. Jang, V. Parpura, and J. A. Kim. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) stimulates autophagy in vascular endothelial cells: a potential role for reducing lipid accumulation. J. Biol. Chem. 288:22693–22705, 2013.
Koo, A., C. F. Dewey, Jr., and G. García-Cardeña. Hemodynamic shear stress characteristic of atherosclerosis-resistant regions promotes glycocalyx formation in cultured endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 304:C137–C146, 2013.
LaRocca, T. J., G. D. Henson, A. Thorburn, A. L. Sindler, G. L. Pierce, and D. R. Seals. Translational evidence that impaired autophagy contributes to arterial ageing. J. Physiol. 590(Pt 14):3305–3316, 2012.
Li, M. W., M. O. Mian, T. Barhoumi, A. Rehman, K. Mann, P. Paradis, and E. L. Schiffrin. Endothelin-1 overexpression exacerbates atherosclerosis and induces aortic aneurysms in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 33:2306–2315, 2013.
Liao, X., J. C. Sluimer, Y. Wang, M. Subramanian, K. Brown, J. S. Pattison, J. Robbins, J. Martinez, and I. Tabas. Macrophage autophagy plays a protective role in advanced atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 15:545–553, 2012.
Mao, K., and D. J. Klionsky. AMPK activates autophagy by phosphorylating ULK1. Circ. Res. 108:787–788, 2011.
Matlung, H. L., A. E. Neele, H. C. Groen, K. van Gaalen, B. G. Tuna, A. van Weert, J. de Vos, J. J. Wentzel, M. Hoogenboezem, J. D. van Buul, E. VanBavel, and E. N. Bakker. Transglutaminase activity regulates atherosclerotic plaque composition at locations exposed to oscillatory shear stress. Atherosclerosis 224:355–362, 2012.
Meley, D., C. Bauvy, J. H. Houben-Weerts, P. F. Dubbelhuis, M. T. Helmond, P. Codogno, and A. J. Meijer. AMP-activated protein kinase and the regulation of autophagic proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 281:34870–34879, 2006.
Miyata, R., K. Hiraiwa, J. C. Cheng, N. Bai, R. Vincent, G. A. Francis, D. D. Sin, and S. F. Van Eeden. Statins attenuate the development of atherosclerosis and endothelial dysfunction induced by exposure to urban particulate matter (PM10). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 272:1–11, 2013.
Mizushima, N., B. Levine, A. M. Cuervo, and D. J. Klionsky. Autophagy fights disease through cellular selfdigestion. Nature 451:1069–1075, 2008.
Moore, J. P., M. Weber, and C. D. Searles. Laminar shear stress modulates phosphorylation and localization of RNA polymerase II on the endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 30:561–567, 2010.
Razani, B., C. Feng, T. Coleman, R. Emanuel, H. Wen, S. Hwang, J. P. Ting, H. W. Virgin, M. B. Kastan, and C. F. Semenkovich. Autophagy links inflammasomes to atherosclerotic progression. Cell Metab. 15:534–544, 2012.
Viegas, K. D., S. S. Dol, M. M. Salek, R. D. Shepherd, R. M. Martinuzzi, and K. D. Rinker. Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus adhesion to human umbilical vein endothelial cells demonstrates wall shear stress dependent behaviour. Biomed. Eng. Online 10:20, 2011.
Wei, D. H., X. Y. Jia, Y. H. Liu, F. X. Guo, Z. H. Tang, X. H. Li, Z. Wang, L. S. Liu, G. X. Wang, Z. S. Jian, and C. G. Ruan. Cathepsin L stimulates autophagy and inhibits apoptosis of ox-LDL-induced endothelial cells: potential role in atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 31:400–406, 2013.
Wei, Y. M., X. Li, M. Xu, J. M. Abais, Y. Chen, C. R. Riebling, K. M. Boini, P. L. Li, and Y. Zhang. Enhancement of autophagy by simvastatin through inhibition of Rac1-mTOR signaling pathway in coronary arterial myocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 31:925–937, 2013.
Wei, D., G. Wang, C. Tang, J. Qiu, J. Zhao, H. Gregersen, and L. Deng. Upregulation of SDF-1 is associated with atherosclerosis lesions induced by LDL concentration polarization. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40:1018–1027, 2012.
White, S. J., E. M. Hayes, S. Lehoux, J. Y. Jeremy, A. J. Horrevoets, and A. C. Newby. Characterization of the differential response of endothelial cells exposed to normal and elevated laminar shear stress. J. Cell. Physiol. 226:2841–2848, 2011.
Yamawaki, H., S. Lehoux, and B. C. Berk. Chronic physiological shear stress inhibits tumor necrosis factor-induced proinflammatory responses in rabbit aorta perfused ex vivo. Circulation 108:1619–1625, 2003.
Young, A., W. Wu, and W. Sun. Benjamin Larman H, Wang N, Li YS, Shyy JY, Chien S, García-Cardeña G. Flow activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in vascular endothelium leads to Krüppel-like factor 2 expression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 29:1902–1908, 2009.
Zago, A. C., J. C. Raudales, G. Attizzani, B. S. Matte, G. I. Yamamoto, J. A. Balvedi, L. Nascimento, B. G. Kosachenco, P. R. Centeno, and A. J. Zago. Local delivery of sirolimus nanoparticles for the treatment of in-stent restenosis. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 81:E124–E129, 2013.
Acknowledgments
The present research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81370378, 30800449), the construct program of the key discipline in Hunan province and key grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11332003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Associate Editor Estefanía Peña oversaw the review of this article.
Fengxia Guo, Xiaohong Li, and Juan Peng contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, F., Li, X., Peng, J. et al. Autophagy Regulates Vascular Endothelial Cell eNOS and ET-1 Expression Induced by Laminar Shear Stress in an Ex Vivo Perfused System. Ann Biomed Eng 42, 1978–1988 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1033-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1033-5