Abstract
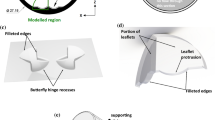
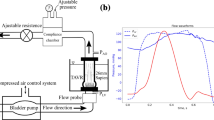
A number of clinical, in vitro and computational studies have shown the potential for thromboembolic complications in bileaflet mechanical heart valves (BMHV), primarily due to the complex and unsteady flows in the valve hinges. These studies have focused on quantitative and qualitative parameters such as velocity magnitude, turbulent shear stresses, vortex formation, and platelet activation to identify potential for blood damage. However, experimental characterization of the whole flow fields within the valve hinges has not yet been conducted. This information can be utilized to investigate instantaneous damage to blood elements and also to validate numerical studies focusing on the hinge’s complex fluid dynamics. The objective of this study was therefore to develop a high-resolution imaging system to characterize the flow fields and global velocity maps in a BMHV hinge. In this study, the steady leakage hinge flow fields representing the diastolic phase during the cardiac cycle in a 23 mm St. Jude Medical regent BMHV in the aortic position were characterized using a two-dimensional micro particle image velocimetry system. Diastolic flow was simulated by imposing a static pressure head on the aortic side. Under these conditions, a reverse flow jet from the aortic to the ventricular side was observed with velocities in the range of 1.47–3.24 m/s, whereas low flow regions were observed on the ventricular side of the hinge with viscous shear stress magnitude up to 60 N/m2. High velocities and viscous shearing may be associated with platelet activation and hemolysis, while low flow zones can cause thrombosis due to increased residence time in the hinge. Overall, this study provides a high spatial resolution experimental technique to map the fluid velocity in the BMHV hinge, which can be extended to investigate micron-scale flow domains in various prosthetic devices under different hemodynamic conditions.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellofiore, A., E. M. Donohue, and N. J. Quinlan. Scale-up of an unsteady flow field for enhanced spatial and temporal resolution of piv measurements: application to leaflet wake flow in a mechanical heart valve. Exp. Fluids 51:161–176, 2011.
Chandran, K. B., A. P. Yoganathan, and S. E. Rittgers. Biofluid Mechanics: The Human Circulation (2nd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2007.
Cooper, B. T., B. N. Roszelle, T. C. Long, S. Deutsch, and K. B. Manning. The 12 cc Penn State pulsatile pediatric ventricular assist device: fluid dynamics associated with valve selection. ASME J. Biomech. Eng. 130:041019, 2008.
Fallon, A. M., N. Shah, U. M. Marzec, J. N. Warnock, A. P. Yoganathan, and S. R. Hanson. Flow and thrombosis at orifices simulating mechanical heart valve leakage regions. ASME J. Biomech. Eng. 128:30–39, 2006.
Giersiepen, M., L. J. Wurzinger, R. Opitz, and H. Reul. Estimation of shear stress-related blood damage in heart valve prostheses—in vitro comparison of 25 aortic valves. Int. J. Artif. Organs 13:300–306, 1990.
Gross, J. M., M. C. S. Shu, F. F. Dai, J. Ellis, and A. P. Yoganathan. Microstructural flow analysis within a bileaflet mechanical heart valve hinge. J. Heart Valve Dis. 5:581–590, 1996.
Keane, R. D., and R. J. Adrian. Theory of cross-correlation analysis of PIV images. Appl. Sci. Res. 49:191–215, 1992.
Kline, S. J., and F. A. McClintock. Describing uncertainties in single-sample experiments. Mech. Eng. 75:3–8, 1953.
Leo, H.-L. An In Vitro Investigation of the Flow Fields Through Bileaflet and Polymeric Prosthetic Heart Valves. Atlanta: Biomedical Engineering Department, Georgia Institute of Technology, 2005.
Leo, H. L., Z. M. He, J. T. Ellis, and A. P. Yoganathan. Microflow fields in the hinge region of the carbomedics bileaflet mechanical heart valve design. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 124:561–574, 2002.
Leo, H. L., H. A. Simon, L. P. Dasi, and A. P. Yoganathan. Effect of hinge gap width on the microflow structures in 27-mm bileaflet mechanical heart valves. J. Heart Valve Dis. 15:800–808, 2006.
Leverett, L. B., E. C. Lynch, C. P. Alfrey, and J. D. Hellums. Red blood-cell damage by shear-stress. Biophys. J. 12:257–273, 1972.
Manning, K. B., V. Kini, A. A. Fontaine, S. Deutsch, and J. M. Tarbell. Regurgitant flow field characteristics of the St. Jude bileaflet mechanical heart valve under physiologic pulsatile flow using particle image velocimetry. Artif. Organs 27:840–846, 2003.
Meinhart, C. D., S. T. Wereley, and J. G. Santiago. PIV measurements of a microchannel flow. Exp. Fluids 27:414–419, 1999.
Meinhart, C. D., S. T. Wereley, and J. G. Santiago. A PIV algorithm for estimating time-averaged velocity fields. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 122:285–289, 2000.
Olsen, M. G., and R. J. Adrian. Out-of-focus effects on particle image visibility and correlation in microscopic particle image velocimetry. Exp. Fluids 29:S166–S174, 2000.
Raffel, M., C. E. Willer, S. T. Wereley, and J. Kompenhans. Particle Image Velocimetry: A Practical Guide. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2007.
Saikrishnan, N., C. H. Yap, N. C. Milligan, N. V. Vasilyev, and A. P. Yoganathan. In vitro characterization of bicuspid aortic valve hemodynamics using particle image velocimetry. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40:1760–1775, 2012.
Simon, H. A. Influence of the Implant Location on the Hinge and Leakage Flow Fields Through Bileaflet Mechanical Heart Valves. Atlanta: Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Department, Georgia Institute of Technology, 2004.
Simon, H. A. Numerical Simulations of the Micro Flow Field in the Hinge Region of Bileaflet Mechanical Heart Valves. Atlanta: Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Department, Georgia Institute of Technology, 2009.
Simon, H. A., L. Ge, F. Sotiropoulos, and A. P. Yoganathan. Simulation of the three-dimensional hinge flow fields of a bileaflet mechanical heart valve under aortic conditions. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:841–853, 2010.
Simon, H. A., H. L. Leo, J. Carberry, and A. P. Yoganathan. Comparison of the hinge flow fields of two bileaflet mechanical heart valves under aortic and mitral conditions. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 32:1607–1617, 2004.
Travis, B. R., U. M. Marzec, H. L. Leo, et al. Bileaflet aortic valve prosthesis pivot geometry influences platelet secretion and anionic phospholipid exposure. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 29:657–664, 2001.
Vennemann, P., K. T. Kiger, R. Lindken, et al. In vivo micro particle image velocimetry measurements of blood-plasma in the embryonic avian heart. J. Biomech. 39:1191–1200, 2006.
Wereley, S. T., and C. D. Meinhart. Recent advances in micro-particle image velocimetry. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 42:557–576, 2010.
Westerweel, J., and F. Scarano. Universal outlier detection for PIV data. Exp. Fluids 39:1096–1100, 2005.
Yoganathan, A. P., H.-L. Leo, B. R. Travis, and H. S. Teoh. Encyclopedia of Comprehensive Structural Integrity. Amsterdam: Elsevier, pp. 795–796, 2003.
Yun, B. M., J. S. Wu, H. A. Simon, et al. A numerical investigation of blood damage in the hinge area of aortic bileaflet mechanical heart valves during the leakage phase. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40:1468–1485, 2012.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Procter & Gamble (P&G) for providing glycerin for our experiments, members of the Cardiovascular Fluid Mechanics Lab at Georgia Tech and Alexandra Low for their valuable inputs. This work was supported by a grant from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (HL-07262).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Ender A Finol oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jun, B.H., Saikrishnan, N. & Yoganathan, A.P. Micro Particle Image Velocimetry Measurements of Steady Diastolic Leakage Flow in the Hinge of a St. Jude Medical® Regent™ Mechanical Heart Valve. Ann Biomed Eng 42, 526–540 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0919-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0919-y