Abstract
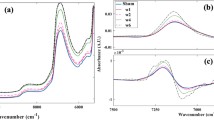
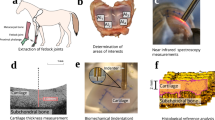
In diseased conditions of cartilage such as osteoarthritis, there is typically an increase in water content from the average normal of 60–85% to greater than 90%. As cartilage has very little capability for self-repair, methods of early detection of degeneration are required, and assessment of water could prove to be a useful diagnostic method. Current assessment methods are either destructive, time consuming, or have limited sensitivity. Here, we investigated the hypotheses that non-destructive near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) of articular cartilage can be used to differentiate between free and bound water, and to quantitatively assess water content. The absorbances centered at 5200 and 6890 cm−1 were attributed to a combination of free and bound water, and to free water only, respectively. The integrated areas of both absorbance bands were found to correlate linearly with the absolute water content (R = 0.87 and 0.86) and with percent water content (R = 0.97 and 0.96) of the tissue. Partial least square models were also successfully developed and were used to predict water content, and percent free water. These data demonstrate that NIRS can be utilized to quantitatively determine water content in articular cartilage, and may aid in early detection of degenerative tissue changes in a laboratory setting, and with additional validations, possibly in a clinical setting.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afara, I., I. Prasadam, R. Crawford, Y. Xiao, and A. Oloyede. Non-destructive evaluation of articular cartilage defects using near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy in osteoarthritic rat models and its direct relation to Mankin score. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 20(11):1367–1373, 2012.
Afara, I., S. Singh, and A. Oloyede. Application of near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy for determining the thickness of articular cartilage. Med. Eng. Phys. 35(1):88–95, 2012.
Arimoto, H., and M. Egawa. Non-contact skin moisture measurement based on near-infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 58:1439–1446, 2004.
Arimoto, H., M. Egawa, and Y. Yamada. Depth profile of diffuse reflectance near-infrared spectroscopy for measurement of water content in skin. Skin Res. Technol. 11:27–35, 2005.
Armstrong, C. G., and V. C. Mow. Variations in the intrinsic mechanical properties of human articular cartilage with age, degeneration, and water content. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 64:88–94, 1982.
Bagratashvili, V. N., E. N. Sobol, A. P. Sviridov, V. K. Popov, A. I. Omel’chenko, and S. M. Howdle. Thermal and diffusion processes in laser-induced stress relaxation and reshaping of cartilage. J. Biomech. 30:813–817, 1997.
Batty, L., S. Dance, S. Bajaj, and B. J. Cole. Autologous chondrocyte implantation: an overview of technique and outcomes. ANZ J. Surg. 81:18–25, 2011.
Baykal, D., O. Irrechukwu, P. C. Lin, K. Fritton, R. G. Spencer, and N. Pleshko. Nondestructive assessment of engineered cartilage constructs using near-infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 64:1160–1166, 2010.
Blanco, M., J. Coello, H. Iturriaga, S. Maspoch, and C. de la Pezuela. Near-infrared spectroscopy in the pharmaceutical industry. Analyst 123:135R–150R, 1998.
Bock, J. E., and R. K. Connelly. Innovative uses of near-infrared spectroscopy in food processing. J. Food Sci. 73:R91–R98, 2008.
Brown, C. P., J. C. Bowden, L. Rintoul, R. Meder, A. Oloyede, and R. W. Crawford. Diffuse reflectance near infrared spectroscopy can distinguish normal from enzymatically digested cartilage. Phys. Med. Biol. 54:5579–5594, 2009.
Brown, C. P., C. Jayadev, S. Glyn-Jones, A. J. Carr, D. W. Murray, A. J. Price, and H. S. Gill. Characterization of early stage cartilage degradation using diffuse reflectance near infrared spectroscopy. Phys. Med. Biol. 56:2299–2307, 2011.
Brown, C. P., A. Oloyede, R. W. Crawford, G. E. R. Thomas, A. J. Price, and H. S. Gill. Acoustic, mechanical and near-infrared profiling of osteoarthritic progression in bovine joints. Phys. Med. Biol. 57:14, 2012.
Büning-Pfaue, H. Analysis of water in food by near infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 82:9, 2003.
Cachet, T., and J. Hoogmartens. The determination of water in erythromycin by Karl Fischer titration. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 6:461–472, 1988.
Canvin, J. M., S. Bernatsky, C. A. Hitchon, M. Jackson, M. G. Sowa, J. R. Mansfield, H. H. Eysel, H. H. Mantsch, and H. S. El-Gabalawy. Infrared spectroscopy: shedding light on synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 42:76–82, 2003.
Caplan, A. I., M. Elyaderani, Y. Mochizuki, S. Wakitani, and V. M. Goldberg. Principles of cartilage repair and regeneration. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 342:254–269, 1997.
Chan, D. D., and C. P. Neu. Probing articular cartilage damage and disease by quantitative magnetic resonance imaging. J. R. Soc. Interface 10:78, 2013.
Czarnik-Matusewicz, B., S. Pilorz, and J. P. Hawranek. Temperature-dependent water structural transitions examined by near-IR and mid-IR spectra analyzed by multivariate curve resolution and two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 544:15–25, 2005.
Diekman, B. O., and F. Guilak. Stem cell-based therapies for osteoarthritis: challenges and opportunities. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 25:119–126, 2013.
Dijkgraaf, L. C., L. G. de Bont, G. Boering, and R. S. Liem. Normal cartilage structure, biochemistry, and metabolism: a review of the literature. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 53:924–929, 1995.
Ding, C., F. Cicuttini, and G. Jones. How important is MRI for detecting early osteoarthritis? Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 4:4–5, 2008.
Duda, G. N., R. U. Kleemann, U. Bluecher, and A. Weiler. A new device to detect early cartilage degeneration. Am. J. Sports Med. 32:693–698, 2004.
Esbensen, K. H. Multivariate Data Analysis in Practice: An Introduction to Multivariate Data Analysis and Experimental Design. Woodbridge: CAMO Software, 2010.
Gill, T. J. The treatment of articular cartilage defects using microfracture and debridement. Am. J. Knee Surg. 13:33, 2000.
Hanifi, A., X. Bi, X. Yang, B. Kavukcuoglu, P. C. Lin, E. Dicarlo, R. G. Spencer, M. P. Bostrom, and N. Pleshko. Infrared fiber optic probe evaluation of degenerative cartilage correlates to histological grading. Am. J. Sports Med. 40(12):2853–2861, 2012.
Hofmann, G. O., J. Marticke, R. Grossstuck, M. Hoffmann, M. Lange, H. K. Plettenberg, R. Braunschweig, O. Schilling, I. Kaden, and G. Spahn. Detection and evaluation of initial cartilage pathology in man: a comparison between MRT, arthroscopy and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR) in their relation to initial knee pain. Pathophysiology 17:1–8, 2010.
Howell, D. Etiopathogenesis of osteoarthritis. In: Arthritis and Allied Conditions, edited by D. J. McCarty. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1989.
Hunziker, E. B. Articular cartilage repair: basic science and clinical progress. A review of the current status and prospects. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 10:432–463, 2002.
Jaffe, F. F., H. J. Mankin, C. Weiss, and A. Zarins. Water binding in the articular cartilage of rabbits. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 56:1031–1039, 1974.
Koff, M. F., K. K. Amrami, and K. R. Kaufman. Clinical evaluation of T2 values of patellar cartilage in patients with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 15:198–204, 2007.
Lawrence, R. C., C. G. Helmick, F. C. Arnett, R. A. Deyo, D. T. Felson, E. H. Giannini, S. P. Heyse, R. Hirsch, M. C. Hochberg, G. G. Hunder, M. H. Liang, S. R. Pillemer, V. D. Steen, and F. Wolfe. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and selected musculoskeletal disorders in the united states. Arthr. Rheum. 41:778–799, 1998.
Li, G., M. Thomson, E. Dicarlo, X. Yang, B. Nestor, M. P. Bostrom, and N. P. Camacho. A chemometric analysis for evaluation of early-stage cartilage degradation by infrared fiber-optic probe spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 59:1527–1533, 2005.
Libnau, F. O., O. M. Kvalheim, A. A. Christy, and J. Toft. Spectra of water in the near- and mid-infrared region. Vib Spectosc 7:243–254, 1994.
Lin, P. C., O. Irrechukwu, R. Roque, B. Hancock, K. W. Fishbein, and R. G. Spencer. Multivariate analysis of cartilage degradation using the support vector machine algorithm. Magn. Reson. Med. 67:1815–1826, 2011.
Lin, P.-C., D. A. Reiter, and R. G. Spencer. Classification of degraded cartilage through multiparametric MRI analysis. J. Magn. Reson. 201:61–71, 2009.
Luck, W. A. P. Structure of water and aqueous solutions. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium held at Marburg in July 1973, edited by W. A. P. Luck. Marburg, 1974.
Lusse, S., H. Claassen, T. Gehrke, J. Hassenpflug, M. Schunke, M. Heller, and C. C. Gluer. Evaluation of water content by spatially resolved transverse relaxation times of human articular cartilage. Magn. Reson. Imaging 18:423–430, 2000.
Mankin, H. J., and A. Z. Thrasher. Water content and binding in normal and osteoarthritic human cartilage. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 57:76–80, 1975.
Marik, W., S. Apprich, G. Welsch, T. Mamisch, and S. Trattnig. Biochemical evaluation of articular cartilage in patients with osteochondrosis dissecans by means of quantitative T2-and T2*-mapping at 3t MRI: a feasibility study. Eur. J. Radiol. 81:923–927, 2012.
Maroudas, A. Distribution and diffusion of solutes in articular cartilage. Biophys. J. 10:365–379, 1970.
Maroudas, A., M. T. Bayliss, N. Uchitel-Kaushansky, R. Schneiderman, and E. Gilav. Aggrecan turnover in human articular cartilage: use of aspartic acid racemization as a marker of molecular age. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 350:61–71, 1998.
Marticke, J. K., A. Hosselbarth, K. L. Hoffmeier, I. Marintschev, S. Otto, M. Lange, H. K. Plettenberg, G. Spahn, and G. O. Hofmann. How do visual, spectroscopic and biomechanical changes of cartilage correlate in osteoarthritic knee joints? Clin. Biomech. 25:332–340, 2010.
Martin, K. In vivo measurements of water in skin by near-infrared reflectance. Appl. Spectrosc. 52:1001–1007, 1998.
Nicolai, B. M., K. Beullens, E. Bobelyn, A. Peirs, W. Saeys, K. I. Theron, and J. Lammertyn. Nondestructive measurement of fruit and vegetable quality by means of NIR spectroscopy: a review. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 46:99–118, 2007.
O’Malley, M. J., and C. R. Chu. Arthroscopic optical coherence tomography in diagnosis of early arthritis. Minim. Invasive Surg. 2011:6, 2011.
Peterfy, C. G. Scratching the surface: articular cartilage disorders in the knee. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 8:409–430, 2000.
Platt, D., J. L. Bird, and M. T. Bayliss. Ageing of equine articular cartilage: structure and composition of aggrecan and decorin. Equine Vet. J. 30:43–52, 1998.
Poole, A. R., T. Kojima, T. Yasuda, F. Mwale, M. Kobayashi, and S. Laverty. Composition and structure of articular cartilage: a template for tissue repair. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 391:S26–S33, 2001.
Recht, M. P., D. W. Goodwin, C. S. Winalski, and L. M. White. MRI of articular cartilage: revisiting current status and future directions. AJR 185:899–914, 2005.
Reiter, D. A., P. C. Lin, K. W. Fishbein, and R. G. Spencer. Multicomponent T2 relaxation analysis in cartilage. Magn. Reson. Med. 61:803–809, 2009.
Ressler, N., Ziauddin, C. Vygantas, W. Janzen, and K. Karachorlu. Improved techniques for near-infrared study of water binding by globular proteins and intact tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. 30:295–302, 1976.
Shiomi, T., T. Nishii, K. Nakata, S. Tamura, H. Tanaka, Y. Yamazaki, K. Murase, H. Yoshikawa, and N. Sugano. Three-dimensional topographical variation of femoral cartilage T2 in healthy volunteer knees. Skelet. Radiol. 42:363–370, 2012.
Sovani, S., and S. P. Grogan. Osteoarthritis: detection, pathophysiology, and current/future treatment strategies. Orthop. Nurs. 32:25–36, 2013.
Spahn, G., H. Plettenberg, E. Kahl, H. M. Klinger, T. Muckley, and G. O. Hofmann. Near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy. A new method for arthroscopic evaluation of low grade degenerated cartilage lesions. Results of a pilot study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 8:47, 2007.
Spahn, G., H. Plettenberg, H. Nagel, E. Kahl, H. M. Klinger, M. Gunther, T. Muckley, and G. O. Hofmann. Karl Fischer titration and coulometry for measurement of water content in small cartilage specimens. Biomed. Tech. (Berl.) 51:355–359, 2006.
Spahn, G., H. Plettenberg, H. Nagel, E. Kahl, H. M. Klinger, T. Muckley, M. Gunther, G. O. Hofmann, and J. A. Mollenhauer. Evaluation of cartilage defects with near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR): an ex vivo study. Med. Eng. Phys. 30:285–292, 2008.
Torzilli, P. A. Water Content and Solute Diffusion Properties in Articular Cartilage. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1990.
Torzilli, P. A., T. C. Adams, and R. J. Mis. Transient solute diffusion in articular cartilage. J. Biomech. 20:203–214, 1987.
Vandermeulen, D. L., and N. Ressler. A near-infrared analysis of water-macromolecule interactions: hydration and the spectra of aqueous solutions of intact proteins. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 199:197–205, 1980.
Walling, P. L., and J. M. Dabney. Moisture in skin by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 40:151–171, 1989.
Wei, L., O. Svensson, and A. Hjerpe. Correlation of morphologic and biochemical changes in the natural history of spontaneous osteoarthrosis in guinea pigs. Arthrit. Rheum. 40:2075–2083, 1997.
West, P. A., M. P. Bostrom, P. A. Torzilli, and N. P. Camacho. Fourier transform infrared spectral analysis of degenerative cartilage: an infrared fiber optic probe and imaging study. Appl. Spectrosc. 58:376–381, 2004.
Xia, Y. MRI of articular cartilage at microscopic resolution. BJR 2:9–17, 2013.
Yin, J., and Y. Xia. Macromolecular concentrations in bovine nasal cartilage by Fourier transform infrared imaging and principal component regression. Appl. Spectrosc. 64:1199, 2010.
Zhou, G. X., Z. Ge, J. Dorwart, B. Izzo, J. Kukura, G. Bicker, and J. Wyvratt. Determination and differentiation of surface and bound water in drug substances by near infrared spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Sci. 92:1058–1065, 2003.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by NIH AR056145 and EB000744 and the Intramural Research Program at NIA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor James Tunnell oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padalkar, M.V., Spencer, R.G. & Pleshko, N. Near Infrared Spectroscopic Evaluation of Water in Hyaline Cartilage. Ann Biomed Eng 41, 2426–2436 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0844-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0844-0