Abstract
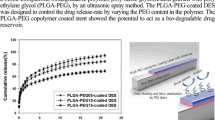
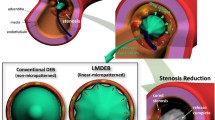
In this report, a balloon-expandable, biodegradable, drug-eluting bifurcation stent (DEBS) that provides a sustainable release of anti-proliferative sirolimus was developed. Biodegradable bifurcation stents, made of polycaprolactone, were first manufactured by injection molding and hot spot welding techniques. Various properties of the fabricated stents, including compression strengths, collapse pressures, and flow pattern in a circulation test, were characterized. The experimental results showed that biodegradable bifurcation stents exhibited comparable mechanical properties with those of metallic stents and superior flow behavior to that of metallic bifurcation stents deployed via the T And small Protrusion approach. Polylactide-polyglycolide (PLGA) copolymer and sirolimus were then dissolved in acetonitrile and coated onto the surface of the stents by a spray coating device. An elution method and a high performance liquid chromatography analysis were utilized to examine the in vitro release characteristics of sirolimus. Biodegradable bifurcation stents released high concentrations of sirolimus for more than 6 weeks, and the total period of drug release could be prolonged by increasing the drug loading of the PLGA/sirolimus coating layers. In addition, the eluted drug could effectively inhibit the proliferation of smooth muscle cells. The developed DEBS in this study may provide a promising strategy for the treatment of cardiovascular bifurcation lesions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya, G., and K. Park. Mechanisms of controlled drug release from drug-eluting stents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 58:387–401, 2006.
Al Suwaidi, J., W. Yeh, H. A. Cohen, K. M. Detre, D. O. Williams, and D. R. Holmes, Jr. Immediate and one-year outcome in patients with coronary bifurcation lesions in the modern era (NHLBI dynamic registry). Am. J. Cardiol. 87:1139–1144, 2001.
Alexis, F., S. S. Venkatraman, S. K. Rath, and F. Boey. In vitro study of release mechanisms of paclitaxel and rapamycin from drug-incorporated biodegradable stent matrices. J. Control. Release 98:67–74, 2004.
Burt, H. M., and W. L. Hunter. Drug-eluting stents: a multidisciplinary success story. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 58:350–357, 2006.
Chen, M. C., Y. Chang, C. T. Liu, W. Y. Lai, S. F. Peng, Y. W. Hung, H. W. Tsai, and H. W. Sung. The characteristics and in vivo suppression of neointimal formation with sirolimus-eluting polymeric stents. Biomaterials 30:79–88, 2009.
Cho, G. Y., C. W. Lee, M. K. Hong, J. J. Kim, S. W. Park, and S. J. Park. Effects of stent design on side branch occlusion after coronary stent placement. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 52:18–23, 2001.
Colombo, A., and E. Karvouni. Biodegradable stents: fulfilling the mission and stepping away. Circulation 102(4):371–373, 2000.
Colombo, A., J. W. Moses, M. C. Morice, J. Ludwig, D. R. Holmes, Jr., V. Spanos, et al. Randomized study to evaluate sirolimus-eluting stents implanted at coronary bifurcation lesions. Circulation 109:1244–1249, 2004.
Daemon, J., and P. W. Serruys. Drug-eluting stent update 2007 Part I: a survey of current and future generation drug-eluting stents: meaningful advances or more of the same? Circulation 116:316–328, 2007.
Daemon, J., and P. W. Serruys. Drug-eluting stent update 2007 Part II: unsettled issues. Circulation 116:961–968, 2007.
Fillinger, M. F., L. N. Sampson, J. L. Cronenwett, R. J. Powell, and R. J. Wagner. Coculture of endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells in bilayer and conditioned media models. J. Surg. Res. 67:169–178, 1997.
Garg, S., and P. W. Serruys. Coronary stents: current status. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 56(2):1–42, 2010.
Gospodarowicz, D., K. Hirabayashi, L. Giguere, and J. P. Tauber. Factors controlling the proliferative rate, final cell density, and life span of bovine vascular smooth muscle cells in culture. J. Cell Biol. 89:568–578, 1981.
Guérin, P., P. Pilet, G. Finet, Y. Gouëffic, J. M. N’Guyen, D. Crochet, I. Tijou, P. Pacaud, and G. Loirand. Drug-eluting stents in bifurcations: bench study of strut deformation and coating lesions. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 3:120–126, 2010.
Hietala, E. M., P. Maasilta, T. Välimaa, A. L. J. Harjula, P. Törmälä, U. S. Salminen, and R. Lassila. Platelet responses and coagulation activation on polylactide and heparin-polycaprolactone-l-lactide-coated polylactide stent struts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 67A:785–791, 2003.
Htay, T., and M. W. Liu. Drug-eluting stent: a review and update. Vascul. Health Risk Manag. 1(4):263–276, 2005.
Jiang, S., X. Ji, L. An, and B. Jiang. Crystallization behavior of PCL in hybrid confined environment. Polymer 42:3901–3907, 2001.
Korpela, A., P. Aarnio, H. Sariola, P. Tormala, and A. Harjula. Bioabsorbable self-reinforced poly-l-lactide, metallic, and silicone stents in the management of experimental tracheal stenosis. Chest 115:490–495, 1999.
Kraitzer, A., L. Ofek, R. Schreiber, and M. Zilberman. Long-term in vitro study of paclitaxel-eluting bioresorbable core/shell fiber structures. J. Contr. Release 126:139–148, 2008.
Laarman, G., M. J. Suttorp, M. T. Dirksen, L. Van Heerebeek, F. Kiemeneij, T. Slagboom, L. R. Van der Wieken, J. G. P. Tijssen, B. Rensing, and M. Patterson. Paclitaxel-eluting versus uncoated stents in primary percutaneous coronary intervention. N. Engl. J. Med. 355:1105–1113, 2006.
Lao, L. L., S. S. Venkatraman, and N. A. Peppas. Modeling of drug release from biodegradable polymer blends. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 70:796–803, 2008.
Lefevre, T., Y. Louvard, M. C. Morice, P. Dumas, C. Loubeyre, A. Benslimane, et al. Stenting of bifurcation lesions: classification, treatments, and results. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 49:274–283, 2000.
Liu, S. J., F. J. Chiang, C. Y. Hsiao, Y. C. Kau, and K. S. Liu. Fabrication of balloon-expandable self-lock drug-eluting polycaprolactone stents using micro-injection molding and spray coating techniques. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:3185–3194, 2010.
Liu, S. J., C. Y. Hsiao, J. K. Chen, K. S. Liu, and C. H. Lee. In vitro release of anti-proliferative paclitaxel from novel balloon-expandable polycaprolactone stents. Mater. Sci. Eng. C: Mater. Biol. Appl. 31:1129–1135, 2011.
Louvard, Y., M. Thomas, V. Dzavik, D. Hildich-Smith, A. R. Galassi, M. Pan, et al. Classification of coronary artery bifurcation lesions and treatment: time for a consensus. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 71:175–183, 2008.
Meier, B., A. R. Gruentzig, S. B. King, III, J. S. Douglas, Jr., J. Hollman, T. Ischinger, et al. Risk of side branch occlusion during coronary angioplasty. Am. J. Cardiol. 53:10–14, 1984.
Meng, B., J. Wang, N. Zhu, Q. Y. Meng, F. Z. Cui, and Y. X. Xu. Study of biodegradable and self-expandable PLLA helical biliary stent in vivo and in vitro. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 17:611–617, 2006.
Murasato, Y. Impact of three-dimensional characteristics of the left main coronary artery bifurcation on outcome of crush stenting. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 69:248–256, 2007.
Nakazawa, G., A. V. Finn, M. Joner, E. Ladich, R. Kutys, E. K. Mont, H. K. Gold, A. P. Burke, F. D. Kolodgie, and R. Virmani. Delayed arterial healing and increased late stent thrombosis at culprit sites after drug-eluting stent placement for acute myocardial infarction patients: an autopsy study. Circulation 118:1138–1145, 2008.
Pan, M., J. Suarez de Lezo, A. Medina, M. Romero, A. Delgado, J. Segura, et al. Drug-eluting stents for the treatment of bifurcation lesions: a randomized comparison between paclitaxel and sirolimus stents. Am. Heart J. 153(15):e1–e7, 2007.
Pires, N. M. M., B. L. Van der Hoeven, M. R. De Vries, L. M. Havekes, B. J. Van Vlijmen, W. E. Hennink, P. H. A. Quax, and J. W. Jukema. Local perivascular delivery of anti-restenotic agents from a drug-eluting poly(ε-caprolactone) stent cuff. Biomaterials 26:5386–5394, 2005.
Serruys, P. W., J. Aoki, D. McClean, M. Pieper, and E. Sousa. The effect of variable dose and release kinetics on neointimal hyperplasia using a novel paclitaxel-eluting stent platform. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 46(2):253–260, 2005.
Song, P. S., D. R. Ryu, Y. B. Song, J.-Y. Hahn, J.-H. Choi, S. H. Lee, et al. Long-term outcomes of sirolimus-eluting stents vs paclitaxel-eluting stents in unprotected left main coronary artery bifurcation lesions. Clin. Cardiol. 34:378–383, 2011.
Steigen, T. K., M. Maeng, R. Wiseth, A. Erglis, I. Kumsars, I. Narbute, et al. Randomized study on simple versus complex stenting of coronary artery bifurcation lesions: the Nordic bifurcation study. Circulation 114:1955–1961, 2006.
Van de Werf, F. Drug-eluting stents in acute myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 355:1169–1170, 2006.
Venkatraman, S. S., T. L. Poh, T. Vinalia, K. H. Mak, and F. Boey. Collapse pressures of biodegradable stents. Biomaterials 24:2105–2111, 2003.
Virmani, R., G. Guagliumi, A. Farb, G. Musumeci, N. Grieco, T. Motta, L. Mihalcsik, M. Tespili, O. Valsecchi, and F. D. Kolodgie. Localized hypersensitivity and late coronary thrombosis secondary to a sirolimus-eluting stent: should we be cautious? Circulation 109:701–705, 2004.
Wang, X., S. S. Venkatraman, F. Boey, J. S. C. Loo, and L. P. Tan. Controlled release of sirolimus from a multilayered PLGA stent matrix. Biomaterials 27:5588–5595, 2006.
Woodruff, M. A., and D. W. Hutmacher. The return of a forgotten polymer-polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 35:1217–1256, 2010.
Yamashita, T., T. Nishida, M. G. Adamian, C. Briguori, M. Vaghetti, N. Corvaja, et al. Bifurcation lesions: two stents versus one stent-immediate and follow-up results. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 35:1145–1151, 2000.
Yang, S., K.-F. Leong, Z. Du, and C.-K. Chua. The design of scaffolds for use in tissue engineering. Part I. Traditional factors. Tissue Eng. 7:679–689, 2001.
Zidar, J. P., M. A. Lincoff, and R. S. Stack. Biodegradable stents. In: Textbook of Interventional Cardiology, 2nd ed., edited by E. J. Topol. New York: Saunders, 1994.
Zilberman, M., K. D. Nelson, and R. C. Eberhart. Mechanical properties and in vitro degradation of bioresorbable fibers and expandable fiber-based stents. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B: Appl. Biomater. 74(2):792–799, 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Jennifer West oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CH., Chen, CJ., Liu, SJ. et al. The Development of Novel Biodegradable Bifurcation Stents for the Sustainable Release of Anti-Proliferative Sirolimus. Ann Biomed Eng 40, 1961–1970 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0556-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0556-x