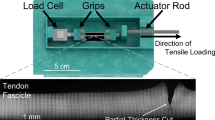
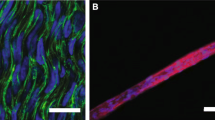
Abstract
Collagen fiber re-alignment is one postulated mechanism of tendon structural response to load. While collagen fiber distribution has been shown to vary by tendon location in the supraspinatus tendon (SST), changes in local re-alignment behavior have not been examined throughout postnatal development. Postnatal tendons, with immature collagen fibrils, may respond to load in a much different manner than collagen fibers with mature fiber–fiber and fiber–matrix connections. Local collagen fiber re-alignment is quantified throughout tensile mechanical testing in a developmental mouse SST model and corresponding mechanical properties measured. Collagen fiber re-alignment occurred during preconditioning for 28 day old tendons, at the toe-region for 10 day tendons and at the linear-region for 4 day tendon midsubstance. Mechanical properties increased with developmental age. Linear modulus was lower at the insertion site compared to the midsubstance location at all time points. Local differences in collagen fiber distributions were found at 10 and 28 days for all mechanical testing points (except the 10 day transition point). This study found that collagen fiber re-alignment depends on developmental age and suggests that collagen fibrillogenesis may influence the tendon’s ability to structurally respond to load. Additionally, results indicate that the insertion site and tendon midsubstance locations develop differently.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansorge, H. L., S. Adams, D. E. Birk, and L. J. Soslowsky. Mechanical, compositional, and structural properties of the post-natal mouse Achilles tendon. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 39:1904–1913, 2011.
Ansorge, H. L., X. Meng, G. Zhang, G. Veit, M. Sun, J. F. Klement, D. P. Beason, L. J. Soslowsky, M. Koch, and D. E. Birk. Type xiv collagen regulates fibrillogenesis: premature collagen fibril growth and tissue dysfunction in null mice. J. Biol. Chem. 284:8427–8438, 2009.
Benjamin, M., T. Kumai, S. Milz, B. M. Boszczyk, A. A. Boszczyk, and J. R. Ralphs. The skeletal attachment of tendons—tendon “Entheses”. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 133:931–945, 2002.
Benjamin, M., R. L. Newell, E. J. Evans, J. R. Ralphs, and D. J. Pemberton. The structure of the insertions of the tendons of biceps brachii, triceps and brachialis in elderly dissecting room cadavers. J. Anat. 180(Pt 2):327–332, 1992.
Birk, D. E., M. V. Nurminskaya, and E. I. Zycband. Collagen fibrillogenesis in situ: fibril segments undergo post-depositional modifications resulting in linear and lateral growth during matrix development. Dev. Dyn. 202:229–243, 1995.
Birk, D. E., E. I. Zycband, S. Woodruff, D. A. Winkelmann, and R. L. Trelstad. Collagen fibrillogenesis in situ: fibril segments become long fibrils as the developing tendon matures. Dev. Dyn. 208:291–298, 1997.
Derwin, K. A., L. J. Soslowsky, W. D. Green, and S. H. Elder. A new optical system for the determination of deformations and strains: calibration characteristics and experimental results. J. Biomech. 27:1277–1285, 1994.
Diamant, J., A. Keller, E. Baer, M. Litt, and R. G. Arridge. Collagen; ultrastructure and its relation to mechanical properties as a function of ageing. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 180:293–315, 1972.
Favata, M. Scarless healing in the fetus: implications and strategies for postnatal tendon repair. Ph.D. thesis, University of Pennsylvania, 2006.
Festing, M. F. Design and statistical methods in studies using animal models of development. ILAR J. 47:5–14, 2006.
Franchi, M., A. Trire, M. Quaranta, E. Orsini, and V. Ottani. Collagen structure of tendon relates to function. ScientificWorldJournal 7:404–420, 2007.
Galatz, L., S. Rothermich, K. VanderPloeg, B. Petersen, L. Sandell, and S. Thomopoulos. Development of the supraspinatus tendon-to-bone insertion: localized expression of extracellular matrix and growth factor genes. J. Orthop. Res. 25:1621–1628, 2007.
Lake, S. P., K. S. Miller, D. M. Elliott, and L. J. Soslowsky. Effect of fiber distribution and realignment on the nonlinear and inhomogeneous mechanical properties of human supraspinatus tendon under longitudinal tensile loading. J. Orthop. Res. 27:1596–1602, 2009.
Lake, S. P., K. S. Miller, D. M. Elliott, and L. J. Soslowsky. Tensile properties and fiber alignment of human supraspinatus tendon in the transverse direction demonstrate inhomogeneity, nonlinearity, and regional isotropy. J. Biomech. 43:727–732, 2010.
Miller, K. S., L. Edelstein, and L. J. Soslowsky. Effect of preconditioning on collagen fiber recruitment: inhomogeneous properties of the rat supraspinatus tendon. In: Proceeding of the ASME 2010 Summer Bioengineering Conference, 2010.
Miller, K. S. S. J. T., N. A. Trasolini, and L. J. Soslowsky. The upper band of the subscapularis tendon in the rat has inferior mechanical properties. In: Transactions of the Orthopaedic Research Society, 2011.
Moore, M. J., and A. De Beaux. A quantitative ultrastructural study of rat tendon from birth to maturity. J. Anat. 153:163–169, 1987.
Nakagawa, Y., T. Majima, and K. Nagashima. Effect of ageing on ultrastructure of slow and fast skeletal muscle tendon in rabbit Achilles tendons. Acta Physiol. Scand. 152:307–313, 1994.
Oryan, A., and A. H. Shoushtari. Histology and ultrastructure of the developing superficial digital flexor tendon in rabbits. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 37:134–140, 2008.
Parry, D. A., A. S. Craig, and G. R. Barnes. Tendon and ligament from the horse: an ultrastructural study of collagen fibrils and elastic fibres as a function of age. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 203:293–303, 1978.
Peltz, C. D., J. J. Sarver, L. M. Dourte, C. C. Wurgler-Hauri, G. R. Williams, and L. J. Soslowsky. Exercise following a short immobilization period is detrimental to tendon properties and joint mechanics in a rat rotator cuff injury model. J. Orthop. Res. 28:841–845, 2010.
Provenzano, P. P., and R. Vanderby, Jr. Collagen fibril morphology and organization: implications for force transmission in ligament and tendon. Matrix Biol. 25:71–84, 2006.
Quinn, K. P., and B. A. Winkelstein. Preconditioning is correlated with altered collagen fiber alignment in ligament. J. Biomech. Eng. 133:064506, 2011.
Ralphs, J. R., R. N. Tyers, and M. Benjamin. Development of functionally distinct fibrocartilages at two sites in the quadriceps tendon of the rat: the suprapatella and the attachment to the patella. Anat. Embryol. (Berl.) 185:181–187, 1992.
Rufai, A., M. Benjamin, and J. R. Ralphs. Development and ageing of phenotypically distinct fibrocartilages associated with the rat Achilles tendon. Anat. Embryol. (Berl.) 186:611–618, 1992.
Schweitzer, R., E. Zelzer, and T. Volk. Connecting muscles to tendons: tendons and musculoskeletal development in flies and vertebrates. Development 137:2807–2817, 2010.
Silver, F. H., J. W. Freeman, and G. P. Seehra. Collagen self-assembly and the development of tendon mechanical properties. J. Biomech. 36:1529–1553, 2003.
Sverdlik, A., and Y. Lanir. Time-dependent mechanical behavior of sheep digital tendons, including the effects of preconditioning. J. Biomech. Eng. 124:78–84, 2002.
Thomopoulos, S., H. M. Kim, S. Y. Rothermich, C. Biederstadt, R. Das, and L. M. Galatz. Decreased muscle loading delays maturation of the tendon enthesis during postnatal development. J. Orthop. Res. 25:1154–1163, 2007.
Thomopoulos, S., G. R. Williams, J. A. Gimbel, M. Favata, and L. J. Soslowsky. Variation of biomechanical, structural, and compositional properties along the tendon to bone insertion site. J. Orthop. Res. 21:413–419, 2003.
Zhang, G., B. B. Young, Y. Ezura, M. Favata, L. J. Soslowsky, S. Chakravarti, and D. E. Birk. Development of tendon structure and function: regulation of collagen fibrillogenesis. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 5:5–21, 2005.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by NIH/NIAMS. We also thank David P. Beason, Jennica J. Tucker, and Elizabeth Feeney for assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Jane Grande-Allen oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, K.S., Connizzo, B.K. & Soslowsky, L.J. Collagen Fiber Re-Alignment in a Neonatal Developmental Mouse Supraspinatus Tendon Model. Ann Biomed Eng 40, 1102–1110 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0490-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0490-3