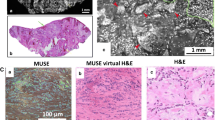
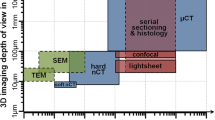
Abstract
Absorption dyes are widely used in traditional cytology and pathology clinical practice, while fluorophores and nanoparticles are more often used in biologic research. Optical projection tomographic microscopy (OPTM) is a platform technology that can image the same specimen in multiple modes in 3D, providing morphologic and molecular information concurrently and in exact co-registration. The depth-of-field of a high numerical aperture objective is extended by scanning the focal plane through the sample to generate an optical projection image. Samples of cells or tissue are brought into the OPTM instrument through a microcapillary tube filled with optical index-matching gel. Multiple optical projection images are taken from different perspectives by rotating the tube. Computed tomography (CT) algorithms are applied to these optical projection images to reconstruct 3D structure of the sample. Image segmentation and analysis based on these 3D images provide quantitative biosignatures for cancer diagnosis that represents a clear improvement over conventional 2D image analysis. In this article, we introduce the OPTM platform, optical Cell-CT, and Tissue-CT instruments, and some applications using these OPTM instruments.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaron, J., E. Rosa, K. Travis, N. Harrison, J. Burt, M. J. Yacaman, and K. Sokolov. Polarization microscopy with stellated gold nanoparticles for robust, in situ monitoring of biomolecules. Opt. Express 16:2153, 2008.
Alanentalo, T., A. Asayesh, H. Morrison, C. E. Loren, D. Holmberg, J. Sharpe, and U. Ahlgren. Tomographic molecular imaging and 3D quantification within adult mouse organs. Nat. Methods 4:31–33, 2007.
Boisselier, E., and D. Astruc. Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38:1759, 2009.
Bonnemain, B. Superparamagnetic agents in magnetic resonance imaging: physicochemical characteristics and clinical applications-A review. J. Drug Target 6:167–174, 1998.
Botcherby, E. J., M. J. Booth, R. Juskaitis, and T. Wilson. Real-time extended depth of field microscopy. Opt. Express 16:21843–21848, 2008.
Carpenter, B., C. MacKay, A. Alnabulsi, M. KacKay, C. Telfer, W. T. Melvin, and G. I. Murray. The roles of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in tumor development and progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1765:85–100, 2005.
Clement, O., N. Siauve, M. Lewin, E. de Keviler, C.-A. Cuenod, and G. Frija. Contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging of the liver: present and future. Biomed. Pharmacother. 52:51–58, 1998.
Connor, E. E., J. Mwamuka, A. Gole, C. J. Murphy, and M. D. Wyatt. Gold nanoparticles are taken up by human cells but do not cause acute cytotoxicity. Small 1:325–327, 2005.
Crow, M. J., G. Grant, J. M. Provenzale, and A. Wax. Molecular imaging and quantitative measurement of epidermal growth factor receptor expression in live cancer cells using immunolabeled gold nanoparticles. Am. J. Roentgenol. 192:1021, 2009.
Denk, W., J. H. Strickler, and W. W. Webb. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science 248:73–76, 1990.
Farkas, D. L., G. Baxter, R. L. DeBiasio, A. Gough, M. A. Nederlof, D. Pane, J. Pane, D. R. Patek, K. W. Ryan, and D. L. Taylor. Multimode light microscopy and the dynamics of molecules, cells and tissues. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 55:785–817, 1993.
Fauver, M., E. J. Seibel, J. R. Rahn, M. G. Meyer, F. W. Patten, T. Neumann, and A. C. Nelson. Three-dimensional imaging of single isolated cell nuclei using optical projection tomography. Opt. Express 13:4210, 2005.
Glasbey, C. A., and N. J. Martin. Multimodal microscopy by digital image processing. J. Microsc. 181:225–237, 1996.
Huang, B., S. A. Jones, B. Brandenburg, and X. Zhuang. Whole-cell 3D STORM reveals interactions between cellular structures with nanometer-scale resolution. Nat. Methods 5:1047–1052, 2008.
Huisken, J., J. Swoger, F. D. Bene, J. Wittbrodt, and E. H. K. Stelzer. Optical sectioning deep inside live embryos by selective plane illumination microscopy. Science 305:1007–1009, 2004.
Kak, A. C., and M. Slaney. Principles of Computerized Tomographic Imaging. New York: IEEE Press, 1988.
Kalele, S. A., N. R. Tiwari, S. W. Gosavi, and S. K. Kulkarni. Plasmon-assisted photonics at the nanoscale. J. Nanophoton. 1:012501, 2007.
Khlebtsov, B. N., V. A. Khanadeev, and N. G. Khlebtsov. Observation of extra-high depolarized light scattering spectra from gold nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 112:12760, 2008.
Klar, T. A., S. Jakobs, M. Dybra, A. Eegner, and S. W. Hell. Fluorescence microscopy with diffraction barrier broken by stimulated emission. PNAS 97:8206–8210, 2000.
Koss, L. G., and M. R. Melamed. Koss’ Diagnostic Cytology and Its Histopathologic Bases. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006.
Lemelle, A., B. Veksler, I. S. Kozhevnikov, G. G. Akchurin, S. A. Piletsky, and I. Meglinski. Application of gold nanoparticles as contrast agents in confocal laser scanning microscopy. Laser Phys. Lett. 6:71, 2009.
McNally, J. G., T. Karpova, J. Cooper, and J. A. Conchello. Three-dimensional imaging by deconvolution microscopy. Methods 19:373–385, 1999.
Medarova, Z., W. Pham, C. Farrar, V. Petkova, and A. Moore. In vivo imaging of siRNA delivery and silencing in tumors. Nat. Med. 13:372–377, 2007.
Meyer, M. G., M. Fauver, J. R. Rahn, T. Neumann, F. W. Patten, E. J. Seibel, and A. C. Nelson. Automated cell analysis in 2D and 3D: a comparative study. Patt. Recognit. 41:141–146, 2009.
Miao, Q., J. Hayenga, M. G. Meyer, T. Neumann, A. C. Nelson, and E. J. Seibel. Resolution improvement in optical projection tomography by the focal scanning method. Opt. Lett. 35:3363–3365, 2010.
Miao, Q., J. Hayenga, M. Meyer, T. Neumann, F. Patten, A. Nelson, and E. Seibel. High resolution optical projection tomographic microscopy for 3D tissue imaging. In: Three-Dimensional, Multidimensional Microscopy: Image Acquisition, Processing XVIII, Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 7904, p. 79040L, 2011.
Miao, Q., J. R. Rahn, A. Tourovskaia, M. G. Meyer, T. Neumann, A. C. Nelson, and E. J. Seibel. Dual-modal three-dimensional imaging of single cells with isometric high resolution using an optical projection tomography microscope. J. Biomed. Opt. 14:064035, 2009.
Miao, Q., J. Yu, M. G. Meyer, J. R. Rahn, T. Neumann, A. C. Nelson, and E. J. Seibel. Dual-modal optical projection tomography microscopy for cancer diagnosis. In: Three-Dimensional, Multidimensional Microscopy: Image Acquisition, Processing XVIII, Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 7570, p. 75700H, 2010.
Miao, Q., J. Yu, J. Rahn, M. Meyer, T. Neumann, A. Nelson, and E. Seibel. Dual-mode optical projection tomography microscope using gold nanorods and hematoxylin-stained cancer cells. Opt. Lett. 35:1037–1039, 2010.
Nandakumar, V., L. Kelbauskas, R. Johnson, and D. Meldrum. Quantitative characterization of preneoplastic progression using single-cell computed tomography and three-dimensional karyometry. Cytometry A 79:25–34, 2011.
Neil, M. A. A., R. Juskaitis, and T. Wilson. Method of obtaining optical sectioning by using structured light in a conventional microscope. Opt. Lett. 22:1905–1907, 1997.
Neumann, T., Q. Miao, J. Yu, M. Fauver, M. Meyer, J. R. Rahn, C. A. Lancaster, E. J. Seibel, and A. C. Nelson. Simultaneous 3D imaging of morphology and nanoparticle distribution in single cells with the Cell-CT technology. In: 30th Annual International IEEE EMBS Conference, pp. 379–381, 2008.
Nitin, N., D. J. Javier, D. M. Roblyer, and R. R. Kortum. Widefield and high-resolution reflectance imaging of gold and silver nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Opt. 12:051505, 2007.
Nitin, N., L. E. W. LaConte, O. Zurkiya, X. Hu, and G. Bao. Functionalization and peptide-based delivery of magnetic nanoparticles as an intracellular MRI contrast agent. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 9:706–712, 2004.
Pawley, J. B. Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy. New York: Springer, 2006.
Raab, S. S., and D. M. Grzybicki. Quality in cancer diagnosis. CA Cancer J. Clin. 60:139–165, 2010.
Reeves, A. P., E. J. Seibel, M. G. Meyer, T. Apanasovich, and A. Biancardi. Nuclear cytoplasm cell evaluation from 3D Optical CT Microscope images. In: Medical Imaging, Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 8315, p. 8315-121, 2012.
Sharpe, J., U. Ahlgren, P. Perry, B. Hill, A. Ross, J. Hecksher-sorensen, R. Baldock, and D. Davidson. Optical projection tomography as a tool for 3D microscopy and gene expression studies. Science 296:541–545, 2002.
Smitha, T., P. Sharada, and H. C. Girish. Morphometry of the basal cell layer of oral leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma using computer-aided image analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 15:26–33, 2011.
Somrak, T. M., and C. M. Keebler. The Manual of Cytotechnology. Chicago: ASCP Press, 1993.
Sueoka, E., N. Sueoka, Y. Goto, S. Matsuyama, H. Nishimura, M. Sato, S. Fujimura, H. Chia, and H. Fujiki. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonulceoprotein B1 as early cancer biomarker for occult cancer of human lungs and bronchial dysplasia. Cancer Res. 61:1896–1902, 2001.
Umen, J. G. The elusive sizer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 17:435–441, 2005.
Walls, J. R., J. G. Sled, J. Sharpe, and R. M. Henkelman. Resolution improvement in emission optical projection tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 52:2755, 2007.
Wax, A., and K. Sokolov. Molecular imaging and darkfield microspectroscopy of live cells using gold plasmonic nanoparticles. Laser Photon. Rev. 3:146, 2009.
Weissleder, R., and M. J. Pittet. Imaging in the era of molecular oncology. Nature 452:580–589, 2008.
Zesking, B. J., C. D. Jordan, W. Timp, L. Trapani, G. Waller, V. Horodincu, D. J. Ehrlich, and P. Matsudaira. Nucleic acid and protein mass mapping by live-cell deep-ultraviolet microscopy. Nat. Methods 4:567–569, 2007.
Zhou, J., J. L. Mulshine, E. J. Unsworth, F. M. Scott, I. M. Avis, M. D. Vos, and A. M. Treston. Purification and characterization of a protein that permits early detection of lung cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 18:10760–10766, 1996.
Acknowledgments
Development of the Cell-CT instrumentation was done in cooperation with VisionGate, Inc., (Phoenix, AZ) at the University of Washington, Eric Seibel (PI). Key technical assistance is provided by the following individuals: Alan Nelson, Mark Fauver, Richard Rahn, Michael Meyer, Thomas Neumann, Jon Hayenga, Christy Lancaster, Wayne Briedford, Anna Touraskaia, David Steinhauer, Tom Abbott, Mathew Watson, Ryland Bryant, Sarah Shimer, Rahul Katdare, Julia Yu, and Greg Kramer. Muntjac cells are a gift from Dr. Roger Schultz and Dr. Lisa McDaniel, Signature Genomic Laboratories, WA. Stellated gold nanoparticles are prepared by Chun-Hsien Wu from Professor Konstantin Sokolov’s lab in the University of Texas in Austin. Cell-CT is a trademark of VisionGate Inc. (www.visiongate3d.com). The Tissue-CT prototype was made possible by an equipment loan of an extended range piezoelectric scanner by Jim Litynski (Piezojena Systems Inc.). Funding is provided by the NSF Collaborative Interdisciplinary Research Program (CBET-1014976, Eric Seibel and Anthony Reeves as PIs). Previous funding includes a gift from VisionGate to Dr. Seibel, and Dr. Seibel and Dr. Reeves have been consultants to VisionGate.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Daniel Elson oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, Q., Reeves, A.P., Patten, F.W. et al. Multimodal 3D Imaging of Cells and Tissue, Bridging the Gap Between Clinical and Research Microscopy. Ann Biomed Eng 40, 263–276 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0411-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0411-5