Abstract
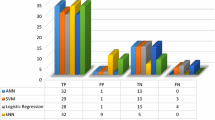
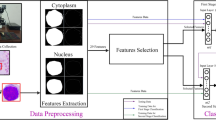
Pattern recognition applied to blood samples for diagnosing leukemia remains an extremely difficult task which frequently leads to misclassification errors due in large part to the inherent problem of data overlap. A novel artificial neural network (ANN) algorithm is proposed for optimizing the classification of multidimensional data, focusing on acute leukemia samples. The programming tool established around the ANN architecture focuses on the classification of normal vs. abnormal blood samples, namely acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). There were 220 blood samples considered with 60 abnormal samples and 160 normal samples. The algorithm produced very high sensitivity results that improved up to 96.67% in ALL classification with increased data set size. With this type of accuracy, this programming tool provides information to medical doctors in the form of diagnostic references for the specific disease states that are considered for this study. The results obtained prove that a neural network classifier can perform remarkably well for this type of flow-cytometry data. Even more significant is the fact that experimental evaluations in the testing phase reveal that as the ALL data considered is gradually increased from small to large data sets, the more accurate are the classification results.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adjouadi, M., and M. Ayala. Introducing neural studio: an artificial neural networks simulator for educational purposes. Comput. Educ. J. 14(3):33–40, 2004.
Adjouadi, M., and N. Fernandez. An orientation-independent imaging technique for the classification of blood cells. J. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 18(2):91–98, 2001.
Adjouadi, M., C. Reyes, J. Riley, and P. Vidal. Adaptive filtering for flow-cytometric particles. J. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 17(3):126–133, 2000.
Adjouadi, M., C. Reyes, P. Vidal, and A. Barreto. An analytical approach to signal reconstruction using Gaussian approximations applied to randomly generated data and flow cytometric data. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 48(10):2839–2849, 2000.
Adjouadi, M., N. Zong, and M. Ayala. Multidimensional pattern recognition and classification of white blood cells using support vector machines. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 22:107–118, 2005.
Ahlstrom, C., P. Hult, P. Rask, et al. Feature extraction for systolic heart murmur classification. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 34(11):1666–1677, 2006.
Albitar, M., T. Manshouri, Y. Shen, et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome is not merely “preleukemia”. Blood 100(3):791–798, 2002.
Beckman-Coulter Corp., FL. AcV Differential and Case Studies, Monograph. Available: http://www.beckmancoulter.com/literature/ClinDiag/AcT5diffCaseStudies.pdf, Bulletin 9151, 2000.
Beckman Coulter Cytometry Equipment. Online: http://www.coulter.com/products/Discipline/Life_Science_Research/pr_disc_flow_cytometry.asp?bhcp=1, December 2006.
Bohnke, A., F. Westphal, A. Schmidt, R. A. El-Awady, and J. Dahm-Daphi. Role of p53 mutations, protein function and DNA damage for the radiosensitivity of human tumour cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 80(1):53–63, 2004.
Buño, I., W. A. Wyatt, A. R. Zinsmeister, J. Dietz-Band, and R. T. Silver. A special fluorescent in situ hybridization technique to study peripheral blood and assess the effectiveness of interferon therapy in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 92(7):2315–2321, 1998.
Burges, C. J. C. A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min. Knowl. Disc. 2(2):121–167, 1998.
Chiu, A. W. L., E. E. Kang, M. Derchansky, et al. Online prediction of onsets of seizure-like events in hippocampal neural networks using wavelet artificial neural networks. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 34(2):282–294, 2006.
Cristianini, N., and J. Shawe-Taylor. An Introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2000.
De Paz, J. F., S. Rodríguez, J. Bajo, and J. M. Corchado. Case-based reasoning as a decision support system for cancer diagnosis: a case study. Int. J. Hybrid Intell. Syst. 6(2):97–110, 2009.
Feki, S., H. El Omri, M. A. Laatiri, S. Ennabli, K. Boukef, and F. Jenhani. Contribution of flow cytometry to acute leukemia classification in Tunisia. Dis. Markers 16(3–4):131–133, 2000.
Foran, D. J., D. Dorin Comaniciu, P. Meer, and L. A. Goodell. Computer-assisted discrimination among malignant lymphomas and leukemia using immunophenotyping, intelligent image repositories, and telemicroscopy. IEEE Trans. Inform. Technol. Biomed. 4(4):265–273, 2000.
Haferlach, T., A. Kohlmann, S. Schnittger, M. Dugas, W. Hiddemann, W. Kern, and C. Schoch. Global approach to the diagnosis of leukemia using gene expression profiling. Blood 106(4):1189–1198, 2005.
Horsch, K., M. L. Giger, L. A. Venta, and C. J. Vyborny. Computerized diagnosis of breast lesions on ultrasound. Med. Phys. 29(2):157–164, 2002.
Kohavi, R., and F. Provost. Glossary of terms. Mach. Learn. 30:271–274, 1998.
Kurth, C., F. Gillam, and B. J. Steinhoff. EEG spike detection with a Kohonen feature map. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 28(11):1362–1369, 2000.
Liu, B., Q. Cui, T. Jiang, and S. Ma. A combinational feature selection and ensemble neural network method for classification of gene expression data. BMC Bioinform. 5:136, 2004. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-5-136.
Lopes Ferrari, M., J. S. Rodrigues Oliveira, M. Romeo, and J. Kerbauy. Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) for BCR/ABL in chronic myeloid leukemia after bone marrow transplantation. Sao Paulo Med. J./Rev. Paul Med. 119(1):8–16, 2001.
Mark, H. F., W. Sikov, H. Safran, T. C. King, and R. C. Griffith. Fluorescent in situ hybridization for assessing the proportion of cells with trisomy 4 in a patient with acute non-lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 25(4):330–335, 1995.
O’Neill, M. C., and L. Song. Neural network analysis of lymphoma microarray data: prognosis and diagnosis near-perfect. BMC Bioinform. 4:13, 2003. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-4-13.
Prasad, B., and W. Badawy. High-throughput identification and classification algorithm for leukemia population statistics. J. Imaging Sci. Technol. 52(3):030509.1–030509.23, 2008.
Reyes, C., and M. Adjouadi. A directional clustering technique for random data classification. J. Cytometry 27(2):126–135, 1997.
Rifkin, R., and A. Klautau. In defense of one-vs-all classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 5:101–141, 2004.
Sabino, D. M. U., Ld. F. Costa, E. G. Rizzatti, and M. A. Zago. A texture approach to leukocyte recognition. Imaging Bioinform. III 10(4):205–216, 2004.
Tilbury, J., P. Eetvelt, J. Garibaldi, J. Curnow, and E. Ifeachor. Receiver operating characteristic analysis for intelligent medical systems—a new approach for finding confidence intervals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 47(7):952–963, 2000.
Tung, W., and C. Quek. GenSo-FDSS: a neural-fuzzy decision support system for pediatric ALL cancer subtype identification using gene expression data. Artif. Intell. Med. 33(1):61–88, 2004.
University of Leicester, Department of Microbiology & Immunology, Cells of the Blood. www.micro.msb.le.ac.uk/MBChB/bloodmap.
Vapnik, V. N. The Ature of Statistical Learning Theory. New York: Springer, 1995.
Zhang, X. S., R. J. Roy, D. Schwender, et al. Discrimination of anesthetic states using mid-latency auditory evoked potential and artificial neural networks. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 29(5):446–453, 2001.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the support provided by the National Science Foundation under Grants CNS-0426125, HRD-0833093, CNS-0520811, CNS-0540592. The authors are grateful for the clinical support provided through the Ware Foundation and the joint Neuro-Engineering Program with Miami Children’s Hospital. We also thank Beckman-Coulter Corporation for providing us the flow-cytometry data, which was critical for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Scott I. Simon oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adjouadi, M., Ayala, M., Cabrerizo, M. et al. Classification of Leukemia Blood Samples Using Neural Networks. Ann Biomed Eng 38, 1473–1482 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-009-9866-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-009-9866-z