Abstract
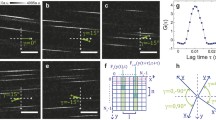
The study of relations between structural organization and functions of microcirculatory networks is a major aim of modern microangiology. Such a structural aspect of microvessels (MVs) as their spatial arrangement has substantial influence on their transport and other functional properties. This paper describes a methodology of spatial correlation analysis for isotropic blood and lymphatic MVs which is based on a stereological estimator of the pair correlation function [g 3D(r)] created recently by the authors for systems of elongated objects. The following main features of the methodology are presented: (i) interpretation of the shape of g 3D(r) curves, (ii) their quantitative description by numerical parameters, and (iii) limitations of the method arising from statistical requirements to MVs under investigation. The methodology is considered in the light of multilevel sampling designs, which are typical for biomedical morphology. The estimator with its methodological framework is applied to perifollicular blood capillaries in the adult rat thyroid. Related methods for studying the spatial arrangement of MVs are thoroughly discussed in the paper.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Antiga, L., B. Ene-Iordache, G. Remuzzi, and A. Remuzzi. Automatic generation of glomerular capillary topological organization. Microvasc. Res. 62:346–354, 2001.
Batra, S., K. Rakusan, and S. E. Campbell. Geometry of capillary networks in hypertrophied rat heart. Microvasc. Res. 41:29–40, 1991.
Bay, R. S., and C. L. Tucker, III. Stereological measurement and error estimates for three-dimensional fiber orientation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 32:240–253, 1992.
Beard, D. A., and J. B. Bassingthwaighte. Modeling advection and diffusion of oxygen in complex vascular networks. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 29:298–310, 2001.
Bennett, R. A., R. N. Pittman, and S. M. Sullivan. Capillary spatial pattern and muscle fiber geometry in three hamster striated muscles. Am. J. Physiol. 260:H579–H585, 1991.
Bentley, M. D., M. Rodriguez-Porcel, A. Lerman, M. H. Sarafov, J. C. Romero, L. I. Pelaez, J. P. Grande, E. L. Ritman, and L. O. Lerman. Enhanced renal cortical vascularization in experimental hypercholesterolemia. Kidney Int. 61:1056–1063, 2002.
Bosan, S., T. Kareco, D. Ruehlmann, K. Y. Chen, and K. R. Walley. Three-dimensional capillary geometry in gut tissue. Microsc. Res. Tech. 61:428–437, 2003.
Cerri, P. S., F. P. de Faria, R. G. Villa, and E. Katchburian. Light microscopy and computer three-dimensional reconstruction of the blood capillaries of the enamel organ of rat molar tooth germs. J. Anat. 204:191–195, 2004.
Eberhardt, C., and A. Clarke. Fibre-orientation measurements in short-fiber-glass composites. 1. Automated, high-angular-resolution measurement by confocal microscopy. Comp. Sci. Technol. 61:1389–1400, 2001.
Flindt, R. Biologie in Zahlen. Stuttgart, New York: Fischer, 1985, p. 280.
Howard, C. V., and M. G. Reed. Unbiased Stereology. Three-Dimensional Measurement in Microscopy. Oxford: BIOS Scientific, 1998, p. 246.
Hubalkova, J., and D. Stoyan. On a qualitative relationship between degree of inhomogeneity and cold crushing strength of refractory castables. Cem. Concr. Res. 33:747–753, 2003.
Itoh, J., A. Serizawa, K. Kawai, Y. Ishii, A. Teramoto, and R. Y. Osamura. Vascular networks and endothelial cells in the rat experimental pituitary glands and in the human pituitary adenomas. Microsc. Res. Tech. 60:231–235, 2003.
Juzkova, R., P. Ctibor, and V. Benes. Analysis of porous structure in plasma-sprayed coating. Image Anal. Stereol. 23:45–52, 2004.
Kayar, S. R., P. G. Archer, A. J. Lechner, and N. Banchero. The closest-individual method in the analysis of the distribution of capillaries. Microvasc. Res. 24:326–341, 1982.
Krasnoperov, R. A., and A. N. Gerasimov. Determination of size distribution of elliptical microvessels from size distribution measurement of their section profiles. Exp. Biol. Med. 228:84–92, 2003.
Krasnoperov, R. A., and A. N. Gerasimov. Stereological method of determining objects’ anisotropy. Patent on invention no. RU2211487. Filed April 26, 2001, Publ. August 27, 2003, p. 33.
Krasnoperov, R. A., and D. Stoyan. Second-order stereology of spatial fibre systems. J. Microsc. 216:156–164, 2004.
Less, J. R., T. C. Skalak, E. M. Sevick, and R. K. Jain. Microvascular architecture in a mammary carcinoma: Branching patterns and vessel dimensions. Cancer Res. 51:265–273, 1991.
Louis, P., and A. M. Gokhale. Computer simulation of spatial arrangement and connectivity of particles in three-dimensional microstructure: Application to model electrical conductivity of polymer matrix composite. Acta Mater. 44:1519–1528, 1996.
Mattfeldt, T., H. Frey, and C. Rose. Second-order stereology of benign and malignant alterations of the human mammary gland. J. Microsc. 171:143–151, 1993.
Mayhew, T. M. Second-order stereology and ultrastructural examination of the spatial arrangements of tissue compartments within glomeruli of normal and diabetic kidneys. J. Microsc. 195:87–95, 1999.
May-Newman, K., O. Mathieu-Costello, J. H. Omens, K. Klumb, and A. D. McCulloch. Transmural distribution of capillary morphology as a function of coronary perfusion pressure in the resting canine heart. Microvasc. Res. 50:381–396, 1995.
Minnich, B., H. Bartel, and A. Lametschwandtner. How a highly complex three-dimensional network of blood vessels regresses: The gill blood vascular system of tadpoles of Xenopus during metamorphosis. A SEM study on microvascular corrosion casts. Microvasc. Res. 64:425–437, 2002.
Murakami, T., T. Miyake, Y. Uno, A. Ohtsuka, T. Taguchi, and T. Sano. The blood vascular architecture of the rat thyroid gland: A scanning electron microscope study of corrosion casts. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 52:15–30, 1989.
Nunan, N., K. Wu, I. M. Young, J. W. Crawford, and K. Ritz. In situ spatial patterns of soil bacterial populations, mapped at multiple scales, in an arable soil. Microb. Ecol. 44:296–305, 2002.
Reed, M. G., and C. V. Howard. Stereological estimation of covariance using linear dipole probes. J. Microsc. 195:96–103, 1999.
Skorjanc, D., F. Jaschinski, G. Heine, and D. Pette. Sequential increases in capillarization and mitochondrial enzymes in low-frequency-stimulated rabbit muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 274:C810–C818, 1998.
Steiniger, B., L. Ruttinger, and P. J. Barth. The three-dimensional structure of human splenic white pulp compartments. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 51:655–664, 2003.
Stoyan, D. Stereological determination of orientations, second-order quantities and correlations for random spatial fibre systems. Biometrical J. 27:411–425, 1985.
Stoyan, D., and H. Stoyan. Fractals, Random Shapes and Point Fields. Methods of Geometrical Statistics. Chichester, UK: Wiley, 1994, p. 389.
Stoyan, D., W. S. Kendall, and J. Mecke. Stochastic Geometry and its Applications. Chichester, UK: Wiley, 1995, p. 436.
Wyss, H. M., E. Tervoort, L. P. Meier, M. Muller, and L. J. Gauckler. Relation between microstructure and mechanical behavior of concentrated silica gels. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 273:455–462, 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krasnoperov, R.A., Stoyan, D. Spatial Correlation Analysis of Isotropic Microvessels: Methodology and Application to Thyroid Capillaries. Ann Biomed Eng 34, 810–822 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-006-9085-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-006-9085-9