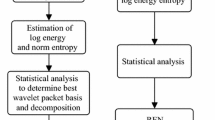
It has been previously shown that wavelet artificial neural networks (WANNs) are able to classify the different states of epileptiform activity and predict the onsets of seizure-like events (SLEs) by offline processing (Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33(6):798–810, 2005) of the electrical data from the in-vitro hippocampal slice model of recurrent spontaneous SLEs. The WANN design entailed the assumption that time-varying frequency information from the biological recordings can be used to estimate the times at which onsets of SLEs would most likely occur in the future. Progressions of different frequency components were captured by the artificial neural network (ANN) using selective frequency inputs from the initial wavelet transform of the biological data. The training of the WANN had been established using 184 SLE episodes in 34 slices from 21 rats offline. Nine of these rats also exhibited periods of interictal bursts (IBs). These IBs were included as part of the training to help distinguish the difference in dynamics of bursting activities between the preictal- and interictal type. In this paper, we present the results of an online processing using WANN on 23 in-vitro rat hippocampal slices from 9 rats having 93 spontaneous SLE episodes generated under low magnesium conditions. Over the test cases, three of the nine rats exhibited over 30 min of IB activities. We demonstrated that the WANN was able to classify the different states, namely, interictal, preictal, ictal, and IB activities with an accuracy of 86.6, 72.6, 84.5, and 69.1%, respectively. Prediction of state transitions into ictal events was achieved using regression of initial “normalized time-to-onset” estimates. The SLE onsets can be estimated up to 36.4 s ahead of their actual occurrences, with a mean error of 14.3 ± 27.0 s. The prediction errors decreased progressively as the actual time-to-onset decreased and more initial “normalized time-to-onset” estimates were used for the regression procedure.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Andrzejak, R. G., K. Lehnertz, F. Mormann, C. Rieke, and P. David. Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: Dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys. Rev. E 64:61907, 2001.
Andrzejak, R. G., F. Mormann, T. Kreuz, C. Rieke, A. Kraskov, C. E. Elger, and K. Lehnertz. Testing the null hypothesis of the nonexistence of a preseizure state. Phys. Rev. E 67(1):010901(R), 2003.
Babloyantz, A., and A. Destexhe. Low-dimensional chaos in an instance of epilepsy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83:3515–3517, 1986.
Basar, E. Brain Function and Oscillations, vol. 1. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1998.
Bishop, C. M. Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition. Clarendon Press, 1995.
Bragin, A., J. Engel, C. L. Wilson, I. Fried, and G. Buzs\(\acute{\rm a}\)ki. High-frequency oscillations in human brain. Hippocampus 9(2):137–142, 1999.
Braunwald, E., A. S. Fauci, D. L. Kasper, S. L. Hauser, D. L. Longo, and J. L. Jameson, eds., Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. McGraw-Hill Professional, 2001.
Chiu, A. W. L., and B. L. Bardakjian. Control of state transitions in an in-silico model of epilepsy using small perturbations. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51(10):1856–1859, 2004.
Chiu, A. W. L., M. Cotic, S. S. Jahromi, H. Khosravani, P. L. Carlen, and B. L. Bardakjian. The effects of high frequency oscillations in hippocampal electrical activities on the classification of epileptiform events using artificial neural networks. J. Neural Eng. 3:9–20, 2006.
Chiu, A. W. L., S. Daniel, H. Khosravani, P. L. Carlen, and B. L. Bardakjian. Prediction of seizure onsets in an in-vitro hippocampal slice model of epilepsy using gaussian-based and wavelet-based artificial neural networks. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33(6):798–810, 2005.
D'Alessandro, M., R. Esteller, G. Vachtsevanos, A. Hinson, J. Echauz, and B. Litt. Epileptic seizure prediction using hybrid feature selection over multiple intracranial EEG electrode contacts: A report of four patients. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 20(5):603–615, 2003.
Draguhn, A., R. D. Traub, D. Schmitz, and J. G. R. Jefferys. Electrical coupling underlies high-frequency oscillations in the hippocampus in vitro. Nature 394:189–192, 1998.
Dreier, J. P., and U. Heinemann. Regional and time dependent variations of low Mg2+ induced epileptiform activity in rat temporal cortex slices. Exp. Brain Res. 87(3):581–596, 1991.
Durand, D. M., and M. Bikson. Suppression and control of epileptiform activity by electrical stimulation: A review. Proc. IEEE 89:1065–1082, 2001.
Dzhala, V. I., and K. J. Staley. Transition from interictal to ictal activity in limbic networks in vitro. J. Neurosci. 23:7873–7880, 2003.
Dzhala, V. I., and K. J. Staley. Mechanisms of fast ripples in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 24(40):8896–8906, 2004.
Engel, J., Jr., P. C. V. Ness, T. B. Rasmussen, and L. M. Ojemann. Outcome with respect to epileptic seizures. In: Surgical Treatment of the Epilepsies, edited by J. Engel Jr. New York: Raven, 1993, pp. 609–622.
Finkel, L. H. Neuroengineering models of brain disease. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2:577–606, 2000.
Gluckman, B., H. Nguyen, S. Weinstein, and S. Schiff. Adaptive electric field control of epileptic seizures. J. Neurosci. 21(2):590–600, 2001.
Haykin, S. Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 1998.
Haykin, S., R. Racine, Y. Xu, and C. Chapman. Monitoring neuronal oscillations and signal transmission between cortical regions using time–frequency analysis of electroencephalographic activity. Proc. IEEE 84(9):1295–1301, 1996.
Iasemidis, L. D. Epileptic seizure prediction and control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 20(5)549–558, 2003.
Iasemidis, L. D., J. C. Principe, and J. C. Sackellares. Measurement and quantification of spatio-temporal dynamics of human epileptic seizures. In: Nonlinear Signal Processing in Medicine, edited by M. Akay. IEEE Press, 1999.
Iasemidis, L. D., and J. C. Sackellares. Chaos theory and epilepsy. Neuroscientist 2:118–126, 1996.
Iasemidis, L. D., D. S. Shiau, W. Chaovalitwongse, J. C. Sackellares, P. M. Pardalos, J. C. Principe, P. R. Carney, A. Prasad, B. Veeramani, and K. Tsakalis. Adaptive epileptic seizure prediction systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 50(5):616–627, 2003.
Jerger, K. K., T. I. Netoff, J. T. Francis, T. Sauer, L. Pecora, S. L. Weinstein, and S. J. Schiff. Comparison of methods for seizure detection. In: Epilepsy as a Dynamic Diseases, edited by J. Milton and P. Jung. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2003, pp. 237–248.
Kalitzin, S. N., J. Parra, D. N. Velis, and F. H. L. da Silva. Enhancement of phase clustering in the EEG/MEG gamma frequency band anticipates transitions to paroxysmal epileptiform activity in epileptic patients with known visual sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 49:1279–1286, 2002.
Khosravani, H., P. L. Carlen, and J. L. Perez-Velazquez. The control of seizure-like activity in rat hippocampal slice. Biophys. J. 84:687–695, 2003.
Lasztoczi, B., K. Antal, L. Nyikos, Z. Emri, and J. Kardos. High-frequency synaptic input contributes to seizure initiation in the low Mg2+ model of epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurosci. 19:1361–1372, 2004.
Lehnertz, K., G. Widman, and C. Elger. Can epileptic seizures be predicted? Evidence from nonlinear time series of brain electrical activity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80:5019–5022, 1998.
Litt, B., R. Esteller, J. Echauz, M. D'Alessandro, R. Shor, T. Henry, and P. Pennell. Epileptic seizures may begin hours in advance of clinical onset: A report of five patients. Neuron 30:51–64, 2001.
Mallat, S. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing. San Diego: Academic Press, 1998.
Milton, J., and P. Jung. Brain defibrillators: Synopsis, problems and future directions. In: Epilepsy as a Dynamic Diseases, edited by J. Milton and P. Jung. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2003, pp. 341–354.
Orb\(\acute{a}\)n, G., T. Kiss, M. Lengyel, and P. \(\acute{E}\)rdi. Hippocampal rhythm generation: Gamma-related theta-frequency resonance in CA3 interneurons. Biol. Cybernet. 84:123–132, 2001.
Osorio, I., M. G. Frei, and S. B. Wilkinson. Real-time automated detection and quantitative analysis of seizures and short-term prediction of clinical onset. Epilepsia 39(6):615–627, 1998.
Perez-Velazquez, J. L., H. Khosravani, A. Lozano, B. L. Bardakjian, P. L. Carlen, and R. Wennberg. Type III intermittency in human partial epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurosci. 11:2571–2576, 1999.
Rafiq, A., R. J. DeLorenzo, and D. A. Coulter. Generation and propagation of epiletiform discharges in a combined entorhinal cortex/hippocampal slice. J. Neurophysiol. 70(5):1962–1974, 1993.
Rafiq, A., Y. Zhang, R. J. Delorenzo, and D. A. Coulter. Long-duration self-sustained epileptiform activity in the hippocampal–parahippocampal slice: A model of status epilepticus. J. Neurophysiol. 74(5):2028–2042, 1995.
Schiff, S. J., K. Jerger, D. H. Duong, T. Chang, M. L. Spano, and W. L. Ditto. Controlling chaos in the brain. Nature 370:615–620, 1994.
Slutzky, M. W., P. Cvitanovic, and D. J. Mogul. Manipulating epileptiform bursting in the rat hippocampus using chaos control and adaptive techniques. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 50(5):559–570, 2003.
So, P., J. T. Francis, T. I. Netoff, B. J. Gluckman, and S. J. Schiff. Periodic orbits: A new language for neuronal dynamics. Biophys. J. 74:2776–2785, 1998.
Sun, M., M. L. Scheuer, and R. J. Sclabassi. Extraction and analysis of early ictal activity in subdural electroencephalogram. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 29(10):878–886, 2001.
Valiante, T., A. W. L. Chiu, and B. L. Bardakjian. Neural codes in human extracranial EEG: Identification of epilepsy features. In: International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Shanghai, China, 2005.
Widman, G., D. Bingmann, K. Lehnertz, and C. E. Elger. Reduced signal complexity of intracellular recordings: A precursor for epileptiform activity? Brain Res. 836:156–163, 1999.
Wolf, A., J. B. Swift, H. L. Swinney, and J. A. Vastano. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Physica D 16:285–317, 1985.
Worrell, G. A., L. Parish, S. D. Cranstoun, R. Jonas, G. Baltuch, and B. Litt. High-frequency oscillations and seizure generation in neocortical epilepsy. Brain 127:1496–1506, 2004.
Young, R. K. Wavelet Theory and Its Applications. Drodrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1993.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work has been supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada (NSERC), the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) and the Krembil Scientist Development Seed Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiu, A.W.L., Kang, E.E., Derchansky, M. et al. Online Prediction of Onsets of Seizure-like Events in Hippocampal Neural Networks Using Wavelet Artificial Neural Networks. Ann Biomed Eng 34, 282–294 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-9029-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-9029-9