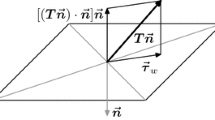
Abstract
Real-time wall shear stress is difficult to monitor precisely because it varies in space and time. Microelectromechanical systems sensor provides high spatial resolution to resolve variations in shear stress in a 3-D bifurcation model for small-scaled hemodynamics. At low Reynolds numbers from 1.34 to 6.7 skin friction coefficients (Cf) varied circumferentially by a factor of two or more within the bifurcation. At a Reynolds number of 6.7, the Cf value at the lateral wall of the bifurcation along the 270∘ plane was 7.1, corresponding to a shear stress value of 0.0061 dyn/cm2. Along the 180∘ plane, Cf was 13 or 0.0079 dyn/cm2, and at the medial wall along the 90∘ plane, Cf was 10.3 or 0.0091 dyn/cm2. The experimental skin friction coefficients correlated with values derived from the Navier–Stokes solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asakura, T., and T. Karino. Flow patterns and spatial distribution of atherosclerotic lesions in human coronary arteries. Circ. Res. 66(4):1045–1066, 1990.
Caro, C. G., J. M. Fitz-Gerald, and R. C. Schroter. Arterial wall shear and distribution of early atheroma in man. Nature 223(211):1159–1160, 1969.
Chandrasekaran, V., A. Chin, T. Nishida, L. N. Cattafesta, and M. Sheplak. Characterization of a Micromachined Thermal Shear Stress Sensor. In: 39th Aerospace Sciences Meeting & Exhibit.: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Reno, NV, 2001.
Chiuu, J. J., C. N. Chen, P. L. Lee, C. T. Yang, H. S. Chuang, S. Chien, and S. Usami. Analysis of the effect of disturbed flow on endothelial cells. J. Biomech. Eng. 120:2–8, 1998.
DePaola, N., M. A. Gimborne, Jr., P. F. Davies, and C. F. Dewey, Jr. Vascular endothelium responds to fluid shear stress gradients. Arterioscler. Thromb. 12:1254–1257, 1992 (published erratum appears in Arterioscler. Thromb. 13(3):465, 1993).
Dewey, C. F. Jr., S. R. Bussolari, M. A. Gimborne, Jr., and P. F. Davies. The dynamic response of vascular endothelial cells to fluid shear stress. J. Biomech. Eng. 103:177–185, 1981.
Dimmeler, S., and A. M. Zeiher. Akt takes center stage in angiogenesis signaling. Circ. Res. 86(1):4–5, 2000.
Ku, D. N. Blood flow in arteries. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 29:399–434, 1997.
Fung, Y. C. Biomechanics:Circulation, Dynamic Similarity. Reynolds and Womersley Numbers. Boundary Layers, 2nd ed. New York: Springer, 1997, pp. 130–132.
Fung, Y. C., and S. Q. Liu. Elementary mechanics of the endothelium of blood vessels. J. Biochem. Eng. 115(1):1–12, 1993.
Glagov, S., C. Zarins, D. P. Giddens, and D. N. Ku. Hemodynamics and atherosclerosis. Insights and perspectives gained from studies of human arteries. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 112(10):1018–1031, 1988.
Haritonnidis, J. H. The measurement of shear stress in fluid mechanics measurements. In Advances in Fluid Mechanics Measurements (Gad-El-Hak, M., ed.) pp. 229–236, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1989.
Ho, C. M., and Y. C. Tai. MEMS and its applications for flow control. J. Fluids Eng. 118:437–447, 1996.
Ho, C. M., and Y. C. Tai. Micro-electro-mechanical-systems (MEMS) and fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30:579–612, 1998.
Hsiai, T. K., S. K. Cho, P. K. Wong, M. H. Ing, A. Salazar, A. Sevanian, M. Navab, L. L. Demer, and C. M. Ho. Monocyte recruitment to endothelial cells in response to oscillatory shear stress. FASEB J. 17(12):1648–1657, 2003.
Hsiai, T. K., S. K. Cho, P. K. Wong, M. H. Ing, A. Salazar, S. Hama, M. Navab, L. L. Demer, and C. M. Ho. Micro sensors: Linking real-time oscillatory shear stress with vascular inflammatory responses. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 32(2):189–201, 2004.
Huang, J. B., C. M. Ho, S. Tung, C. Liu, and Y. C. Tai. Micro thermal shear stress sensor with and without cavity underneath. In: IEEE Proc. Instruments Measurement Technology Conf. (IMTC/95). 1995.
Hwang, J., M. H. Ing, A. Salazar, B. Lassegue, K. Griendling, M. Navab, A. Sevanian, and T. K. Hsiai. Pulsatile versus oscillatory shear stress regulates NADPH oxidase subunit expression: Implication for native LDL oxidation. Circ. Res. 93(12):1225–1232, 2003.
Ku, D. N., D. P. Giddens, C. K. Zarins, and S. Glagov. Pulsatile flow and atherosclerosis in the human carotid bifurcation. Positive correlation between plaque location and low oscillating shear stress. Arteriosclerosis 5(3):293–302, 1985.
Liu, C., J. B. Huang, Z. Zhu, F. Jinag, S. Tung, Y. C. Tai, and C. M. Ho. A micromachines flow shear-stress sensor based on thermal transfer principles. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 8(1):96–98, 1999.
Sheplak, M., V. Chandrasekaran, A. Cain, T. Nishida, and L. N. Cattafesta. Characterization of a silicon-micromachined thermal shear-stress sensor. AIAA J. 40(6), 2002.
Milkiewicz, M., M. D. Brown, S. Egginton, and O. Hudlicka. Association between shear stress, angiogenesis, and VEGF in skeletal muscles in vivo. Microcirculation 8(4):229–241, 2001.
Nerem, R. M., R. W. Alexander, D. C. Chappell, R. M. Medford, S. E. Varner, and W. R. Taylor. The study of the influence of flow on vascular endothelial biology Am. J. Med. Sci. 316:169–175, 1998.
Patan, S., L. Munn, and R. K. Jain. Intussusceptive microvascular growth in a human colon adenocarcinoma xenograft: A novel mechanism of tumor angiogenesis. Microvasc. Res. 51(2):260–272, 1996.
Scharfstein, H., W. H. Gutstein, and L. Lewis. Changes of boundary layer flow in model systems: Implications for initiation of endothelial injury. Circ. Res. 13:580–584, 1963.
Seiler, F., and A. George. The Laser-Doppler-Velocimeter (LDV) used in the ISL shock tunnel. In: 0th International Symposium on Applications of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics. 2000.
Shyy, Y. J., H. J. Hsieh, S. Usami, and S. Chien. Fluid shear stress induces a biphasic response of human monocyte chemotactic protein 1 gene expression in vascular endothelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91(11):4678–4682, 1994.
Soundararajan, G., M. Rouhanizadeh, H. Yu, E. S. Kim, and T. K. Hsiai. MEMS shear stress sensors for microcirculation. Sens. Actuators 118(1):25–32, 2005.
Karino, T. Microscopic structure of disturbed flows in the arterial and venous systems, and its implication in the localization of vascular diseases. Int. Angiol. 5(4):297–313, 1986.
Traub, O., and B. C. Berk. Laminar shear stress: Mechanisms by which endothelial cells transduce an atheroprotective force. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol}. 18(5):677–685, 1998.
Zarins, C. K., D. P. Giddens, B. K. Bharadvaj, V. S. Sottiurai, R. F. Mabon, S. Glagov. Carotid bifurcation atherosclerosis. Quantitative correlation of plaque localization with flow velocity profiles and wall shear stress. Circ. Res. 53(4):502–514, 1983.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rouhanizadeh, M., Lin, T.C., Arcas, D. et al. Spatial Variations in Shear Stress in a 3-D Bifurcation Model at Low Reynolds Numbers. Ann Biomed Eng 33, 1360–1374 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-6542-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-6542-9