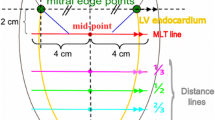
Abstract
Magnetic-resonance (MR) phase velocity mapping (PVM) shows promise in measuring the mitral regurgitant volume. However, in its conventional nonsegmented form, MR-PVM is slow and impractical for clinical use. The aim of this study was to evaluate the accuracy of rapid, segmented k-spaceMR-PVM in quantifying the mitral regurgitant flow through a control volume (CV) method. Two segmented MR-PVM schemes, one with seven (seg-7) and one with nine (seg-9) lines per segment, were evaluated in acrylic regurgitant mitral valve models under steady and pulsatile flow. A nonsegmented (nonseg) MR-PVM acquisition was also performed for reference. The segmented acquisitions were considerably faster (<10 min) than the nonsegmented (>45 min). The regurgitant flow rates and volumes measured with segmented MR-PVM agreed closely with those measured with nonsegmented MR-PVM (differences <5%, p>0.05), when the CV was large enough to exclude the region of flow acceleration and aliasing from its boundaries. The regurgitant orifice shape (circular vs. slit-like) and the presence of aortic outflow did not significantly affect the accuracy of the results under both steady and pulsatile flow (p>0.05). This study shows that segmented k-space MR-PVM canaccurately quantify the flow through regurgitant orifices using the CV method and demonstrates great clinical potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogren, H. G., and M. H. Buonocore. Blood flow measurements in the aorta and major arteries with MR velocity mapping. J. Magn. Reson. Imag. 4:119–130, 1994.
Bryant, D. J., J. A. Payne, D. N. Firmin, and D. B. Longmore. Measurement of flow with NMR imaging using a gradient pulse and phase difference technique. J. Comp. Assist. Tomogr. 8:588–593, 1984.
Cape, E. G., Y. H. Kim, R. S. Heinrich, R. Y. Grimes, E. Muralidharan., J. D. Broder, E. Schwammenthal., A. P. Yoganathan, and R. A. Levine. Cardiac motion can alter proximal isovelocity surface-area calculations of regurgitant flow. J. Am. Col. Cardiol. 22:1730–1737, 1993.
Chatzimavroudis, G. P., P. G. Walker, J. N. Oshinski, R. H. Franch, R. I. Pettigrew, and A. P. Yoganathan. Slice location dependence of aortic regurgitation measurements with MR phase velocity mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 37:545–551, 1997.
Chatzimavroudis, G. P., J. N. Oshinski, R. I. Pettigrew, P. G. Walker, R. H. Franch, and A. P. Yoganathan. Quantification of mitral regurgitation with magnetic resonance phase velocity mapping using a control volume method. J. Magn. Reson. Imag. 8:577–582, 1998.
Chatzimavroudis, G. P., H. Zhang., S. S. Halliburton, J. R. Moore, O. P. Simonetti, P. R. Schvartzman, A. E. Stillman, and R. D. White. Clinical blood flow quantification with segmented k-space magnetic resonance phase velocity mapping. J. Magn. Reson. Imag. 17:65–71, 2003.
Chatzimavroudis, G. P., J. N. Oshinski, R. H. Franch, P. G. Walker, A. P. Yoganathan, and R. I. Pettigrew. Evaluation of the precision of magnetic resonance phase velocity mapping for blood flow measurements. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 3:11–19, 2001.
Croft, C. H., K. Lipscomb., K. Mathis., B. G. Firth, P. Nicod., G. Tilton., M. D. Winniford, and L. D. Hillis. Limitations of qualitative angiographic grading in aortic or mitral regurgitation. Am. J. Cardiol. 53:1593–1598, 1984.
Dulce, M. C., G. H. Mostbeck, M. O’Sullivan, M. Cheitlin., G. R. Caputo, and C. B. Higgins. Severity of aortic regurgitation: Interstudy reproducibility of measurements with velocity-encoded cine MR imaging. Radiology 185:235–240, 1992.
Frayne, R., D. A. Steinman, C. R. Ethier, and B. K. Rutt. Accuracy of MR phase contrast velocity measurements for unsteady flow. J. Magn. Reson. Imag. 5:428–431, 1995.
Hopmeyer, J., A. A. Fontaine, S. Yang., R. A. Levine, and A. P. Yoganathan. The effect of aortic outflow on the quantification of mitral regurgitation by the flow convergence method. J. Am. Soc. Echo. 9:44–57, 1996.
Kilner, P. J., G. Z. Yang, R. H. Mohiaddin, D. N. Firmin, and D. B. Longmore. Helical and retrograde secondary flow patterns in the aortic13 arch studied by three-directional magnetic resonance velocity mapping. Circulation 88:2235–2247, 1993.
Klipstein, R. H., D. N. Firmin, S. R. Underwood, R. S. Rees, and D. B. Longmore. Blood flow patterns in the human aorta studied by magnetic resonance. Br. Heart J. 58:316–323, 1987.
Kondo, C., G. R. Caputo, R. Semelka., E. Foster., A. Shimakawa., and C. B. Higgins. Right and left ventricular stroke volume measurements with velocity-encoded cine MR imaging: In-vitro and in-vivo validation. Am. J. Roentgenol. 157:9–16, 1991.
Kraft, K. A., D. Y. Fei, and P. P. Fatouros. Quantitative phase-velocity MR imaging of in-plane laminar flow: Effect of fluid velocity, vessel diameter, and slice thickness. Med. Phys. 19:79–85, 1992.
McKinnon, G. C., J. F. Debatin, D. R. Wetter, and G. K. Von Schulthess. Interleaved echo planar flow quantitation. Magn. Reson. Med. 32:263–267, 1994.
Meier, D., S. Maier., and P. Bosiger. Quantitative flow measurements on phantoms and on blood vessels with MR. Magn. Reson. Med. 8:25–34, 1988.
Mohiaddin, R. H., S. L. Wann, R. Underwood., D. N. Firmin, S. Rees., and D. B. Longmore. Vena caval flow: Assessment with cine MR velocity mapping. Radiology 177:537–541, 1990.
Moran, P. R. A flow velocity zeugmatographic interlace for NMR imaging in humans. Magn. Reson. Imag. 1:197–203, 1982.
Pelc, L. R., N. J. Pelc, S. C. Rayhill, L. J. Castro, G. H. Glover, R. J. Herfkens, D. C. Miller, and R. B. Jeffrey. Arterial and venous blood flow: Noninvasive quantification with MR imaging. Radiology 185:809–812, 1992.
Perry, G. J., F. Helmcke., N. C. Nanda, C. Byard., and B. Soto. Evaluation of aortic insufficiency by Doppler color flow mapping. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 9:952–959, 1987.
Recusani, F., G. S. Bargiggia, A. P. Yoganathan, A. Raisaro., L. M. Valdes-Cruz, H. W. Sung, C. Bertucci., M. Gallati., V. A. Moises, I. A. Simpson, L. Tronconi., and D. J. Sahn. A new method for quantification of regurgitant flow rate using color Doppler flow imaging of the flow convergence region proximal to a discrete orifice. An in vitro Study Circulation 83:594–604, 1991.
Sechtem, U., P. W. Pflugfelder, M. M. Cassidy, R. D. White, M. D. Cheitlin, N. B. Schiller, and C. B. Higgins. Mitral or aortic regurgitation: Quantification of regurgitant volumes with cine MR imaging. Radiology 167:425–430, 1988.
Suzuki, J., G. R. Caputo, C. Kondo., and C. B. Higgins. Cine MR imaging of valvular heart disease: Display and imaging parameters affect the size of the signal void caused by valvular regurgitation. Am. J. Roentgenol. 155:723–727, 1990.
Thomsen, C., M. Cortsen., L. Sondergaard., O. Henriksen., and F. Stahlberg. A segmented k-space velocity mapping protocol for quantification of renal artery blood flow during breath-holding. J. Magn. Reson. Imag. 5:393–401, 1995.
Underwood, S. R., D. N. Firmin, R. H. Klipstein, R. S. Rees, and D. B. Longmore. Magnetic resonance velocity mapping: Clinical application of a new technique. Br. Heart J. 57:404–412, 1987.
Veyrat, C., A. Ameur., C. Gourtchiglouian., A. Lessana., G. Abitbol., and D. Kalmanson. Calculation of pulsed Doppler left ventricular outflow tract regurgitant index for grading the severity of aortic regurgitation. Am. Heart J. 108:507–515, 1984.
Walker, P. G., S. Oyre., E. M. Pedersen, K. Houlind., F. S. Guenet, and A. P. Yoganathan. A new control volume method for calculating valvular regurgitation. Circulation 92:579–586, 1995.
Walker, P. G., K. Houlind., C. Djurhuus., W. Y. Kim, and E. M. Pedersen. Motion correction for the quantification of mitral regurgitation using the control volume method. Magn. Reson. Med. 43:726–733, 2000.
Zhang, H., S. S. Halliburton, J. R. Moore, O. P. Simonetti, P. R. Schvartzman, R. D. White, and G. P. Chatzimavroudis. Ultra-fast flow quantification with segmented k-space magnetic resonance phase velocity mapping. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 30:120–128, 2002.
Zhang, H., S. S. Halliburton, J. R. Moore, O. P. Simonetti, R. D. White, and G. P. Chatzimavroudis. Evaluation of the accuracy of in-plane velocity measurements with segmented k-space magnetic resonance phase velocity mapping. BMES Annual Meeting, Houston, TX, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Halliburton, S.S., White, R.D. et al. Fast Measurements of Flow through Mitral Regurgitant Orifices with Magnetic Resonance Phase Velocity Mapping. Ann Biomed Eng 32, 1618–1627 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-004-7815-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-004-7815-4