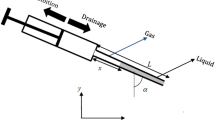
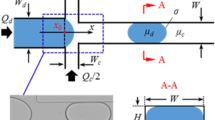
Abstract
It has been reported in recent experimental and numerical studies that the forced gas-liquid displacement in a partially wettable capillary tube can give rise to entrainment of a liquid film and generation of Taylor bubbles at a large displacement rate. However, simulations and hydrodynamic theory of Gao et al. (J. Fluid Mech., 2019, vol 859: 308–320) predicted an abrupt drop of the contact line velocity Cacl at the onset of wetting transition, which conflicted with the experiments of Zhao et al. (Phys. Rev. Lett., 2018, vol 120: 084501), who suggested a continuous variation of Cacl. To resolve this discrepancy, we performed experiments of gas-liquid displacement, focusing on the contact line velocity close to the threshold. It is found that Cacl is indeed discontinuous, confirming the validity of the hydrodynamic description of the moving contact line. After an abrupt drop, Cacl increases to a constant for a slight raise of the displacement rate. The failure of detecting this discontinuity in previous experiments is due to the low resolution of the displacement rate. The propagating velocity and the length of the generated bubbles are presented and agree well with the existing theory. Variation of the liquid slug length with the displacement rate is also presented.
摘要
近期关于气液驱替的实验和数值研究表明, 在不完全浸润和大驱替速度条件下可在毛细管壁面上产生液膜并最终演化为泰 勒气泡. 基于数值模拟和流体动力学理论, Gao等证明接触线速度Cacl在这种润湿状态转换的临界条件附近会出现突降. 这种突降 在Zhao等的实验中并未被发现, 因此他们认为Cacl是连续变化的. 为了解决这种矛盾, 我们重新开展了毛细管中的气液驱替实验, 重点 关注临界条件附近的接触线速度变化. 我们发现Cacl确实具有不连续性, 证实了采用流体动力学理论描述移动接触线的有效性. 在突降 发生后, Cacl会随着驱替速度的增加迅速上升到一个常值. 在前人实验中, 由于驱替速度的分辨率较低, 未能检测到这种不连续性. 我们 给出了气泡运动速度和长度的变化规律, 发现与现有理论非常吻合. 此外, 还研究了气泡间的液塞长度随驱替速度的变化.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. J. Weinstein, and K. J. Ruschak, Coating flows, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 36, 29 (2004)
S. Kumar, Liquid transfer in printing processes: liquid bridges with moving contact lines, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 47, 67 (2015)
D. Bonn, J. Eggers, J. Indekeu, J. Meunier, and E. Rolley, Wetting and spreading, Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 739 (2009)
J. H. Snoeijer, and B. Andreotti, Moving contact lines: scales, regimes, and dynamical transitions, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 45, 269 (2013)
T. D. Blake, and K. J. Ruschak, A maximum speed of wetting, Nature 282, 489 (1979)
J. G. Petrov, and R. V. Sedev, On the existence of a maximum speed of wetting, Colloids Surf. 13, 313 (1985)
R. V. Sedev, and J. G. Petrov, The critical condition for transition from steady wetting to film entrainment, Colloids Surf. 53, 147 (1991)
J. H. Snoeijer, G. Delon, M. Fermigier, and B. Andreotti, Avoided critical behavior in dynamically forced wetting, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 174504 (2006)
J. Eggers, Hydrodynamic theory of forced dewetting, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 094502 (2004).
J. Eggers, Existence of receding and advancing contact lines, Phys. Fluids 17, 082106 (2005)
J. H. Snoeijer, B. Andreotti, G. Delon, and M. Fermigier, Relaxation of a dewetting contact line. Part 1. A full-scale hydrodynamic calculation, J. Fluid Mech. 579, 63 (2007).
G. Delon, M. Fermigier, J. H. Snoeijer, and B. Andreotti, Relaxation of a dewetting contact line. Part 2. Experiments, J. Fluid Mech. 604, 55 (2008).
T. S. Chan, J. H. Snoeijer, and J. Eggers, Theory of the forced wetting transition, Phys. Fluids 24, 072104 (2012)
P. Gao, L. Li, J. J. Feng, H. Ding, and X. Y. Lu, Film deposition and transition on a partially wetting plate in dip coating, J. Fluid Mech. 791, 358 (2016)
J. Qin, and P. Gao, Asymptotic theory of fluid entrainment in dip coating, J. Fluid Mech. 844, 1026 (2018)
D. Quéré, On the minimal velocity of forced spreading in partial wetting (in French), C. R. Acad. Sci. Ser. II 313, 313 (1991)
G. Callegari, A. Calvo, and J. P. Hulin, Dewetting processes in a cylindrical geometry, Eur. Phys. J. E 16, 283 (2005)
B. Zhao, A. A. Pahlavan, L. Cueto-Felgueroso, and R. Juanes, Forced Wetting Transition and Bubble Pinch-Off in a Capillary Tube, Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 084501 (2018)
P. Gao, A. Liu, J. J. Feng, H. Ding, and X. Y. Lu, Forced dewetting in a capillary tube, J. Fluid Mech. 859, 308 (2019)
C. E. Wu, H. W. Du, J. Qin, E. Q. Li, and P. Gao, Experiment on bubble formation through dynamical wetting transition in a square capillary, AIP Adv. 11, 075107 (2021)
L. D. Landau, and B. V. Levich, Dragging of a liquid by a moving plate, Acta Physicochim. URSS 17, 42 (1942)
B. V. Derjaguin, Thickness of liquid layer adhering to walls of vessels on their emptying, Acta Physicochim. URSS 20, 349 (1943)
P. Gao, L. Li, and X. Y. Lu, Dewetting films with inclined contact lines, Phys. Rev. E 91, 023008 (2015)
Y. Xia, J. Qin, and P. Gao, Dynamical wetting transition on a chemically striped incline, Phys. Fluids 32, 022101 (2020)
F. P. Bretherton, The motion of long bubbles in tubes, J. Fluid Mech. 10, 166 (1961)
G. I. Taylor, Deposition of a viscous fluid on the wall of a tube, J. Fluid Mech. 10, 161 (1961)
R. Golestanian, and E. Raphaël, Relaxation of a moving contact line and the Landau-Levich effect, Europhys. Lett. 55, 228 (2001).
R. Golestanian, and E. Raphaël, Dissipation in dynamics of a moving contact line, Phys. Rev. E 64, 031601 (2001).
F. Fairbrother, and A. E. Stubbs, 119. Studies in electro-endosmosis. Part VI. The “bubble-tube” method of measurement, J. Chem. Soc. 1, 527 (1935)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11972340, 11672287, 11932019, and 11621202), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDB22040103), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, CE., Qin, J. & Gao, P. Experiment on gas-liquid displacement in a capillary. Acta Mech. Sin. 38, 321386 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-021-09021-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-021-09021-x