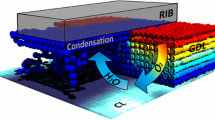
Abstract
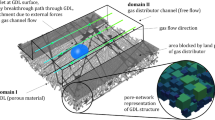
A pore network model (PNM) is developed for gas diffusion layer (GDL) in the cathode side of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). The model is coupled to network models of reactant oxygen and electron transport inside GDL and also to simple models of catalyst layer and membrane. The coupled model captures the simultaneous effect of reactant and charge access to reaction sites and the resulting water generation, allowing it a transient nature up to reaching the steady state, which is a notable modification to the available PNMs which assume uniform invasion of liquid water from catalyst layer. The results show strongly non-uniform water saturation distributions inside GDL with maxima under the current collector ribs. As an extra feature, the model can predict time evolution of oxygen concentration and water generation rate at catalyst layer as a result of liquid water build-up in GDL. Also included is a dry case coupled model in order to be compared with the main model. The local water blockages in GDL inflict an average of 38.8% loss on the produced limiting current of the fuel cell. Finally, the coupling allows prediction of concentration overvoltages which emerges to be most pronounced in the under-rib region.
Graphic abstract

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larminie, J., Dicks, A.: Fuel Cell Systems Explained, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (2003)
Weber, A.Z., Borup, R.L., Darling, R.M., et al.: A critical review of modeling transport phenomena in polymer-electrolyte fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 161(12), F1254–F1299 (2014)
Kim, S.G., Lee, S.J.: A review on experimental evaluation of water management in a polymer electrolyte fuel cell using X-ray imaging technique. J. Power Sources 230, 101–108 (2013)
Wang, Z.H., Wang, C.Y., Chen, K.S.: Two-phase flow and transport in the air cathode of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 94(1), 40–50 (2001)
Qin, C., Rensink, D., Fell, S., et al.: Two-phase flow modeling for the cathode side of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell. J. Power Sources 197, 136–144 (2012)
Rebai, M., Prat, M.: Scale effect and two-phase flow in a thin hydrophobic porous layer. Application to water transport in gas diffusion layers of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 192(2), 534–543 (2009).
Nazemian, M., Molaeimanesh, G.R.: Impact of carbon paper structural parameters on the performance of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell cathode via lattice Boltzmann method. Acta Mech. Sin. 36(2), 367–380 (2020)
Zhang, D., Cai, Q., Gu, S.: Three-dimensional lattice-Boltzmann model for liquid water transport and oxygen diffusion in cathode of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell with electrochemical reaction. Electrochim. Acta 262, 282–296 (2018)
Zhou, X., Niu, Z., Bao, Z., et al.: Two-phase flow in compressed gas diffusion layer: Finite element and volume of fluid modeling. J. Power Sources 437, 226933 (2019)
Sinha, P.K., Wang, C.Y.: Pore-network modeling of liquid water transport in gas diffusion layer of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell. Electrochim. Acta 52(28), 7936–7945 (2007)
Medici, E.F., Allen, J.S.: The effects of morphological and wetting properties of porous transport layers on water movement in PEM fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 157(10), 1505–1514 (2010)
Lee, K.J., Nam, J.H., Kim, C.J.: Pore-network analysis of two-phase water transport in gas diffusion layers of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 54(4), 1166–1176 (2009)
Luo, G., Ji, Y., Wang, C.Y., et al.: Modeling liquid water transport in gas diffusion layers by topologically equivalent pore network. Electrochim. Acta 55(19), 5332–5341 (2010)
Médici, E.F., Allen, J.S.: Evaporation, two phase flow, and thermal transport in porous media with application to low-temperature fuel cells. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 65, 779–788 (2013)
Lee, K.J., Nam, J.H., Kim, C.J.: Steady saturation distribution in hydrophobic gas-diffusion layers of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells: A pore-network study. J. Power Sources 195(1), 130–141 (2010)
Ceballos, L., Prat, M.: Invasion percolation with inlet multiple injections and the water management problem in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 195(3), 825–828 (2010)
Wu, R., Zhu, X., Liao, Q., et al.: Determination of oxygen effective diffusivity in porous gas diffusion layer using a three-dimensional pore network model. Electrochim. Acta 55(24), 7394–7403 (2010)
Wu, R., Zhu, X., Liao, Q., et al.: A pore network study on water distribution in bi-layer gas diffusion media: Effects of inlet boundary condition and micro-porous layer properties. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 35(17), 9134–9143 (2010)
Kuttanikkad, S.P., Prat, M., Pauchet, J.: Pore-network simulations of two-phase flow in a thin porous layer of mixed wettability: Application to water transport in gas diffusion layers of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 196(3), 1145–1155 (2011)
Wu, R., Zhu, X., Liao, Q., et al.: Liquid and oxygen transport in defective bilayer gas diffusion material of proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 38(10), 4067–4078 (2013)
Lee, K.J., Kang, J.H., Nam, J.H.: Liquid water distribution in hydrophobic gas-diffusion layers with interconnect rib geometry: An invasion-percolation pore network analysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 39(12), 6646–6656 (2014)
Qin, C.: Water transport in the gas diffusion layer of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell: Dynamic pore-network modeling. J. Electrochem. Soc. 162(9), F1036–F1046 (2015)
Qin, C.Z., Hassanizadeh, M.S., Van Oosterhout, M.L.: Pore-network modeling of water and vapor transport in the micro porous layer and gas diffusion layer of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell. Computation 4(2), 21 (2016)
Straubhaar, B., Pauchet, J., Prat, M.: Pore network modelling of condensation in gas diffusion layers of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 102, 891–901 (2016)
Fazeli, M., Hinebaugh, J., Fishman, Z., et al.: Pore network modeling to explore the effects of compression on multiphase transport in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell gas diffusion layers. J. Power Sources 335, 162–171 (2016)
Carrere, P., Prat, M.: Liquid water in cathode gas diffusion layers of PEM fuel cells: Identification of various pore filling regimes from pore network simulations. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 129, 1043–1056 (2019)
Qin, C.Z., Guo, B., Celia, M., et al.: Dynamic pore-network modeling of air-water flow through thin porous layers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 202, 194–207 (2019)
Zhan, N., Wu, W., Wang, S.: Pore network modeling of liquid water and oxygen transport through the porosity-graded bilayer gas diffusion layer of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 306, 264–276 (2019)
Turhan, A., Kim, S., Hatzell, M., et al.: Impact of channel wall hydrophobicity on through-plane water distribution and flooding behavior in a polymer electrolyte fuel cell. Electrochim. Acta 55(8), 2734–2745 (2010)
Deevanhxay, P., Sasabe, T., Tsushima, S., et al.: Investigation of water accumulation and discharge behaviors with variation of current density in PEMFC by high-resolution soft X-ray radiography. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 36(17), 10901–10907 (2011)
Lamibrac, A., Roth, J., Toulec, M., et al.: Characterization of liquid water saturation in gas diffusion layers by X-ray tomographic microscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 163(3), F202–F209 (2016)
Eller, J., Roth, J., Marone, F., et al.: Operando properties of gas diffusion layers: Saturation and liquid permeability. J. Electrochem. Soc. 164(2), F115–F126 (2017)
Zenyuk, I.V., Medici, E., Allen, J., et al.: Coupling continuum and pore-network models for polymer-electrolyte fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 40(46), 16831–16845 (2015)
Aghighi, M., Hoeh, M.A., Lehnert, W., et al.: Simulation of a full fuel cell membrane electrode assembly using pore network modeling. J. Electrochem. Soc. 163(5), F384–F392 (2016)
Belgacem, N., Prat, M., Pauchet, J.: Coupled continuum and condensation–evaporation pore network model of the cathode in polymer-electrolyte fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42(12), 8150–8165 (2017)
Aghighi, M., Gostick, J.: Pore network modeling of phase change in PEM fuel cell fibrous cathode. J. Appl. Electrochem. 47(12), 1323–1338 (2017)
Belgacem, N., Pauchet, J., Prat, M.: On the current distribution at the channel–rib scale in polymer-electrolyte fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43(10), 5112–5123 (2018)
Eller, J., Rosén, T., Marone, F., et al.: Progress in in situ X-ray tomographic microscopy of liquid water in gas diffusion layers of PEFC. J. Electrochem. Soc. 158(8), B963–B970 (2011)
Lenormand, R., Touboul, E., Zarcone, C.: Numerical models and experiments on immiscible displacements in porous media. J. Fluid Mech. 189, 165–187 (1988)
Singh, M., Mohanty, K.K.: Dynamic modeling of drainage through three-dimensional porous materials. Chem. Eng. Sci. 58(1), 1–18 (2003)
Tranter, T.G., Gostick, J.T., Burns, A.D., et al.: Capillary hysteresis in neutrally wettable fibrous media: A pore network study of a fuel cell electrode. Transp. Porous Media 121(3), 597–620 (2018)
Liang, J., Li, Y., Wang, R., Jiang, J.: Cross-dimensional model of the oxygen transport behavior in low-Pt proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Chem. Eng. J. 400, 125796 (2020)
O'Hayre, R., Cha, S.W., Colella, W., et al.: Fuel Cell Fundamentals. (3rd edn.) Wiley (2016)
Mann, R.F., Amphlett, J.C., Peppley, B.A., et al.: Application of Butler-Volmer equations in the modelling of activation polarization for PEM fuel cells. J. Power Sources 161(2), 775–781 (2006)
Springer, T.E., Zawodzinski, T.A., Gottesfeld, S.: Polymer electrolyte fuel cell model. J. Electrochem. Soc. 138(8), 2334–2342 (1991)
Holzer, L., Pecho, O., Schumacher, J., et al.: Microstructure-property relationships in a gas diffusion layer (GDL) for polymer electrolyte fuel cells, Part I: effect of compression and anisotropy of dry GDL. Electrochim. Acta 227, 419–434 (2017)
Becker, J., Flückiger, R., Reum, M., et al.: Determination of material properties of gas diffusion layers: experiments and simulations using phase contrast tomographic microscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 156(10), B1175–B1181 (2009)
Nitta, I., Hottinen, T., Himanen, O., et al.: Inhomogeneous compression of PEMFC gas diffusion layer: Part I. experimental. J. Power Sources 171(1), 26–36 (2007).
Caulk, D.A., Baker, D.R.: Heat and water transport in hydrophobic diffusion media of PEM fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 157(8), B1237–B1244 (2010)
Reum, M., Wokaun, A., Büchi, F.N.: Measuring the current distribution with submillimeter resolution in PEFCs: III Influence of the flow field geometry. J. Electrochem. Soc. 156(10), 1225–1231 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gholipour, H., Kermani, M.J. & Zamanian, R. Coupled pore network model for the cathode gas diffusion layer in PEM fuel cells. Acta Mech. Sin. 37, 331–348 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-020-01005-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-020-01005-7