Abstract
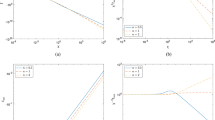
The pre-multiplied spanwise energy spectra of streamwise velocity fluctuations are investigated in this paper. Two distinct spectral peaks in the spanwise spectra are observed in low-Reynolds-number wall-bounded turbulence. The spectra are calculated from direct numerical simulation (DNS) of turbulent channel flows and zero-pressure-gradient boundary layer flows. These two peaks locate in the near-wall and outer regions and are referred to as the inner peak and the outer peak, respectively. This result implies that the streamwise velocity fluctuations can be separated into large and small scales in the spanwise direction even though the friction Reynolds number \(Re_\tau \) can be as low as 1000. The properties of the inner and outer peaks in the spanwise spectra are analyzed. The locations of the inner peak are invariant over a range of Reynolds numbers. However, the locations of the outer peak are associated with the Reynolds number, which are much higher than those of the outer peak of the pre-multiplied streamwise energy spectra of the streamwise velocity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marusic, I., McKeon, B.J., Monkewitz, P.A., et al.: Wall-bounded turbulent flows at high reynolds numbers: recent advances and key issues. Phys. Fluids 22, 065103 (2010)
Kline, S.J., Reynolds, W.C., Schraub, F.A., et al.: The structure of turbulent boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 30, 741–773 (1967)
Smith, C.R., Metzler, S.P.: The characteristics of low-speed streaks in the near-wall region of a turbulent boundary-layer. J. Fluid Mech. 129, 27–54 (1983)
Marusic, I., Mathis, R., Hutchins, N.: High reynolds number effects in wall turbulence. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 31, 418–428 (2010)
Jiménez, J., Pinelli, A.: The autonomous cycle of near-wall turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 389, 335–359 (1999)
Schoppa, W., Hussain, F.: Coherent structure generation in near-wall turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 453, 57–108 (2002)
Wang, Y.S., Huang, W.X., Xu, C.X.: On hairpin vortex generation from near-wall streamwise vortices. Acta Mech. Sin. 31, 139–152 (2015)
Hutchins, N., Marusic, I.: Large-scale influences in near-wall turbulence. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 365, 647–664 (2007)
Smits, A.J., McKeon, B.J., Marusic, I.: High-Reynolds number wall turbulence. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 43, 353–375 (2011)
Lee, M., Moser, R.D.: Direct numerical simulation of turbulent channel flow up to \(Re_\tau \approx \) 5200. J. Fluid Mech. 774, 395–415 (2015)
Hutchins, N., Marusic, I.: Evidence of very long meandering features in the logarithmic region of turbulent boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 579, 1–28 (2007)
Balakumar, B.J., Adrian, R.J.: Large- and very-large-scale motions in channel and boundary-layer flows. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 365, 665–681 (2007)
Kim, K.C., Adrian, R.J.: Very large-scale motion in the outer layer. Phys. Fluids 11, 417 (1999)
del Álamo, J.C., Jiménez, J.: Linear energy amplification in turbulent channels. J. Fluid Mech. 559, 205–213 (2006)
McKeon, B.J., Sharma, A.S.: A critical-layer framework for turbulent pipe flow. J. Fluid Mech. 658, 336–382 (2010)
Townsend, A.A.: Equilibrium layers and wall turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 11, 97–120 (1961)
Townsend, A.A.: The Structure of Turbulent Shear Flow. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1980)
Hoyas, S., Jiménez, J.: Scaling of the velocity fluctuations in turbulent channels up to \(Re_{\tau }\) = 2003. Phys. Fluids 18, 011702 (2006)
Ganapathisubramani, B., Hutchins, N., Monty, J.P., et al.: Amplitude and frequency modulation in wall turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 712, 61–91 (2012)
Tomkins, C.D., Adrian, R.J.: Spanwise structure and scale growth in turbulent boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 490, 37–74 (2003)
Abe, H., Kawamura, H., Choi, H.: Very large-scale structures and their effects on the wall shear-stress fluctuations in a turbulent channel flow up to Re = 640. J. Fluids Eng. 126, 835–843 (2004)
Iwamoto, K., Kasagi, N., Suzuki, Y.: Dynamical roles of large-scale structures in turbulent channel flow. Comput. Mech. WCCM VI in Conjunction with APCOM 4, 5–10 (2004)
EI Khoury, G.K., Schlatter, P., Brethouwer, G., et al.: Turbulent pipe flow: statistics, Re-dependence, structures and similarities with channel and boundary layer flows. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 506, 012010 (2014)
Sillero, J.A., Jiménez, J., Moser, R.D.: One-point statistics for turbulent wall-bounded flows at reynolds numbers up to \(\delta ^+\) = 2000. Phys. Fluids 25, 105102 (2013)
Hwang, Y.: Statistical structure of self-sustaining attached eddies in turbulent channel flow. J. Fluid Mech. 767, 254–289 (2015)
Lozano-Duran, A., Jiménez, J.: Effect of the computational domain on direct simulations of turbulent channels up to \(Re_\tau \)=4200. Phys. Fluids 26, 011702 (2014)
Perry, A.E., Henbest, S., Chong, M.S.: A theoretical and experimental study of wall turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 165, 163–199 (1986)
Perlman, E., Burns, R., Li, Y., et al.: Data exploration of turbulence simulations using a database cluster. In: ACM/IEEE Conference on High Performance Networking and Computing, SC 2007, November 10-16, Reno, Nevada, USA, 1–11 (2007)
Li, Y., Perlman, E., Wan, M.P., et al.: A public turbulence database cluster and applications to study lagrangian evolution of velocity increments in turbulence. J. Turbulence 9, 1–29 (2008)
Graham, J., Kanov, K., Yang, X.I.A., et al.: A web services accessible database of turbulent channel flow and its use for testing a new integral wall model for les. J. Turbulence 17, 181–215 (2016)
Mathis, R., Hutchins, N., Marusic, I.: Large-scale amplitude modulation of the small-scale structures in turbulent boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 628, 311–337 (2009)
Mathis, R., Hutchins, N., Marusic, I.: A predictive inner-outer model for streamwise turbulence statistics in wall-bounded flows. J. Fluid Mech. 681, 537–566 (2011)
Vallikivi, M., Ganapathisubramani, B., Smits, A.J.: Spectral scaling in boundary layers and pipes at very high Reynolds numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 771, 303–326 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 11302238, 11232011, 11572331, and 11490551). The authors would like to acknowledge the support from the Strategic Priority Research Program (Grant XDB22040104), the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant QYZDJ-SSW-SYS002), and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program 2013CB834100 : Nonlinear Science).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HP., Wang, SZ. & He, GW. The spanwise spectra in wall-bounded turbulence. Acta Mech. Sin. 34, 452–461 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-017-0731-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-017-0731-2