Abstract
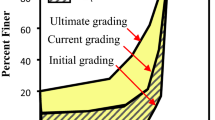
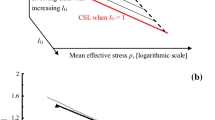
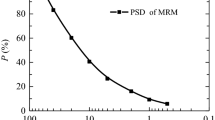
Dilation and breakage energy dissipation of four different granular soils are investigated by using an energy balance equation. Due to particle breakage, the dilation curve does not necessarily pass through the origin of coordinates. Breakage energy dissipation is found to increase significantly at the initial loading stage and then gradually become stabilised. The incremental dissipation ratio between breakage energy and plastic work exhibits almost independence of the confining pressure. Accordingly, a plastic flow rule considering the effect of particle breakage is suggested. The critical state friction angle is found to be a combination of the basic friction between particles and the friction contributed by particle breakage.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xiao, Y., Liu, H.L., Sun, Y., et al.: Stress-dilatancy behaviors of coarse granular soils in three-dimensional stress space. Eng. Geol. 195, 104–110 (2015)
Sun, Y., Xiao, Y., Zheng, C., et al.: Modelling long-term deformation of granular soils incorporating the concept of fractional calculus. Acta Mech. Sin. 32, 112–124 (2016)
McDowell, G.: A family of yield loci based on micro mechanics. Soils Found. 40, 133–137 (2000)
Mortara, G.: A constitutive framework for the elastoplastic modelling of geomaterials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 63, 139–152 (2015)
Lian, J., Barlat, F., Baudelet, B.: Plastic behaviour and stretchability of sheet metals. Part II: effect of yield surface shape on sheet forming limit. Int. J. Plast. 5, 131–147 (1989)
François, M.: A plasticity model with yield surface distortion for non proportional loading. Int. J. Plast. 17, 703–717 (2001)
Yu, M.H.: Twin shear stress yield criterion. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 25, 71–74 (1983)
Qu, Y.Q., Yin, S.N.: Drucker’s and Ilyushin’s postulate of plasticity. Acta Mech. Sin. 5, 465–473 (1981)
Hassanlourad, M., Salehzadeh, H., Shahnazari, H.: Dilation and particle breakage effects on the shear strength of calcareous sands based on energy aspects. Int. J. Civil Eng. 6, 108–119 (2008)
Fu, Z., Chen, S., Peng, C.: Modeling cyclic behavior of rockfill materials in a framework of generalized plasticity. Int. J. Geomech. 14, 191–204 (2014)
Ueng, T.S., Chen, T.J.: Energy aspects of particle breakage in drained shear of sands. Geotechnique 50, 65–72 (2000)
Ueng, T.S., Lee, C.J.: Deformation behavior of sand under shear-particulate approach. J. Geotech. Eng. 116, 1625–1640 (1990)
Xiao, Y., Liu, H.L., Desai, C., et al.: Effect of intermediate principal-stress ratio on particle breakage of rockfill material. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 142, 06015017 (2015)
Wang, J., Yan, H.: DEM analysis of energy dissipation in crushable soils. Soils Found. 52, 644–657 (2012)
Sun, Q., Jin, F., Zhou, G.D.: Energy characteristics of simple shear granular flows. Granul. Matter. 15, 119–128 (2013)
Qi, Y., Huang, J.J., Chen, M.X.: Eenergy dissipation characteristics of crushable granules under dynamic excitations. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 47, 252–259 (2014)
Yan, J., Shen, Y., Huang, G., et al.: Energy-based method for analyzing the collapse characteristics of silt subjected to changes of principal stress orientation. J. Test. Eval. 39, 1–6 (2011)
Rowe, P.W.: The stress-dilatancy relation for static equilibrium of an assembly of particles in contact. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 269, 500–527 (1962)
Sun, Y., Liu, H.L., Yang, G.: Yielding function for coarse aggregates considering gradation evolution induced by particle breakage. Rock Soil Mech. 34, 3479–3484 (2013)
Einav, I.: Breakage mechanics–part I: theory. J. Mech. Phys. Solid. 55, 1274–1297 (2007)
Casini, F., Viggiani, G.B., Springman, S.: Breakage of an artificial crushable material under loading. Granul. Matter. 15, 661–673 (2013)
Xiao, Y., Liu, H., Chen, Y., et al.: Strength and deformation of rockfill material based on large-scale triaxial compression tests. II: influence of particle breakage. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 140, 04014071 (2014)
Qin, H.Y., Liu, H.L., Gao, Y.F., et al.: Research on strength and deformation behavior of coarse aggregatesbased on large-scale triaxial tests. Rock Soil Mech. 25, 1575–1580 (2004)
Yamamuro, J.A., Lade, P.V.: Drained sand behavior in axisymmetric tests at high pressures. J. Geotech. Eng. 122, 109–119 (1996)
Lade, P.V., Yamamuro, J.A.: Undrained sand behavior in axisymmetric tests at high pressures. J. Geotech. Eng. 122, 120–129 (1996)
Guo, P., Su, X.: Shear strength, interparticle locking, and dilatancy of granular materials. Can. Geotech. J. 44, 579–591 (2007)
Lade, P.V., Yamamuro, J.A., Bopp, P.A.: Significance of particle crushing in granular materials. J. Geotech. Eng. 122, 309–316 (1996)
Jia, Y.F., Chi, S.C., Lin, G.: Constitutive model for coarse granular aggregates incorporating particle breakage. Rock Soil Mech. 30, 3261–3267 (2009)
Shen, C.K., Chi, S.C., Jia, Y.F.: A constitutive model for coarse granular soil incorporating particle breakage. Rock Soil Mech. 31, 2111–2115 (2010)
Hanley, K.J., O’Sullivan, C., Huang, X.: Particle-scale mechanics of sand crushing in compression and shearing using DEM. Soils Found. 55, 1100–1112 (2015)
Luzzani, L., Coop, M.R.: On the relationship between particle breakage and the critical state of sands. Soils Found. 42, 71–82 (2002)
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant 106112015CDJXY200008), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 51509024), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant 2016M590864).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Xiao, Y. & Ji, H. Dilation and breakage dissipation of granular soils subjected to monotonic loading. Acta Mech. Sin. 32, 1065–1074 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-016-0569-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-016-0569-z